Comprehensive Training Curriculum On Business Communication edu ppt
What is it
- EduDecks are professionally-created comprehensive decks that provide complete coverage of the subject under discussion
- These are also innovatively-designed for a powerful learning experience and maximum retention
Who is it for?
- EduDecks are for Trainers who want to add punch and flair to program and leave a lasting impact on their trainees
- They are also for Teachers who want to win over their students with content as well design
Why EduDecks?
- EduDecks provide an A-Z coverage of courses on any topic and covers it in both great depth and wide scope
- These slides are also professionally-designed to deliver a punch to your programs
Why Corporate Trainers love us?
- Content created by Industry experts, active in their fields
- Relevant concepts supplemented with industry case studies
- Visually appealing slides with 100% accurate & relevant data
Why Teachers love us?
- Comprehensive curriculum covering all aspects of the topic
- Relevant examples provided with the topics
- Just download and amaze your audience without making any content changes
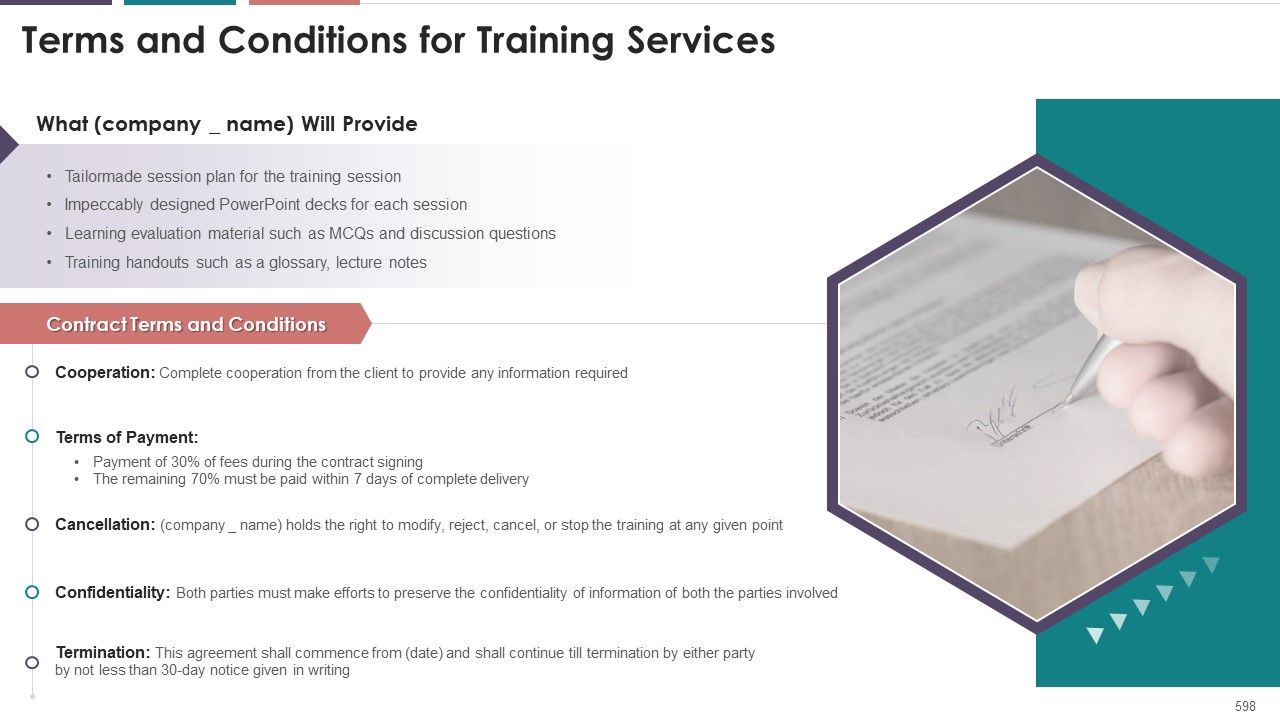
What you will get
- 12 Structured Sessions
- 20+ Thought Provoking Questions
- 600+ Professionally Designed Slides
- 50+ Objective Type Questions
- Hands on Activities
- Real Life Case Studies
- Detailed Instructor Notes
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- All Decks , All Modules , All Courses , Edu Tech , Business Communication Course , Business Communication Skills , Business Communication Skills , Business Communication Skills , Communication Strategy
Create an Immersive Training Experience
Created by Subject Matter Experts
Professionally Designed Slides
Structured Sessions
Comprehensive Curriculum
Detailed Teaching Notes
Real-Life Case Studies
Assessment Questions
Client Proposal
Complete Curriculum
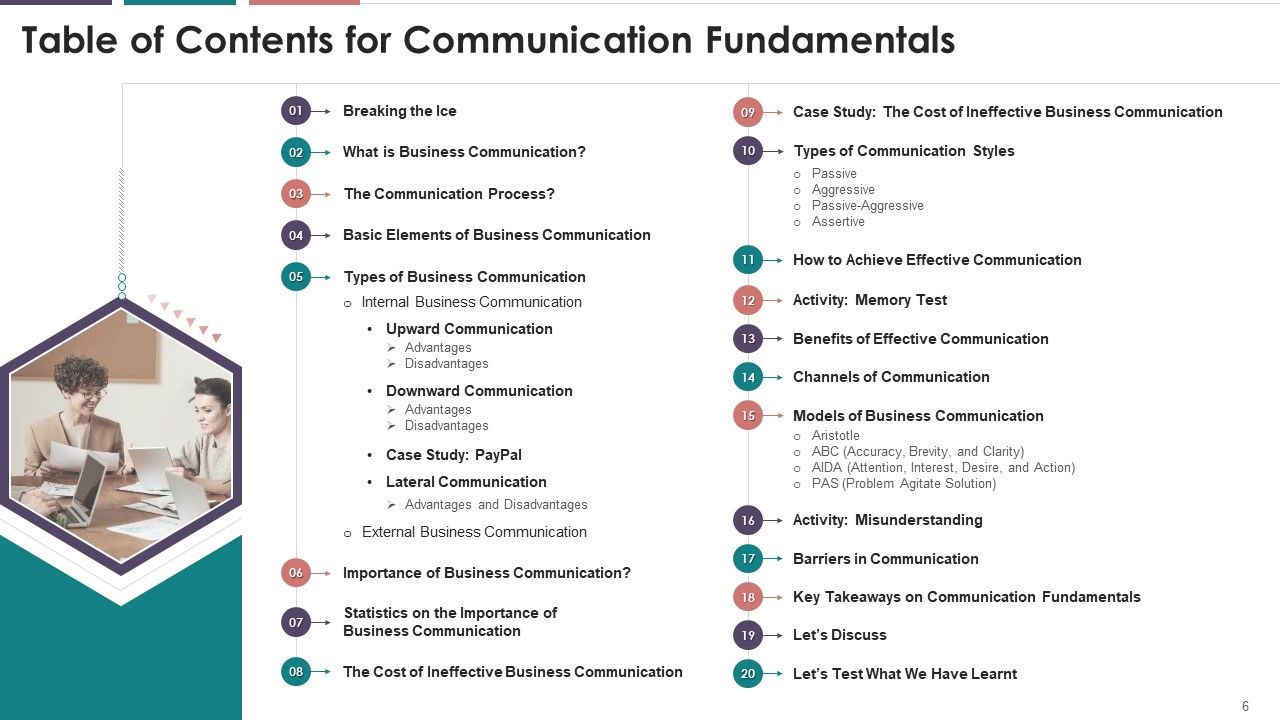
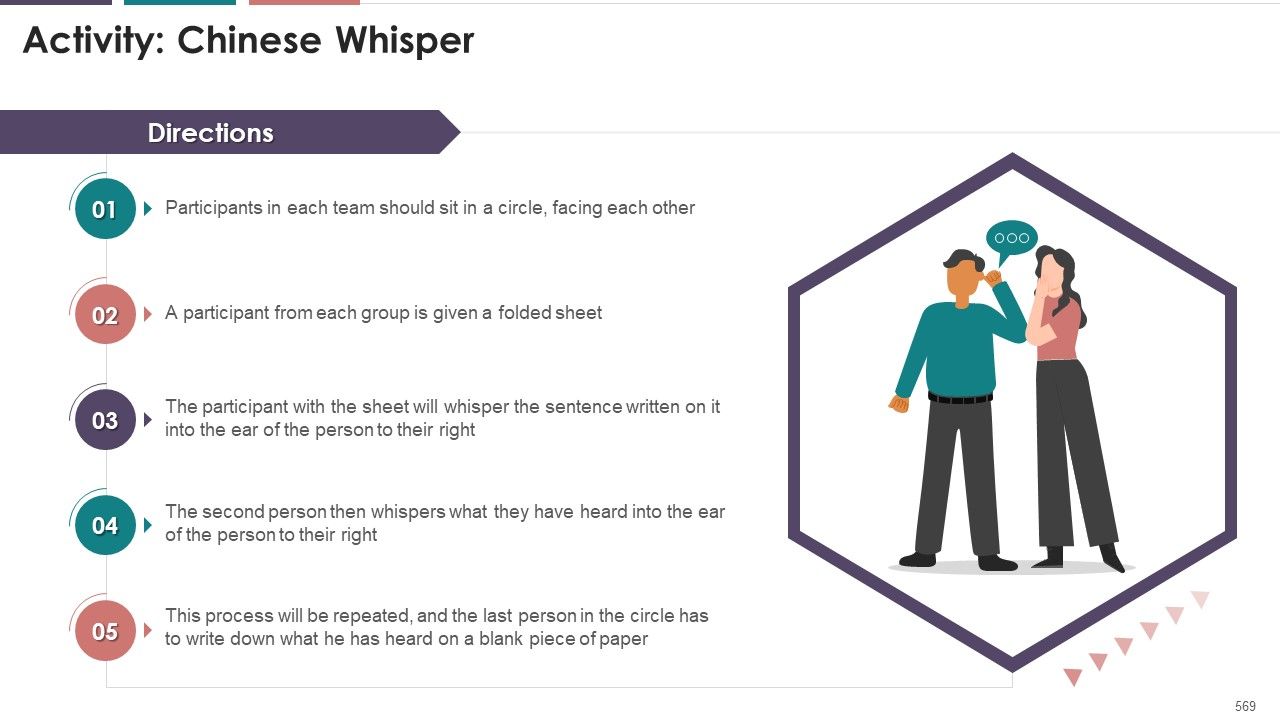
- Breaking the Ice
- What is Business Communication?
- The Communication Process
- Basic Elements of Business Communication
- Types of Business Communication
- Internal Business Communication
- Upward Communication
- Advantages
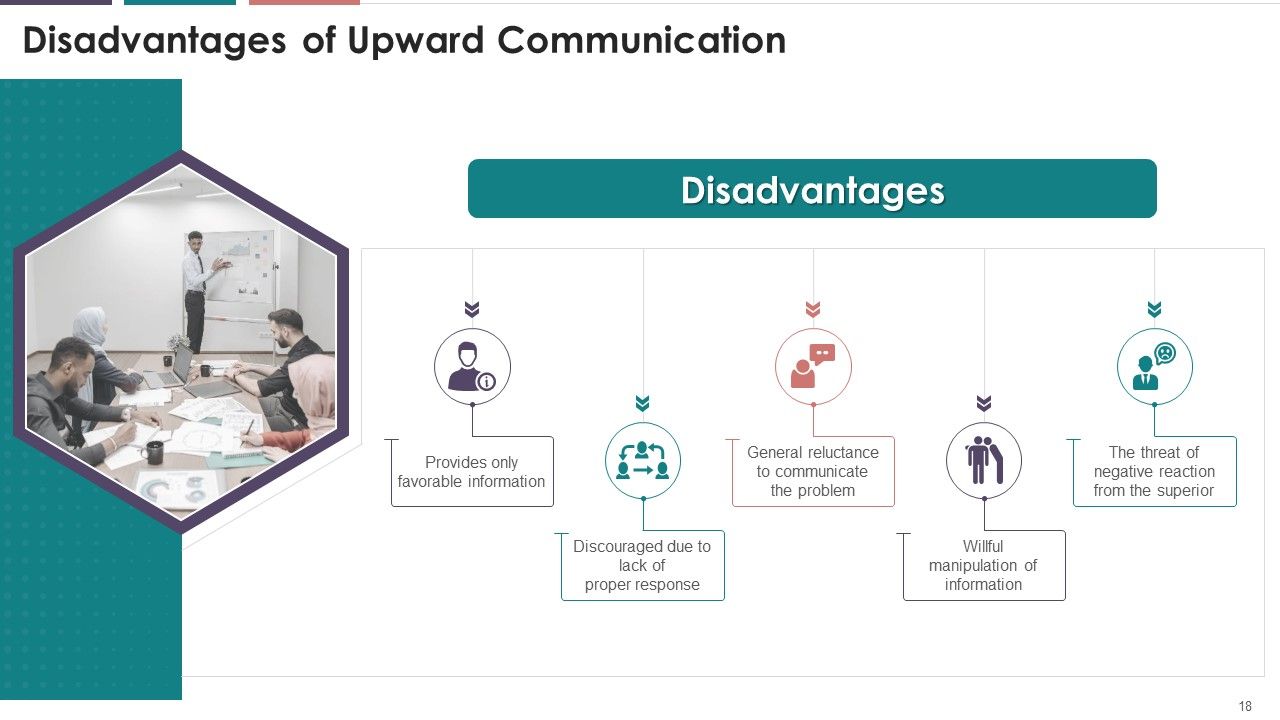
- Disadvantages
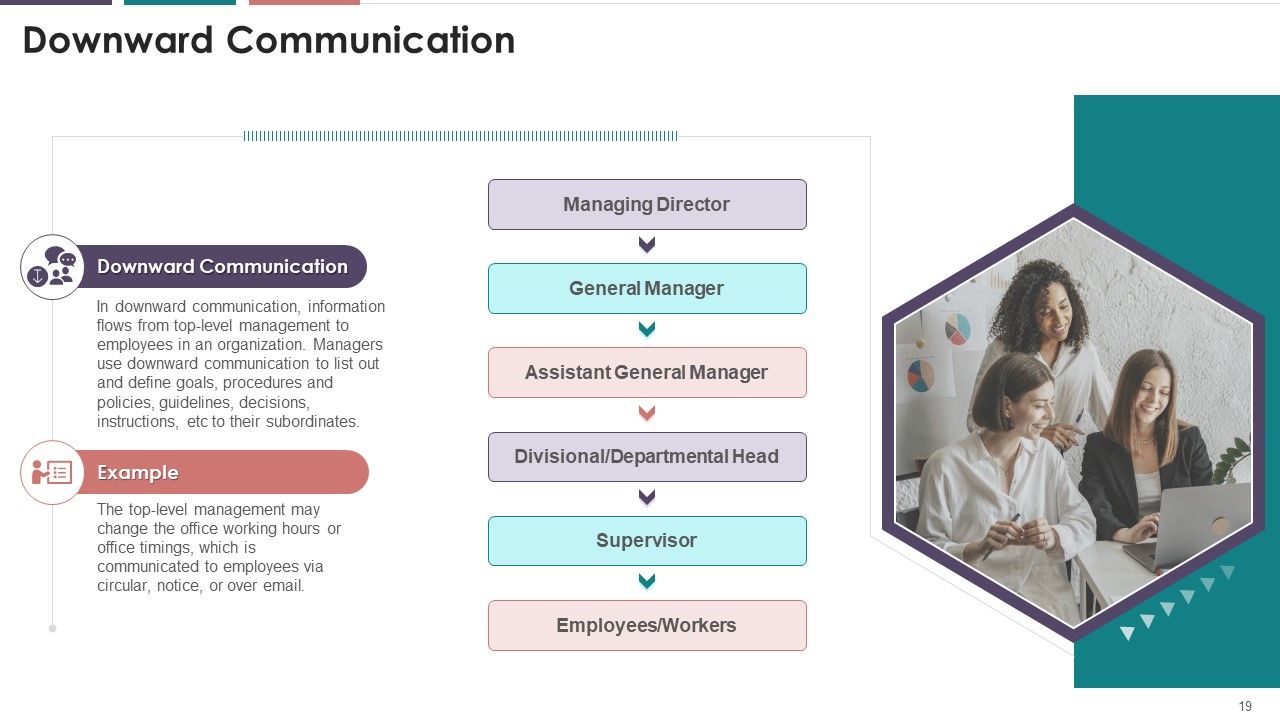
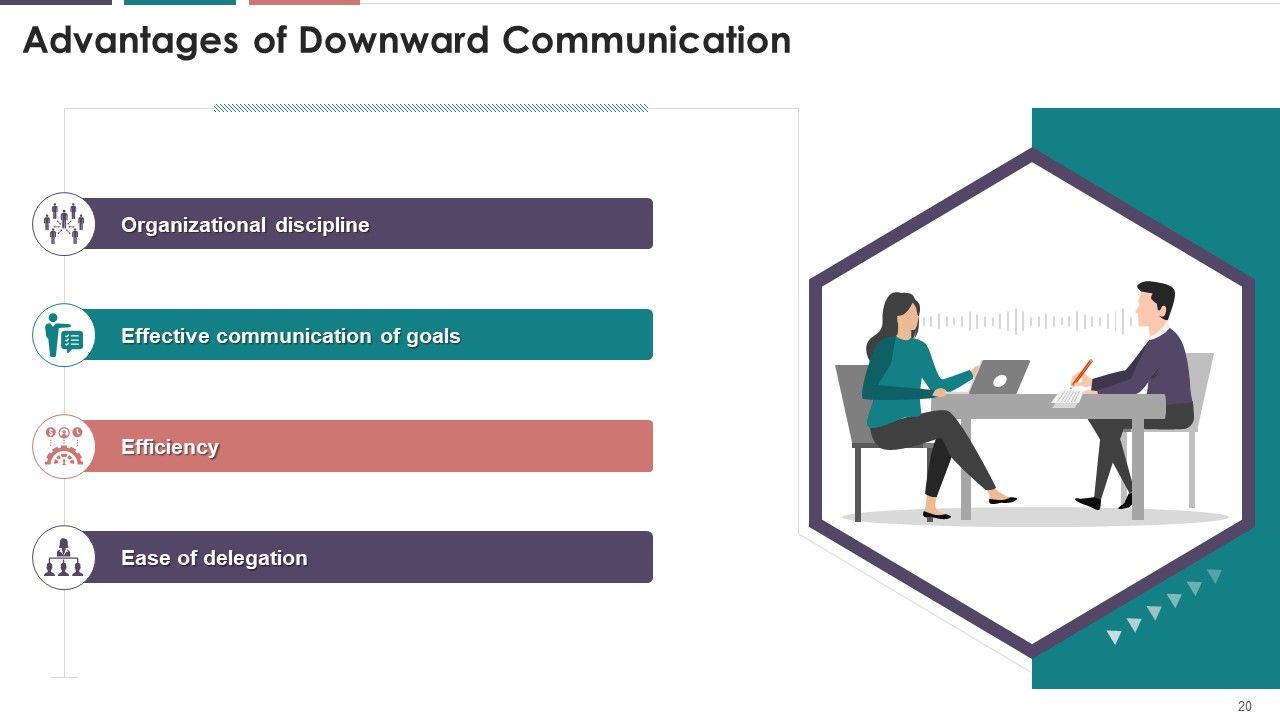
- Downward Communication
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Case Study: PayPal
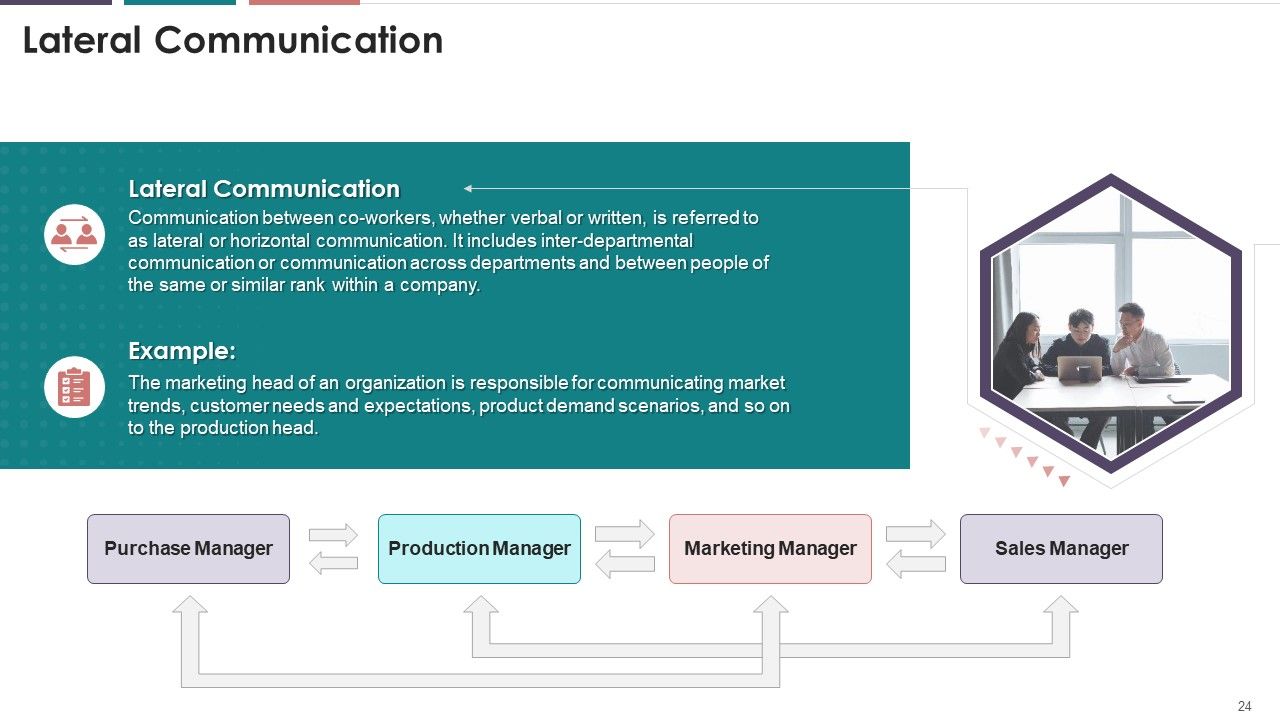
- Lateral communication
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- External Business Communication
- Importance of Business Communication
- Statistics on the Importance of Business Communication
- The Cost of Ineffective Business Communication
- Case Study: The Cost of Ineffective Business Communication
- Types of Communication Styles
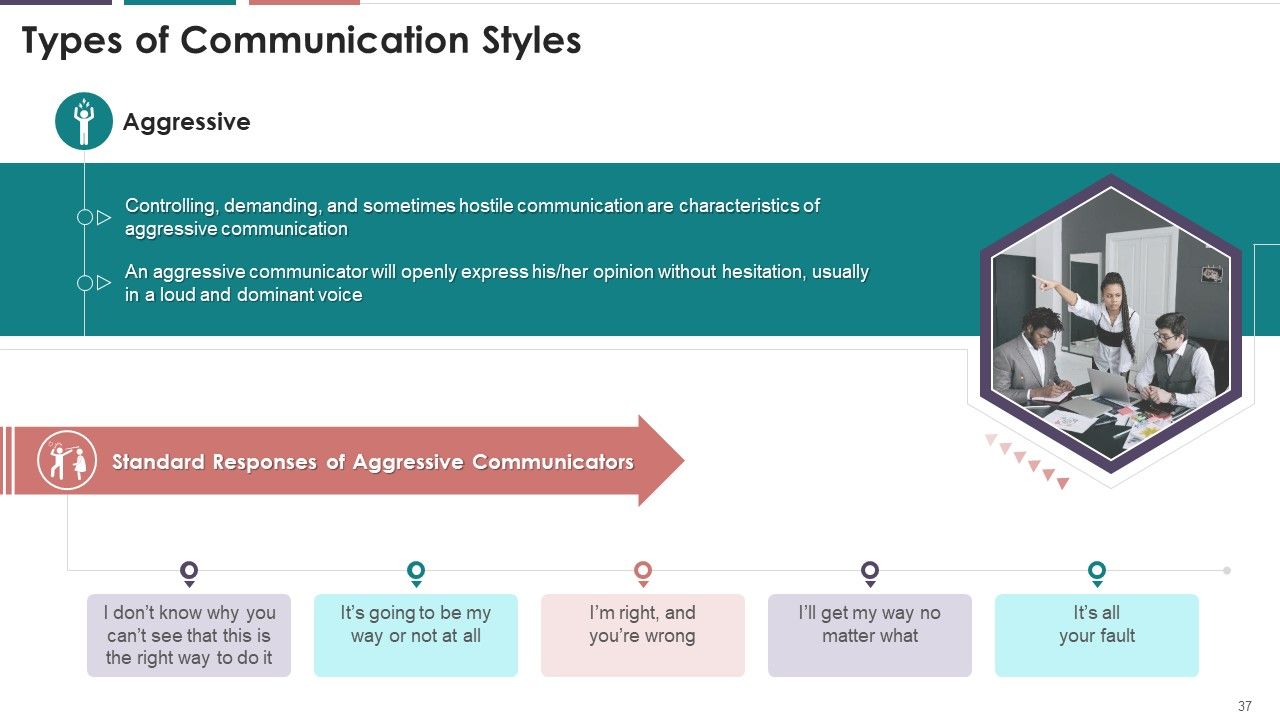
- Passive
- Aggressive
- Passive-Aggressive
- Assertive
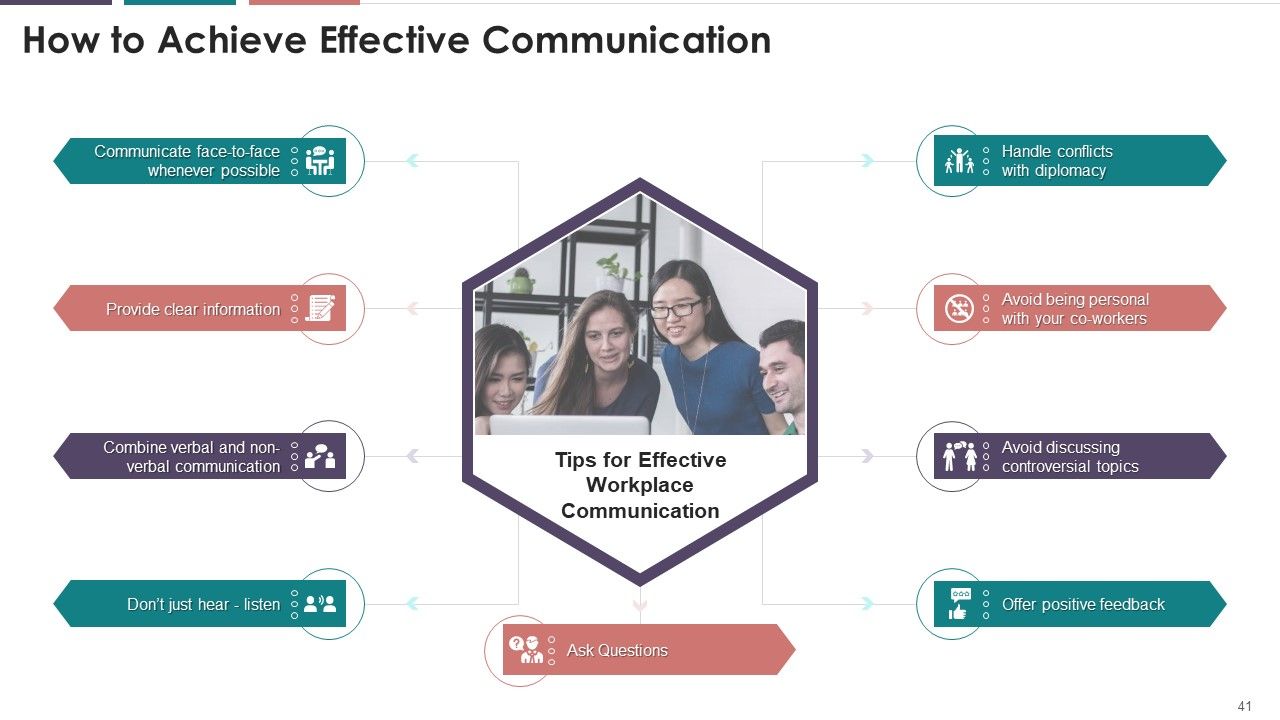
- How to Achieve Effective Communication
- Activity: Memory Test
- Benefits of Effective Communication
- Channels of Communication
- Models of Business Communication
- Aristotle
- ABC (Accuracy, Brevity, and Clarity)
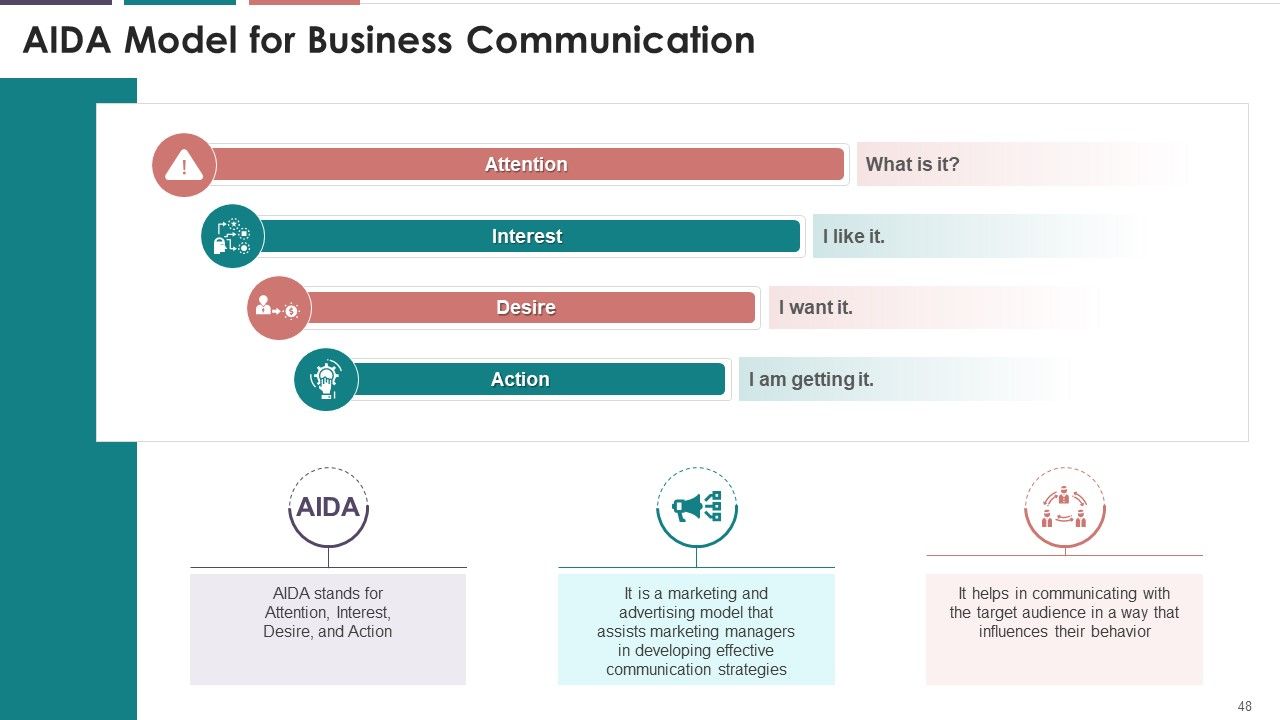
- AIDA (Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action)
- PAS (Problem Agitate Solution)
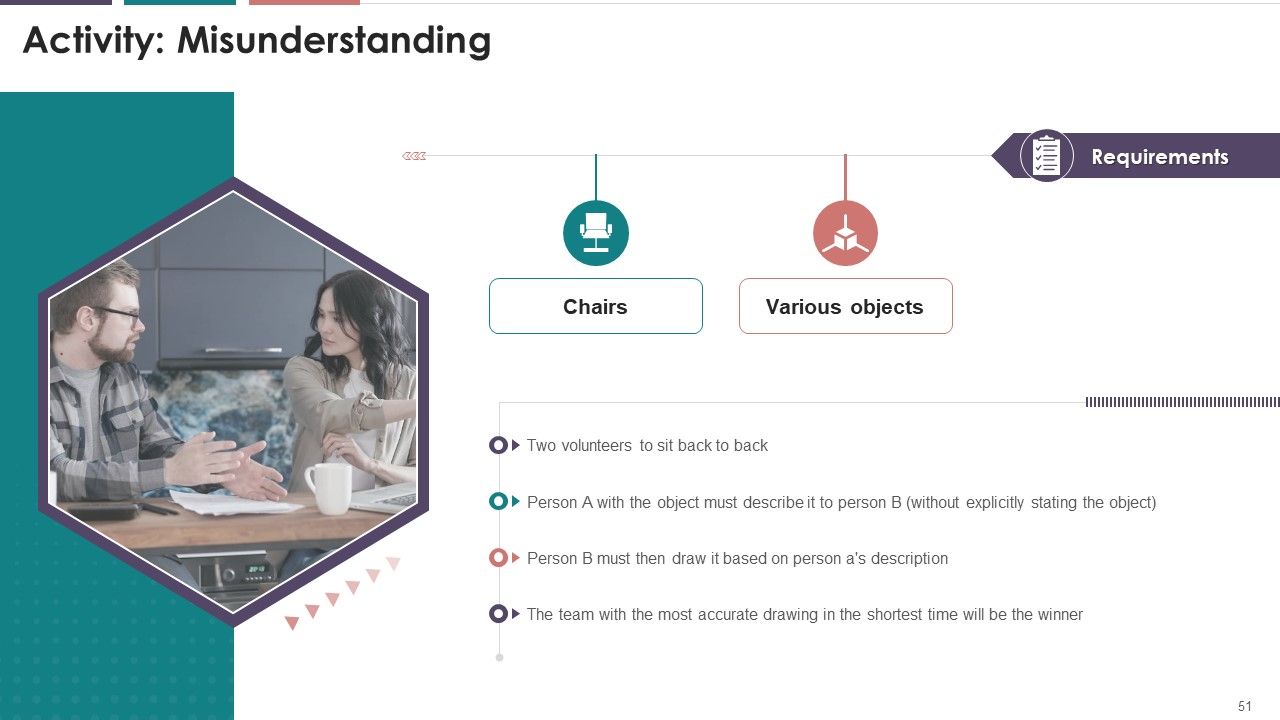
- Activity: Misunderstanding
- Barriers in Communication
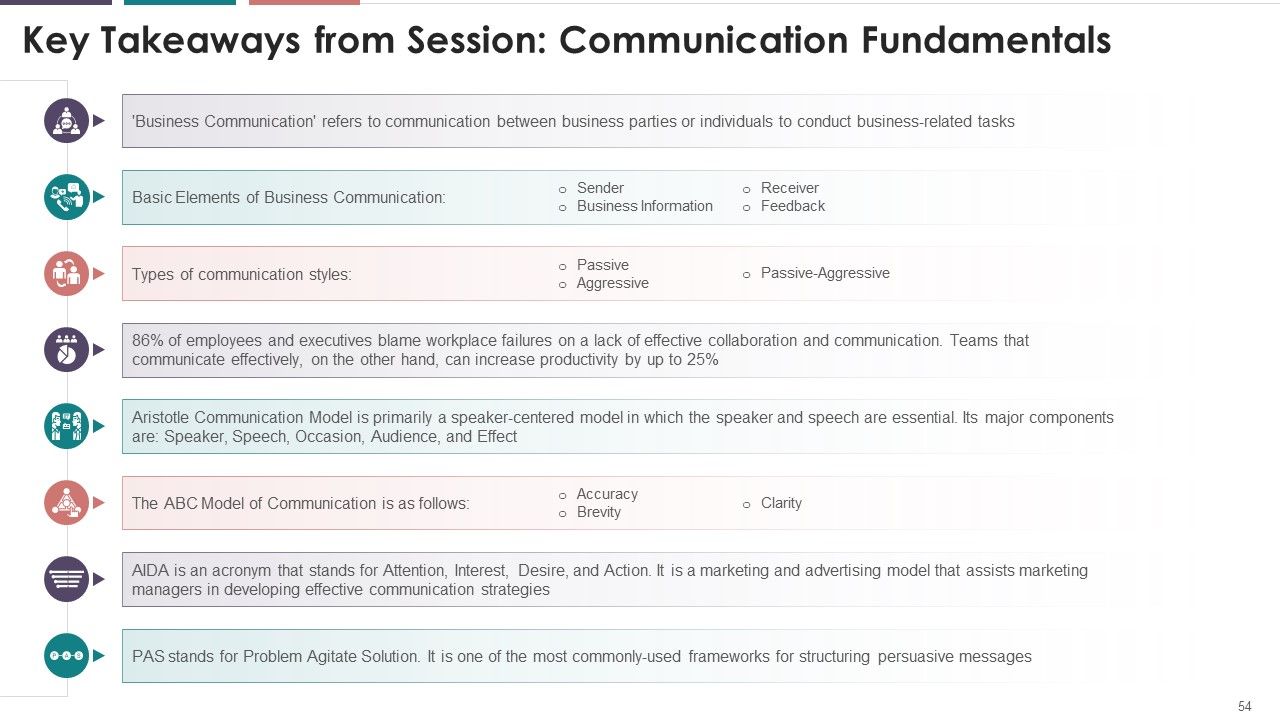
- Key Takeaways on Communication Fundamentals
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Business Writing Basics
- Written Communication and its Importance
- Types of Business Writing
- Types of Business Messages
- 3Ps of Business Writing
- Principles of Great Writing - Logos, Pathos, Ethos
- Key Takeaways for Business Writing Basics Session
- Prewriting Strategies: Effective Business Writing
- Principles of Good Business Writing
- Steps for Effective Business Writing
- HABITS Framework (Heading, Artwork, Bold, Italics, Typeface, and Space)
- Improve Written Communication in the Workplace
- Activity: Short Words are Better
- Activity: Misplaced Words
- Recommendations for Writing Concisely
- Tips for Writing more Readable Sentences
- Strategies to turn Flabby Writing into Lean Prose
- Dos and Don’ts of Business Writing
- Key Takeaways for Effective Business Writing
- Best Practices of Grammar
- Punctuation Marks
- Comma
- Activity: The Comma
- Periods
- Question Marks
- Quotation
- Colons
- Parentheses
- Capitalization
- Activity: Capital Letters
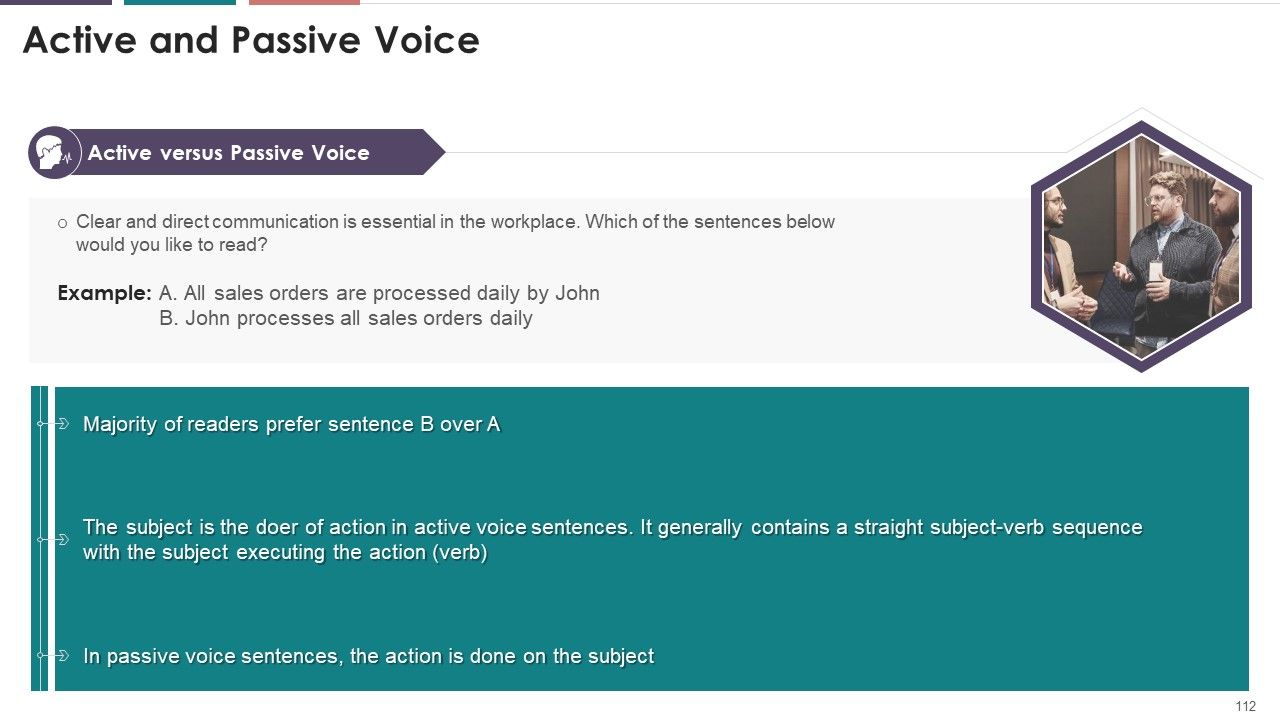
- Active and Passive Voice
- Why Should I Use Active Voice?
- When Should I Use Passive Voice?
- Activity: Active Versus Passive Voice Sentences
- Post-Writing Strategies
- Proofreading and Editing
- Common Errors
- Key Takeaways for Best Practices of Grammar
- Writing Business Email
- How to Write an Effective Email
- Basic Email Etiquette
- Dos and Don’ts of Business Email
- Example of Bad Email
- Activity: Email Writing
- Cold Email
- How to Write a Cold Email that Actually Get Responses
- Problem-Agitate-Solve (PAS) – Cold Email Example
- Attention-Interest-Desire-Action (AIDA) - Cold Email Example
- Writing Memos
- Business Memo Template
- Activity: Writing Business Memos
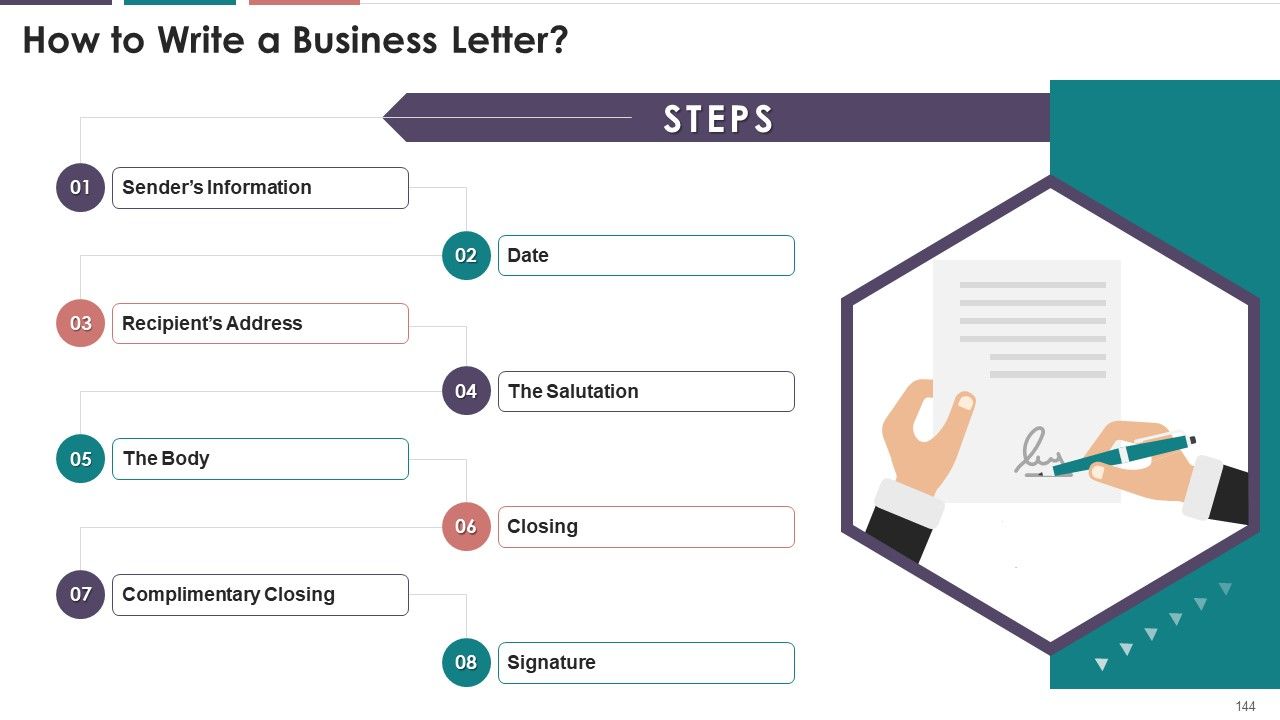
- Writing a Business Letter
- How to Write a Business Letter
- Activity: Writing a Business Letter
- Key Takeaways for Writing Business Email, Letters and Memos
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Introduction to Listening
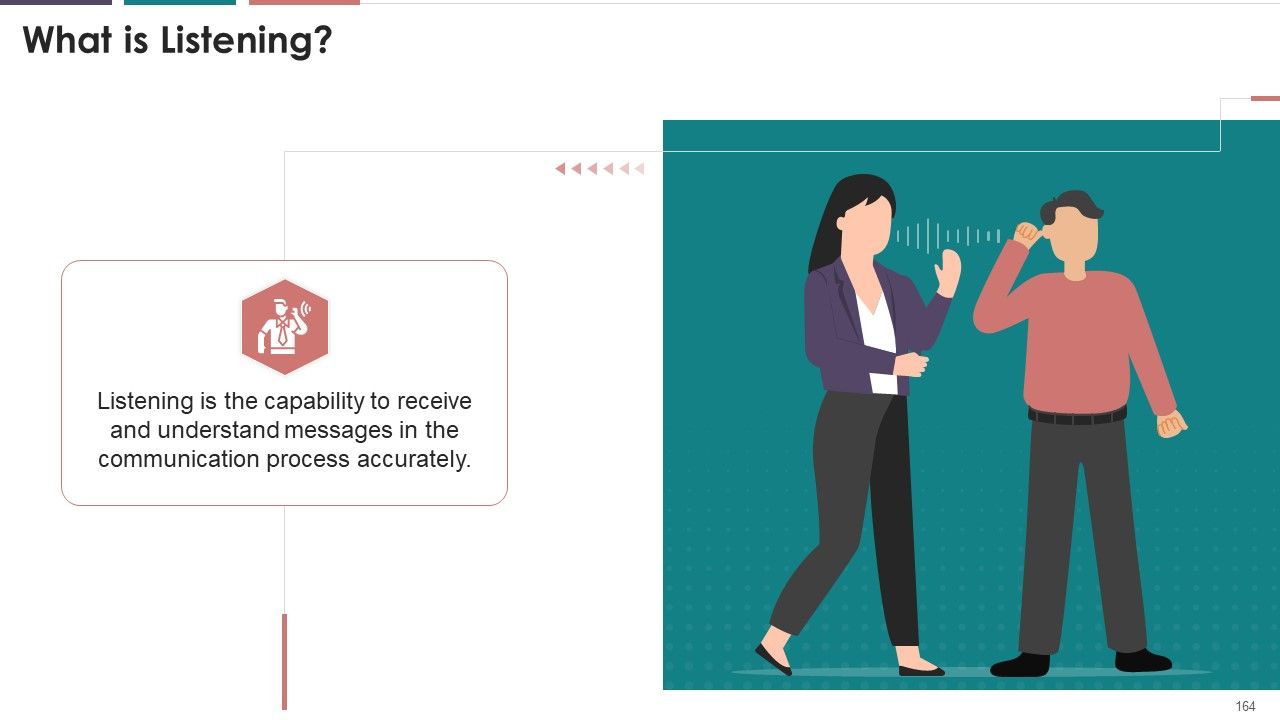
- What is Listening?
- Principles of Listening
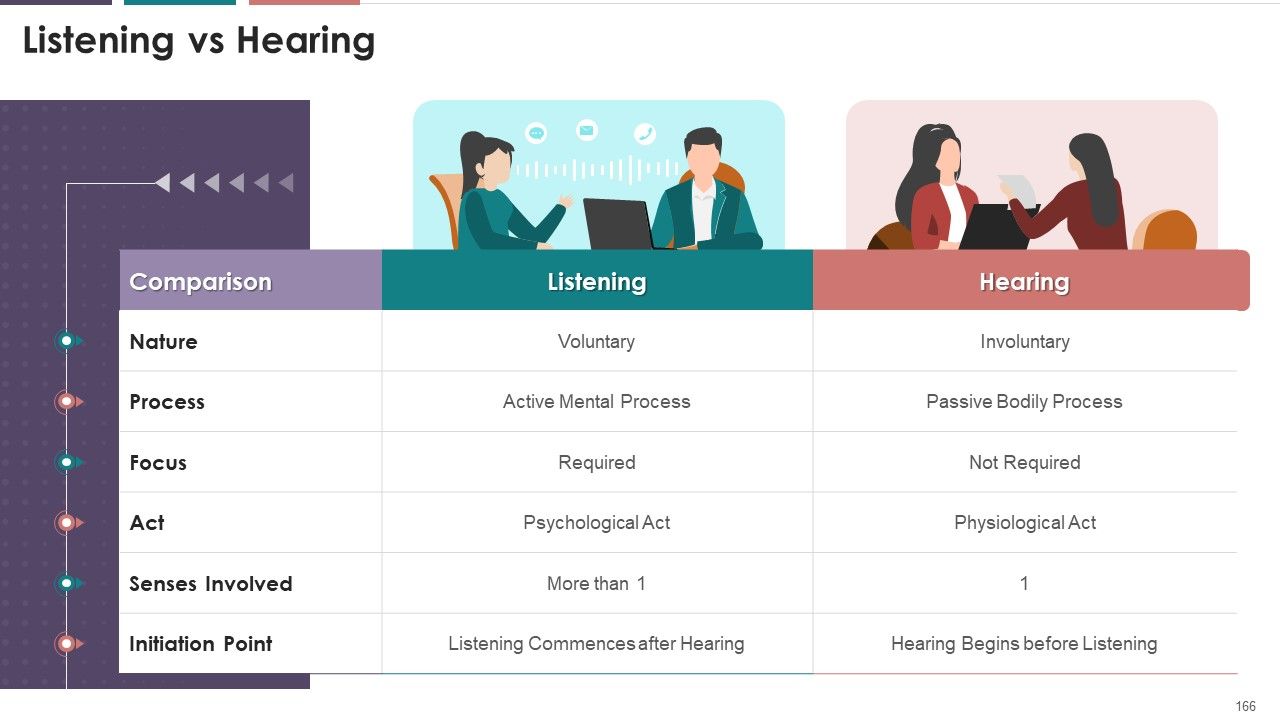
- Listening vs Hearing
- Key Statistics for Listening
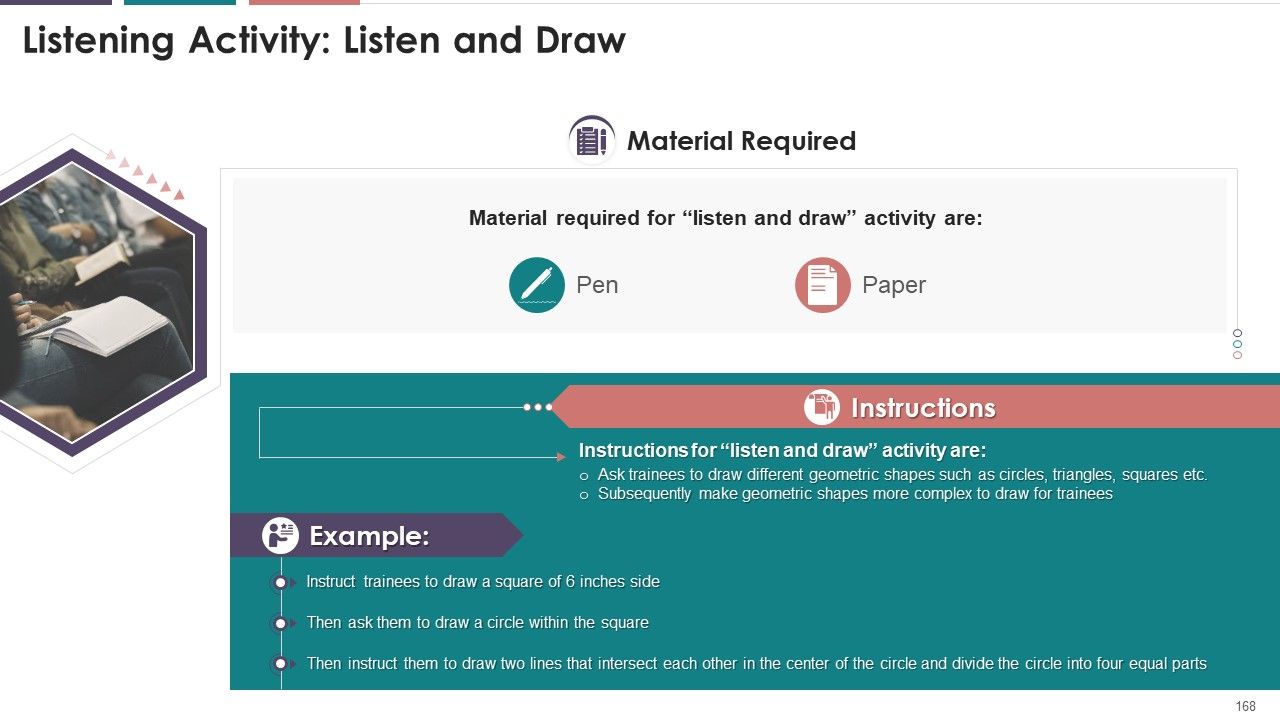
- Activity: Listen and Draw
- Major Objectives of Listening
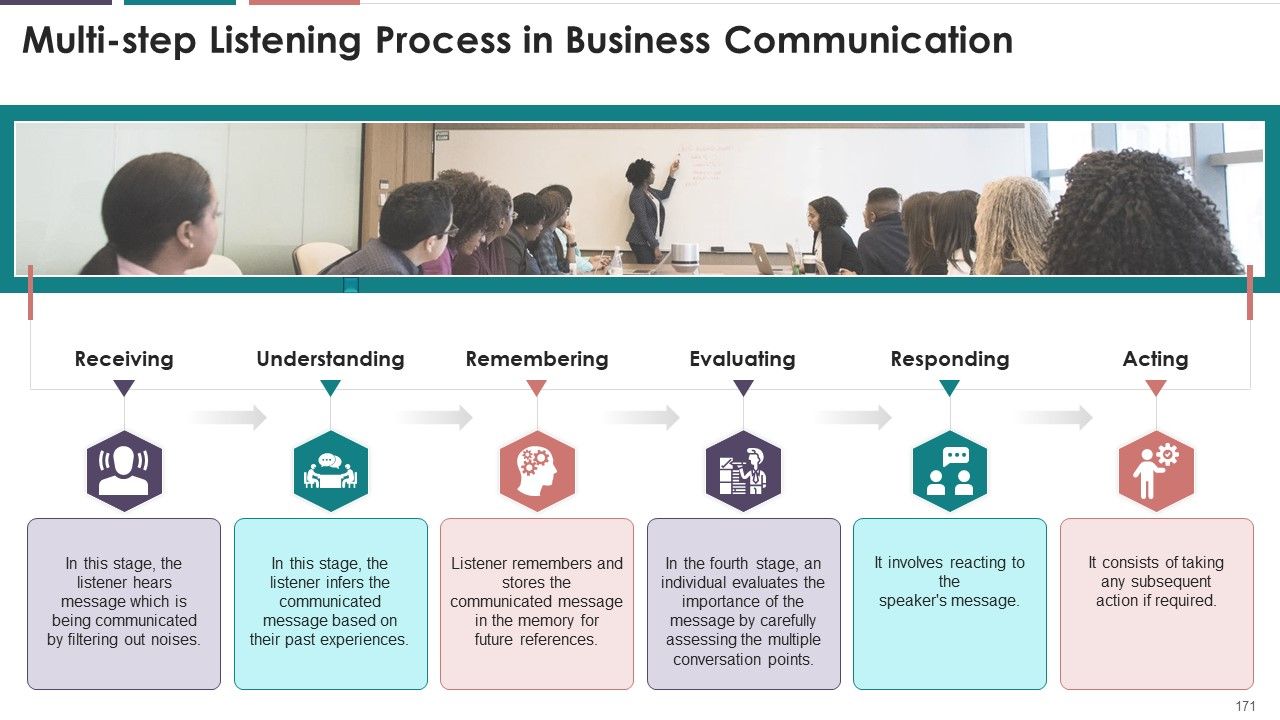
- Multistep Listening Process
- Listening is Important!
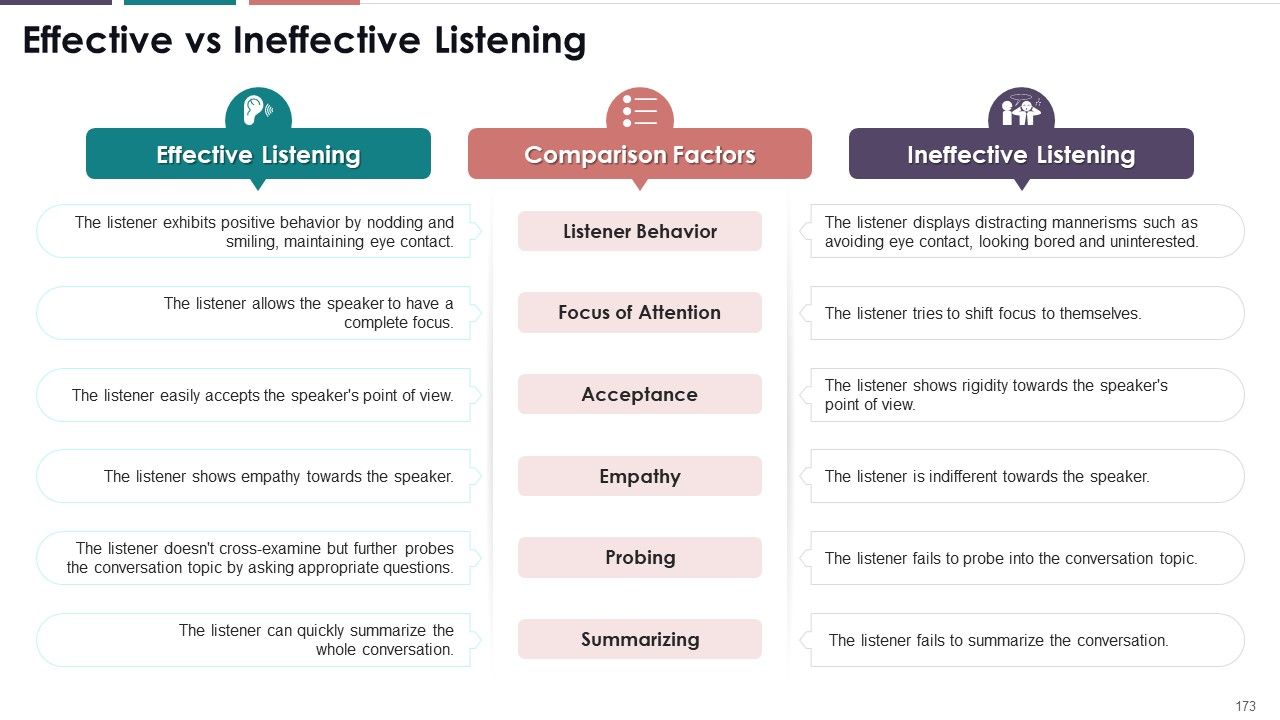
- Effective vs Ineffective Listening
- Listening Activity: Drawing Twin
- Effective Listening Types
- Discriminative Listening
- Comprehensive Listening
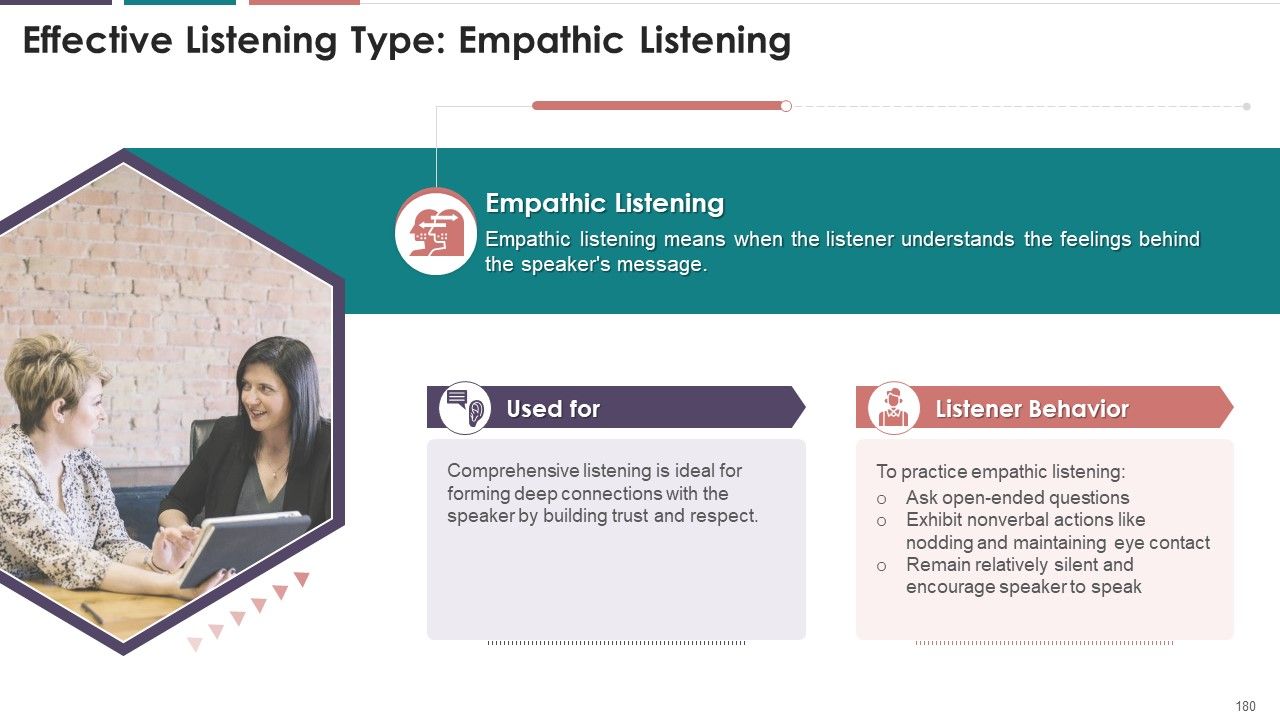
- Empathic Listening
- Analytical Listening
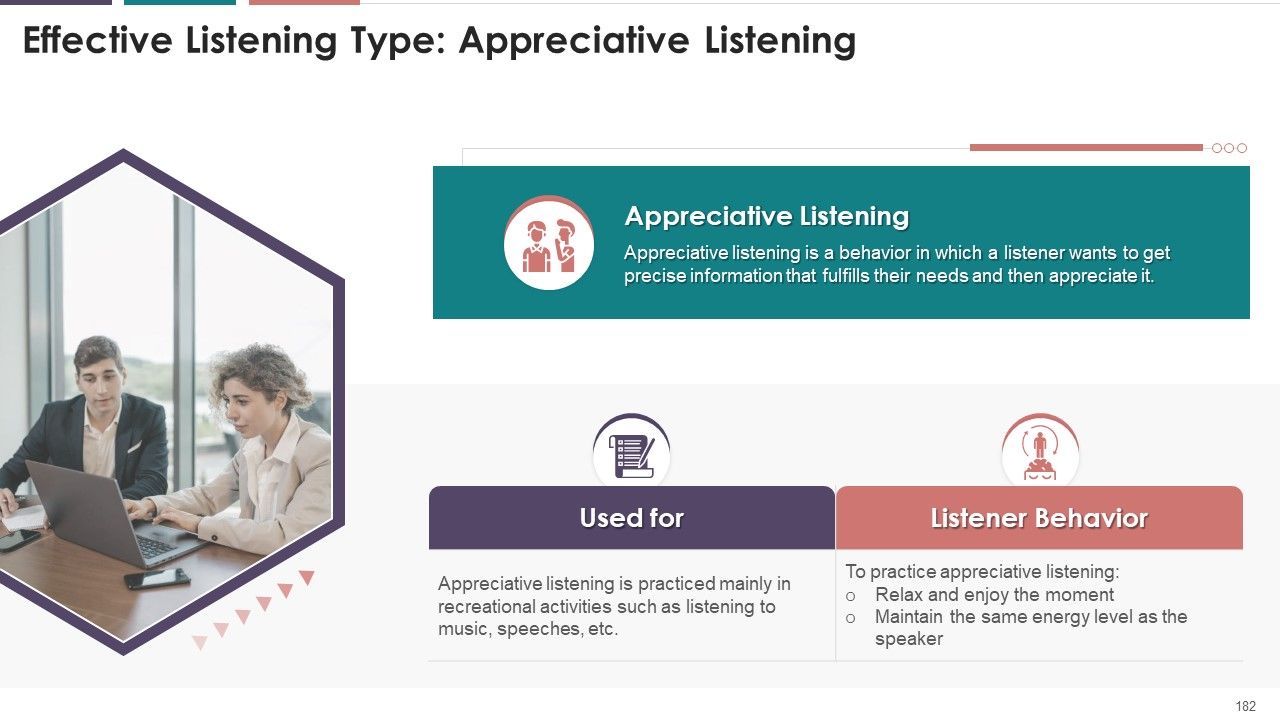
- Appreciative Listening
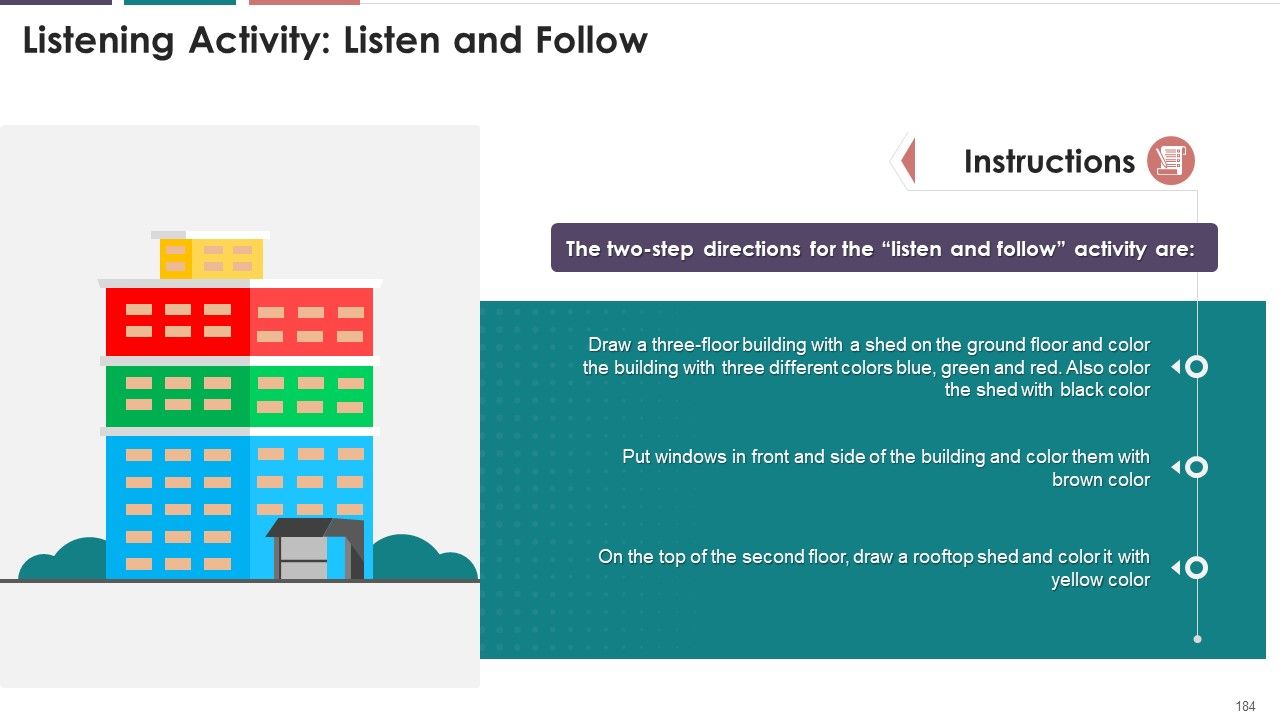
- Activity: Listen and Follow
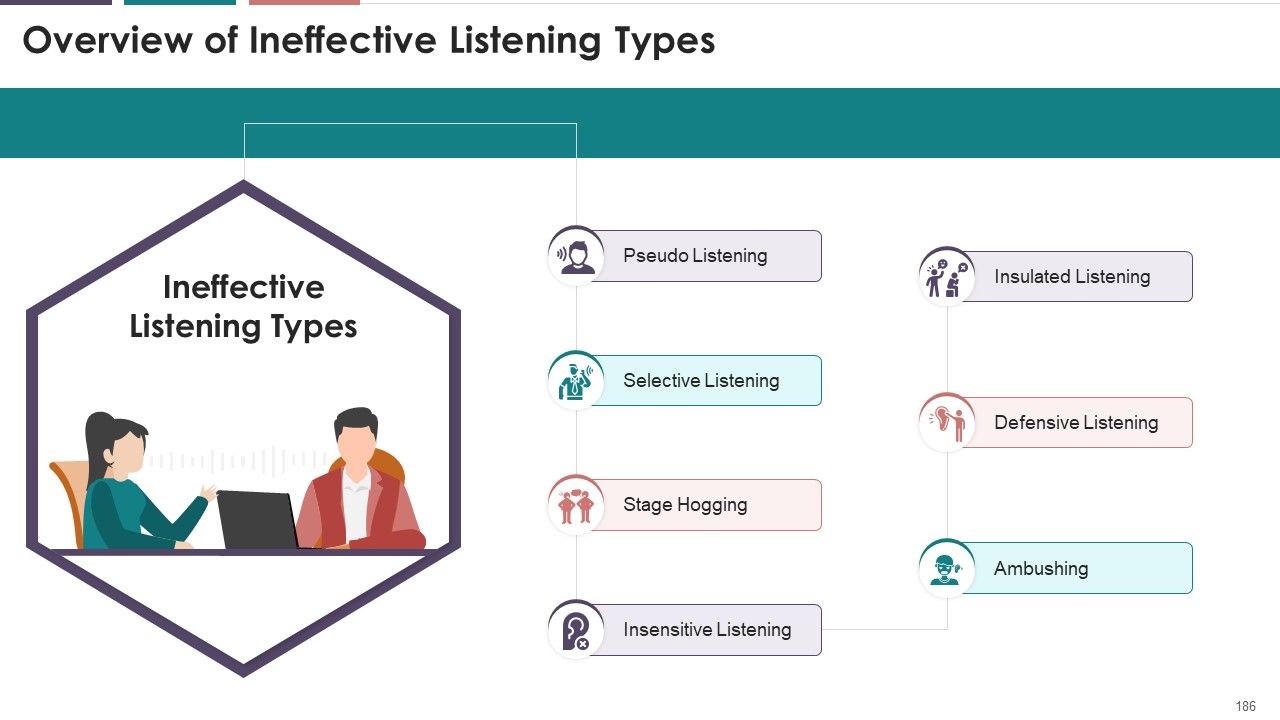
- Ineffective Listening Types
- Pseudo Listening
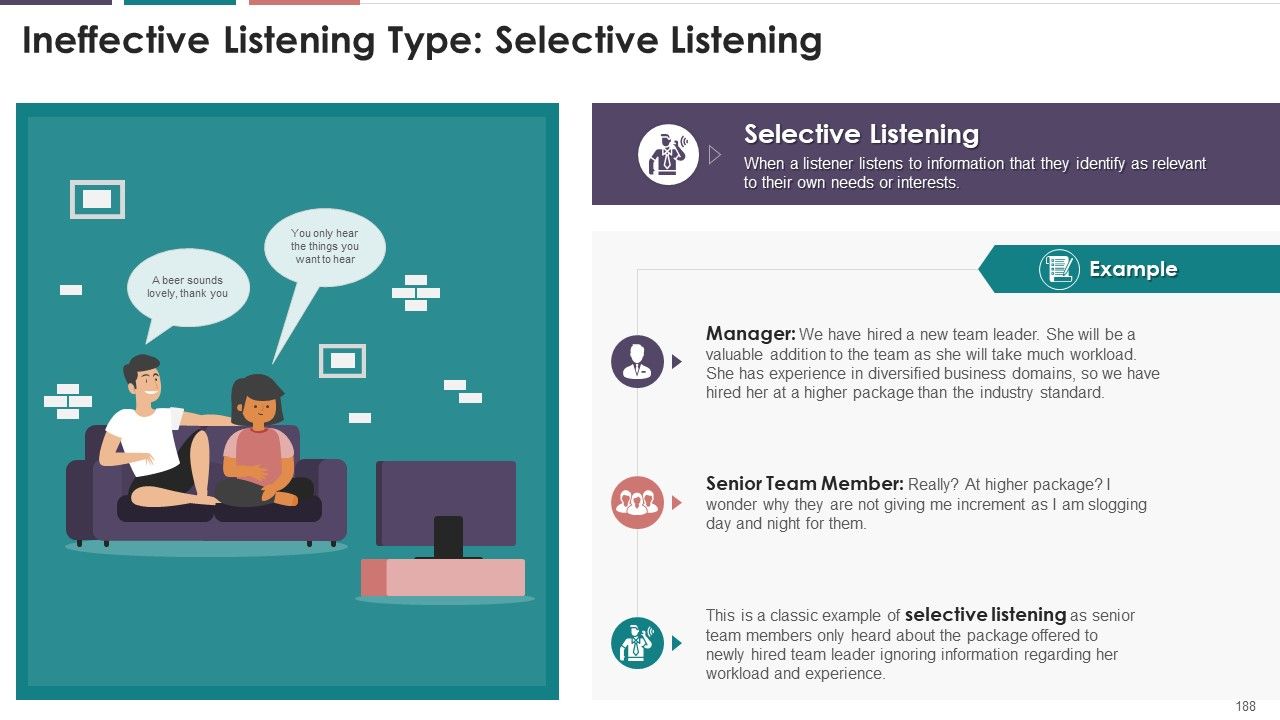
- Selective Listening
- Stage Hogging
- Insensitive Listening
- Ambushing
- Defensive Listening
- Insulated Listening
- Introduction to Active Listening
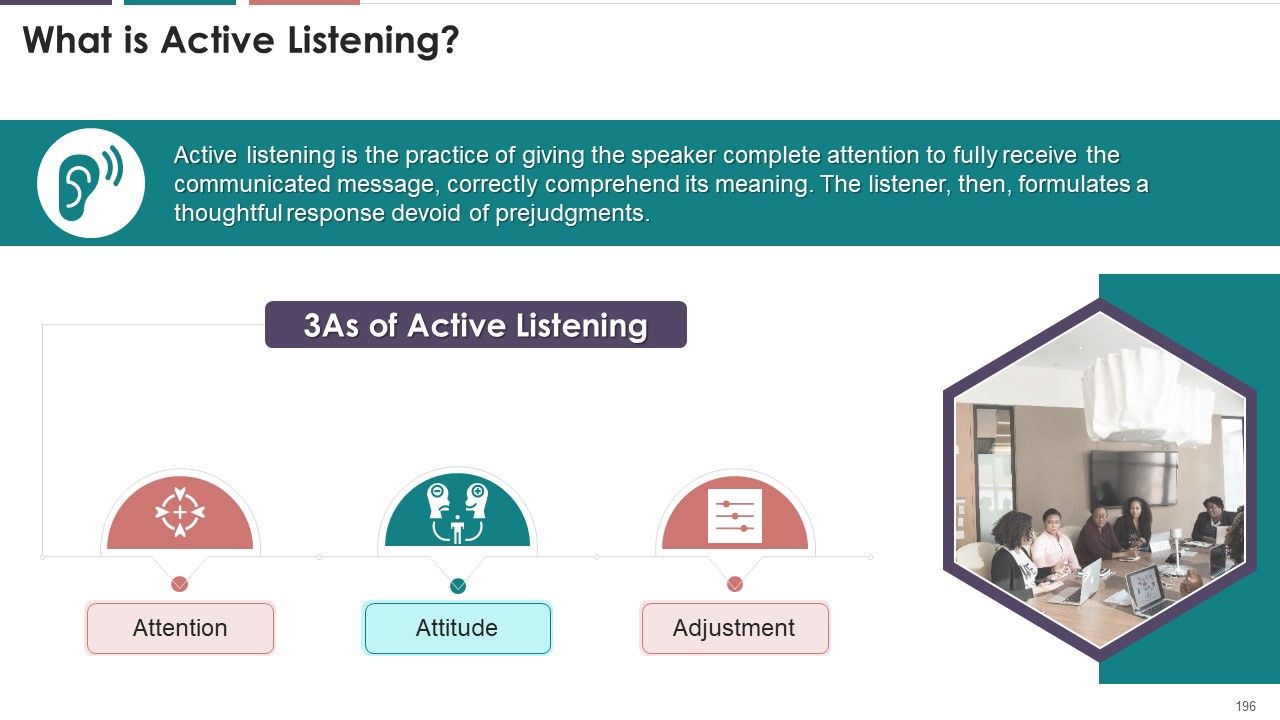
- What is Active Listening?
- 3 As of Active Listening
- Active vs Passive Listening
- Activity: Active Listening Roleplay
- Active Listening Benefits
- How to become an Active Listener?
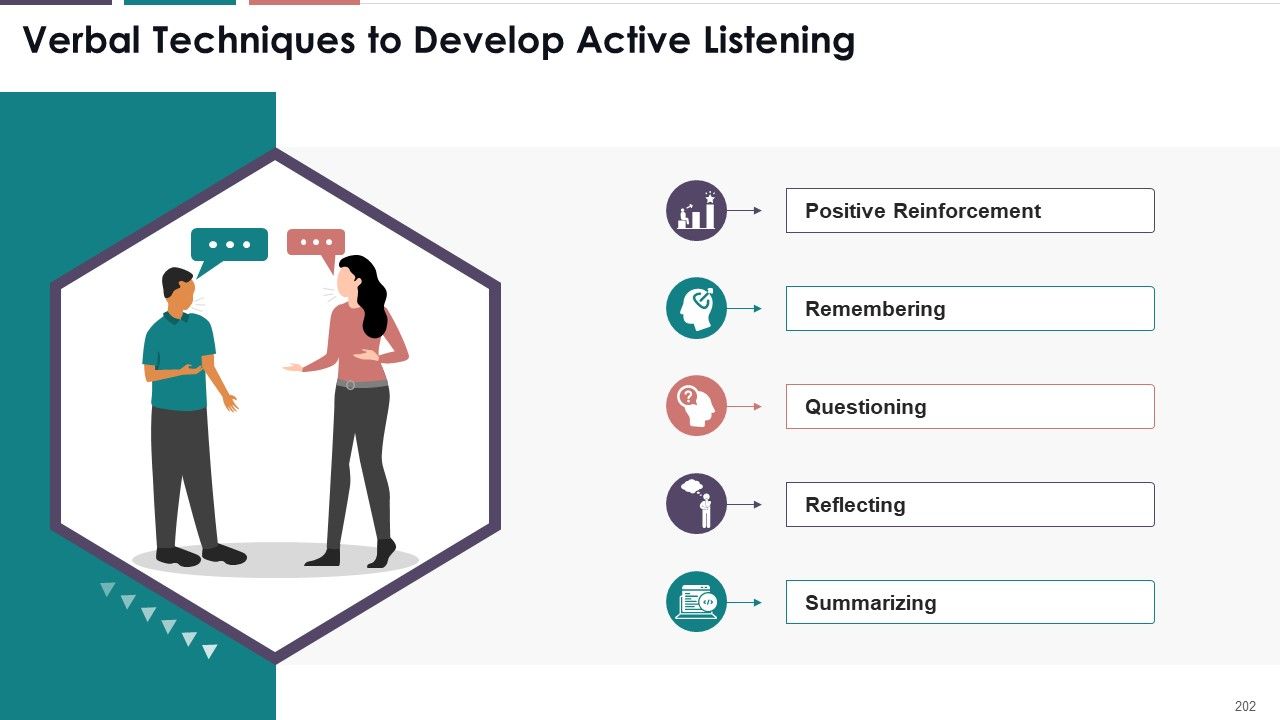
- Verbal Techniques to Develop Active Listening
- Positive Reinforcement
- Remembering
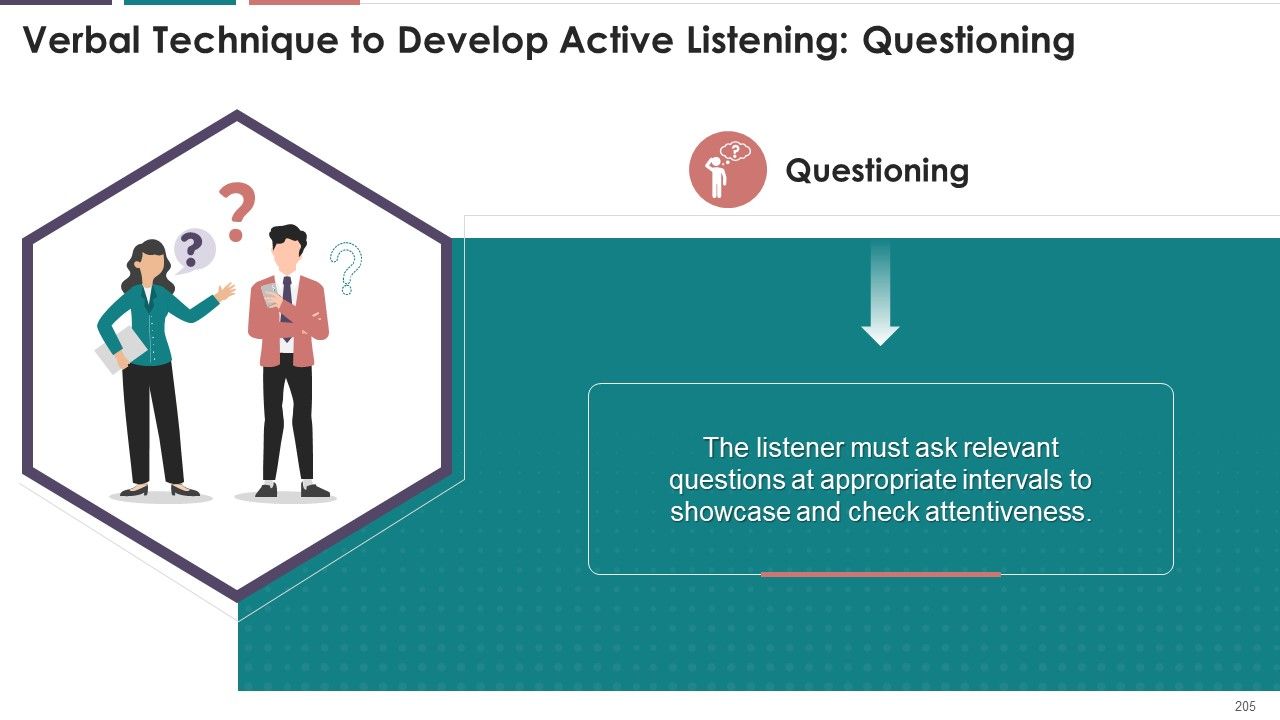
- Questioning
- Reflecting
- Summarizing
- Activity: Active Listening Roleplay
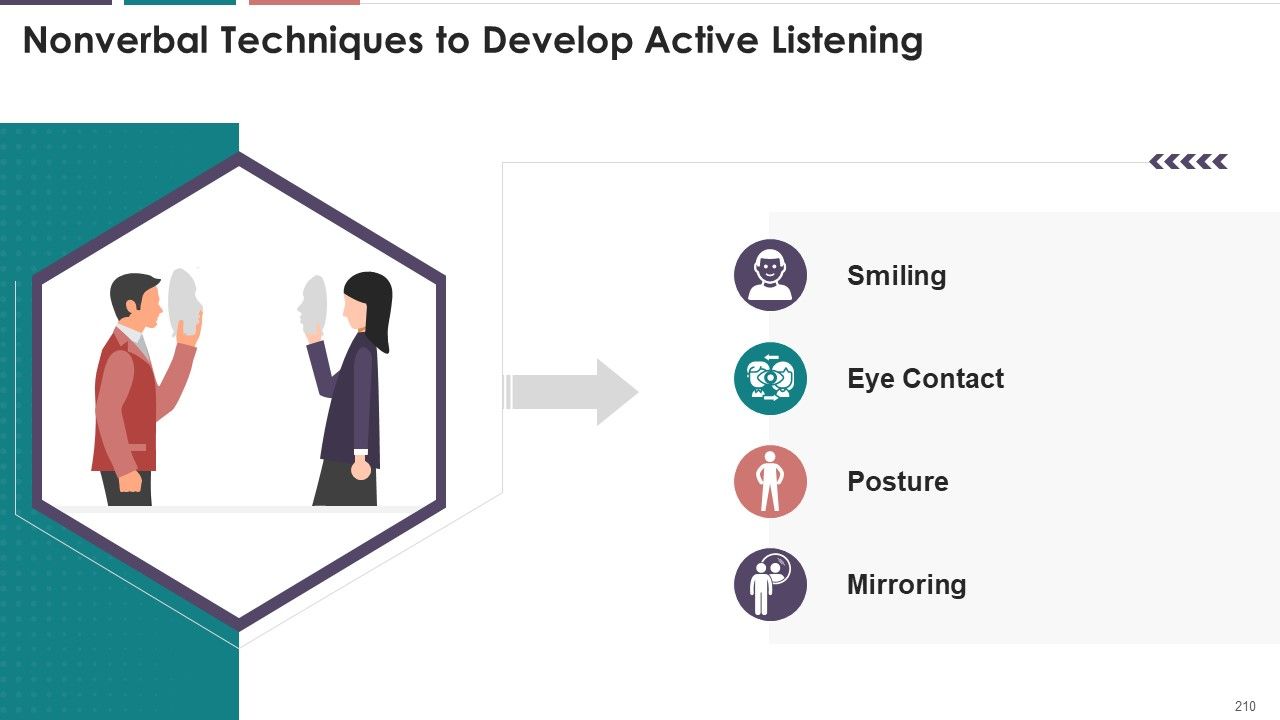
- Nonverbal Techniques to Develop Active Listening
- Smiling
- Eye Contact
- Posture
- Mirroring
- Activity: Active Listening Roleplay
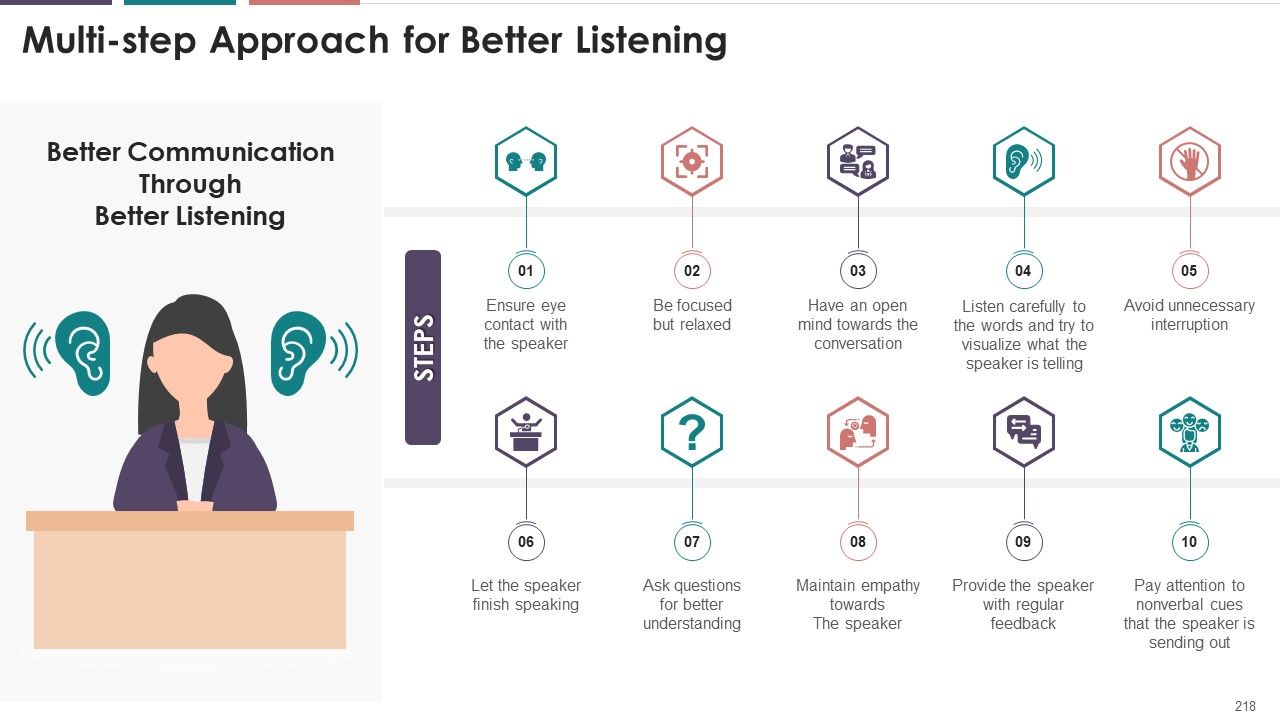
- Multistep Approach for Better Listening
- Feedback Acknowledgement in Listening
- Active Listening Approach for Giving Feedback
- Active Listening Approach for Receiving Feedback
- Key Barriers to Effective Listening
- External Distractions
- Speaker Distractions
- Message Intent
- Emotional Language
- Personal Perspective
- Key Takeaways from Session
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Concept of Speaking
- Meaning
- Significance of Effective Speaking
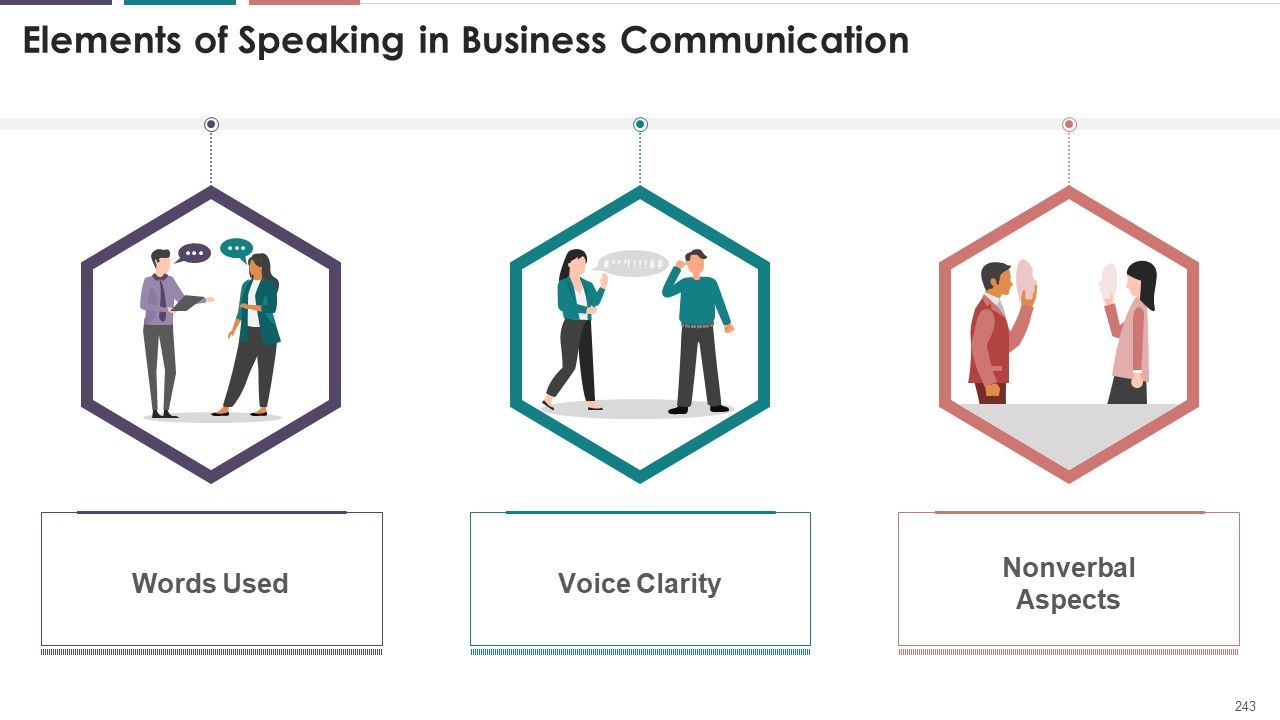
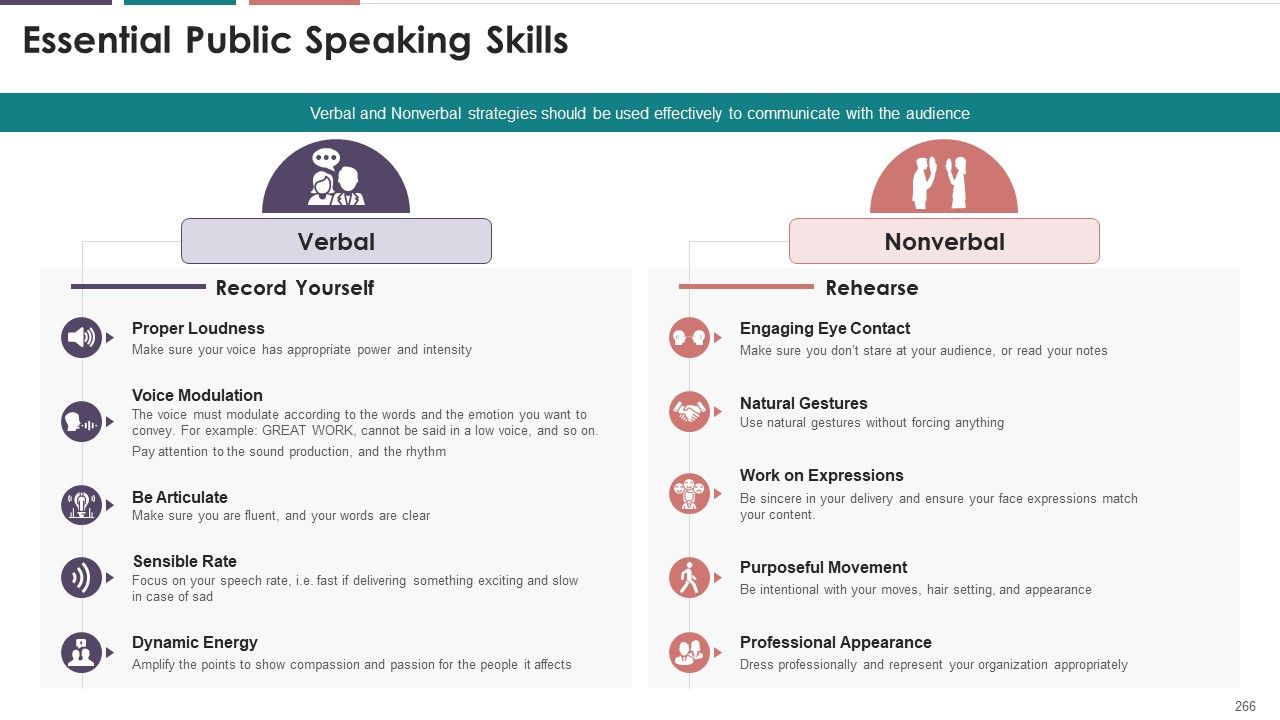
- Elements of Speaking
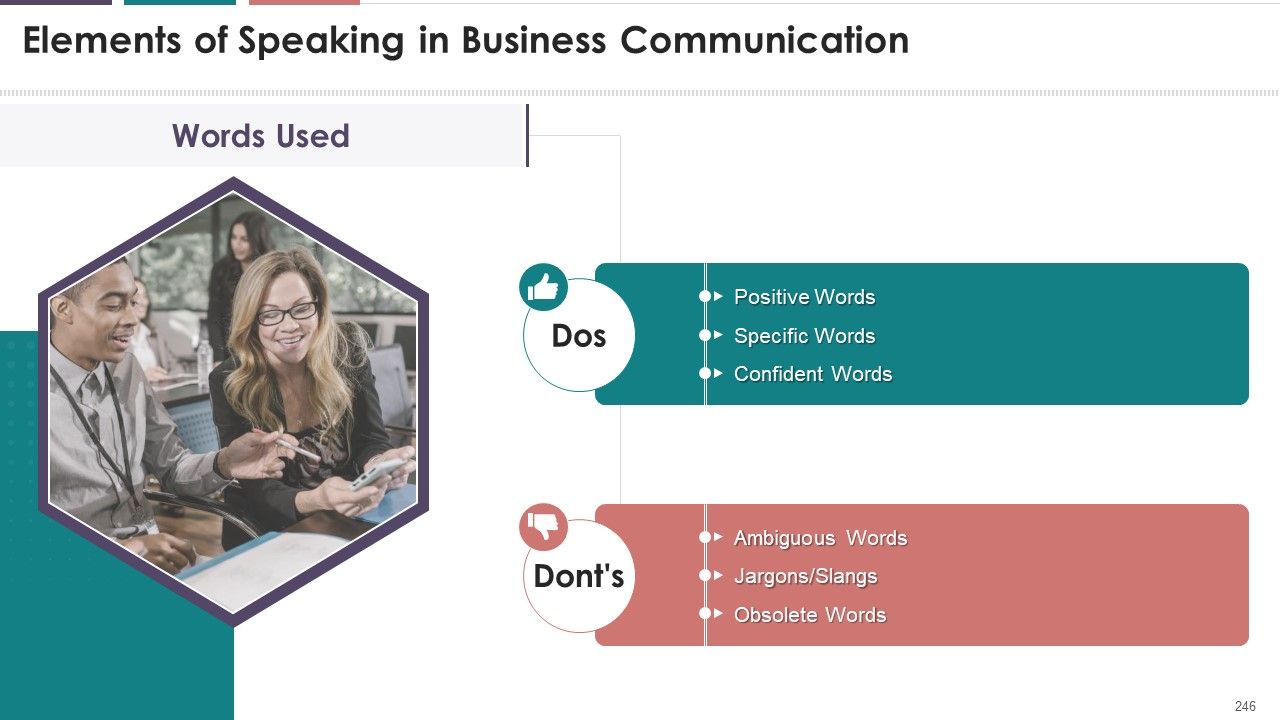
- Words Used
- Voice Clarity
- Nonverbal Aspects
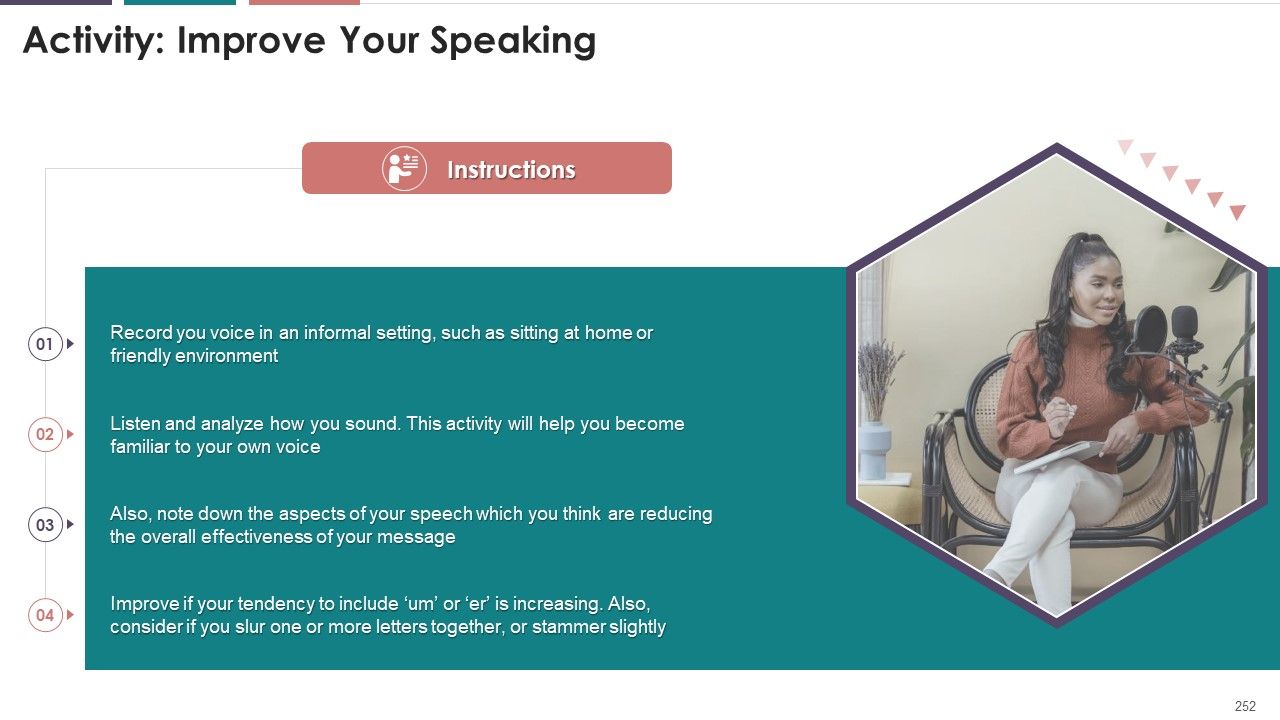
- Activity: Improve your Speaking
- Types of Speaking:
- Speaking to Inform
- Speaking to Persuade
- Speaking to Actuate
- Speaking to Entertain
- Activity: Tell a Group Story
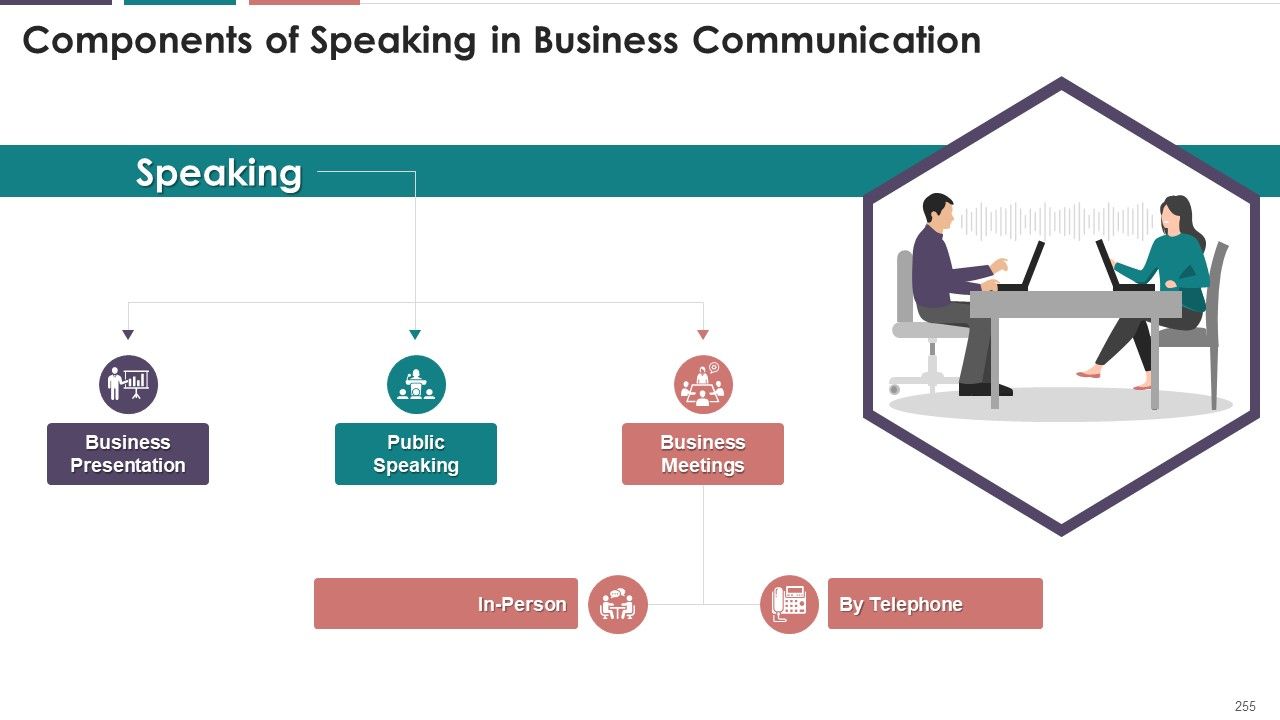
- Components of Speaking
- Business Presentations
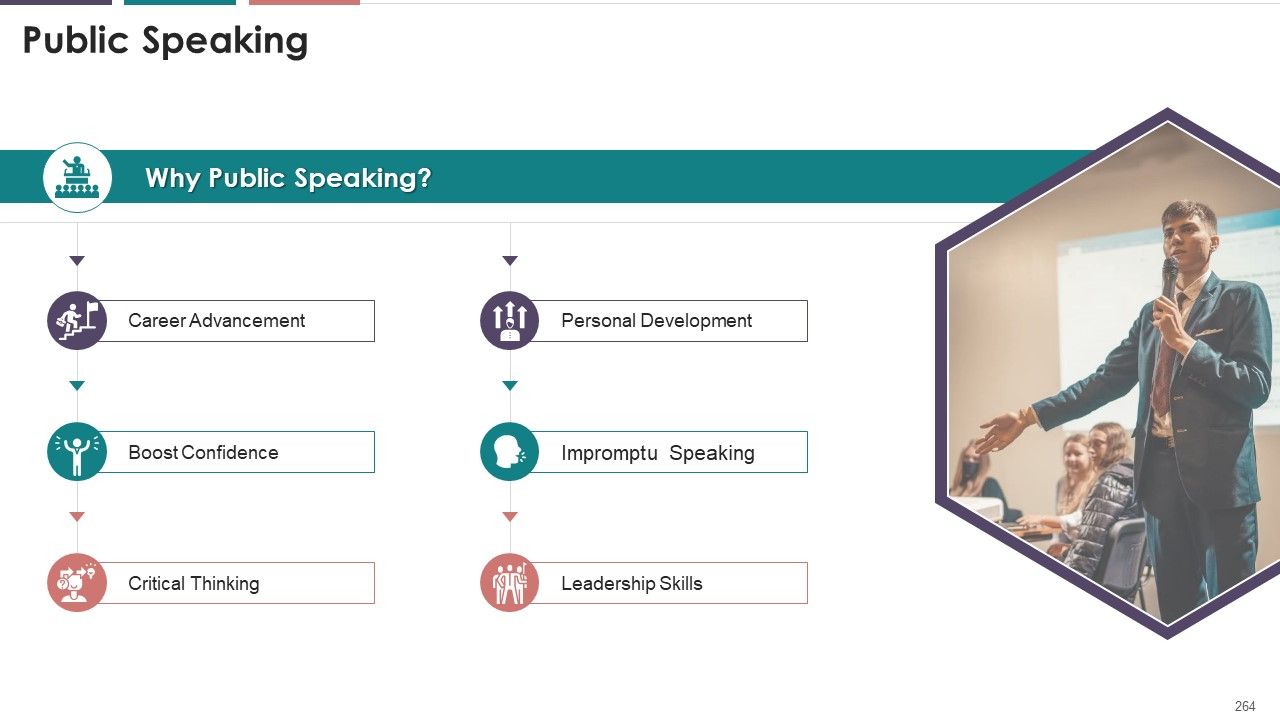
- Public Speaking
- Activity: One Minute off-the-cuff
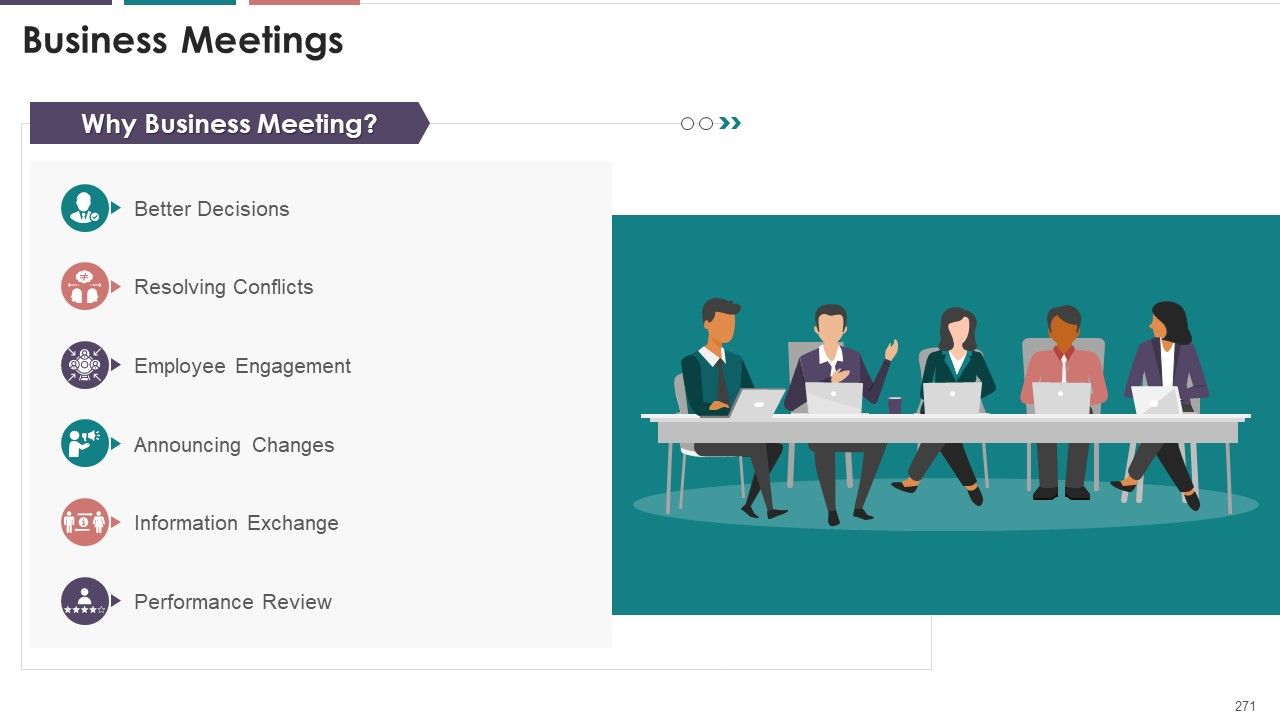
- Business Meetings
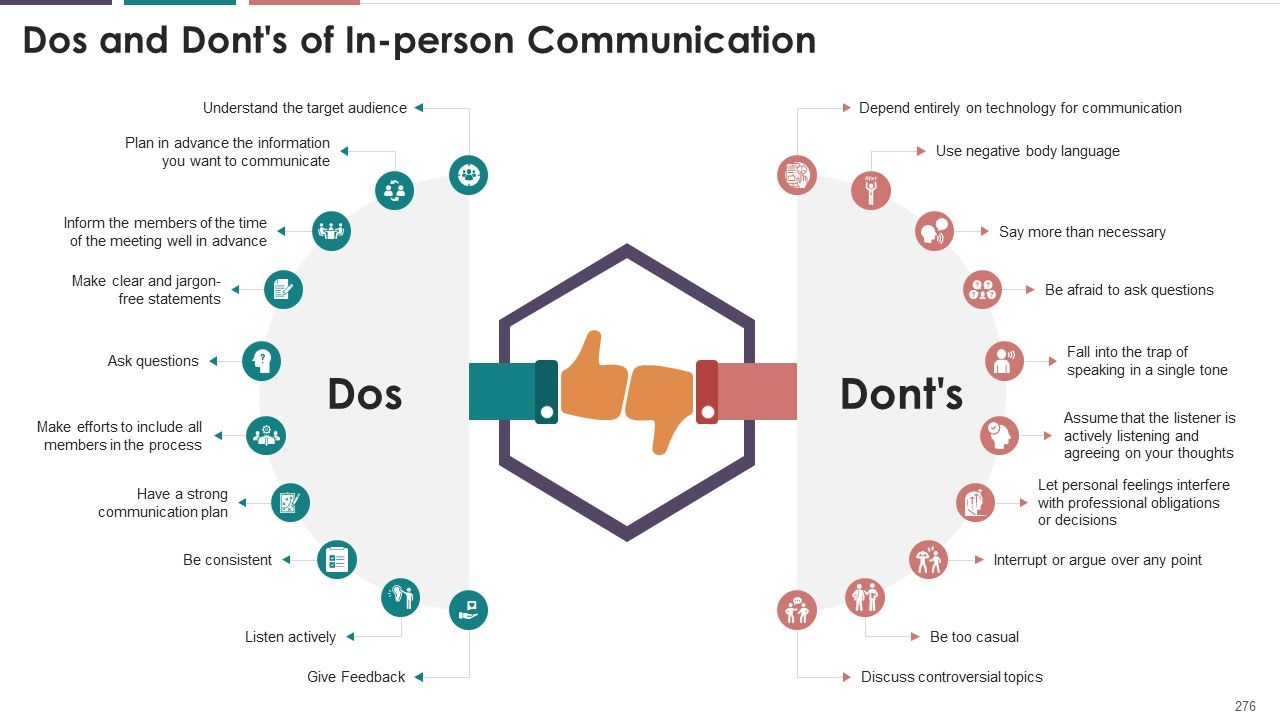
- In-Person
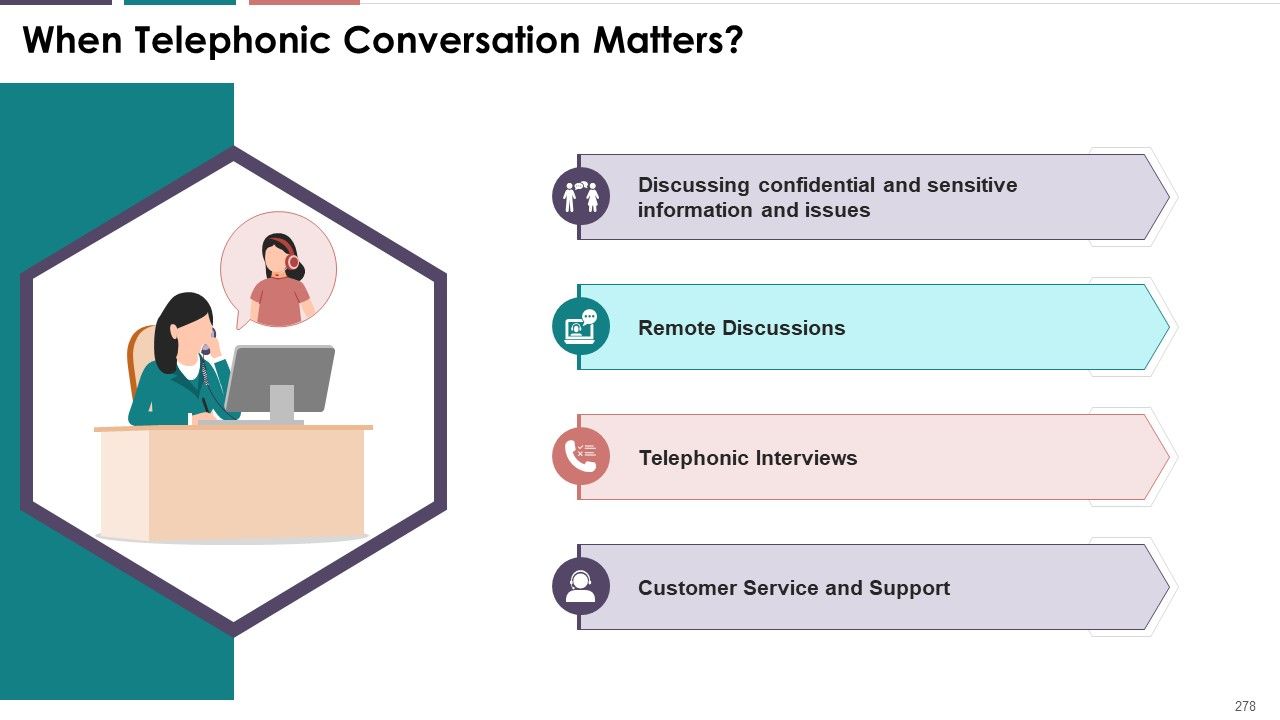
- Over Telephone
- Activity: Develop Effective Speaking Skills
- Techniques of Effective Speaking
- Identify and Focus on the Audience
- Begin with the Purpose of Speech
- Tell a Story
- Inclusion and Structuring of Content
- Work on the Speech Rate
- Feedback and Follow-Up Session
- Activity: Telephone Exercise
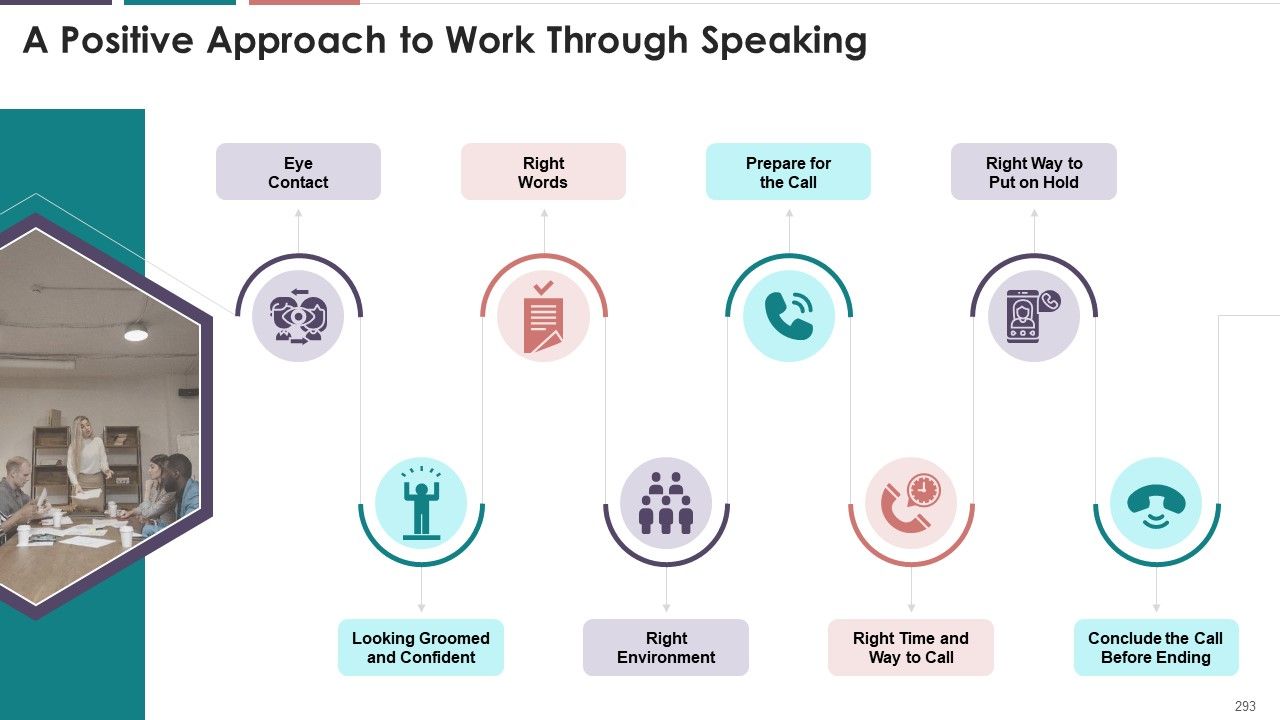
- Putting a Positive Approach to Work through Speaking
- PVLEGS Framework
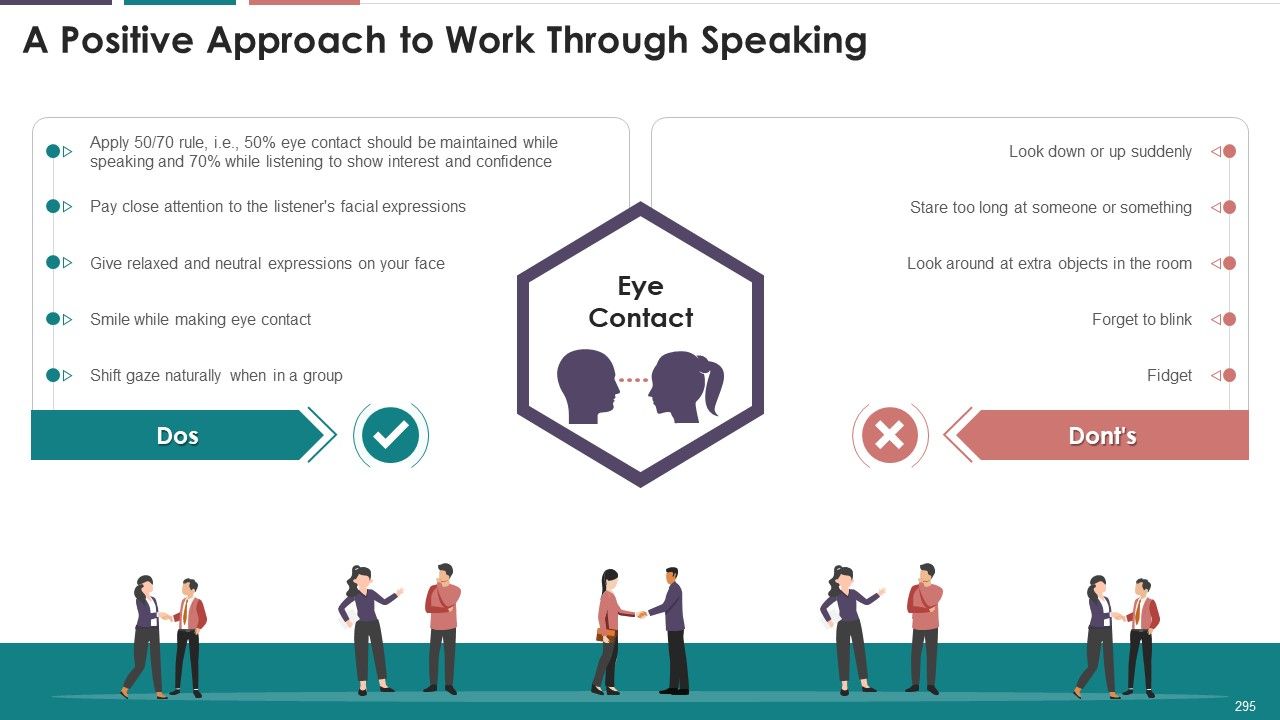
- Eye Contact
- Look Alert and Confident
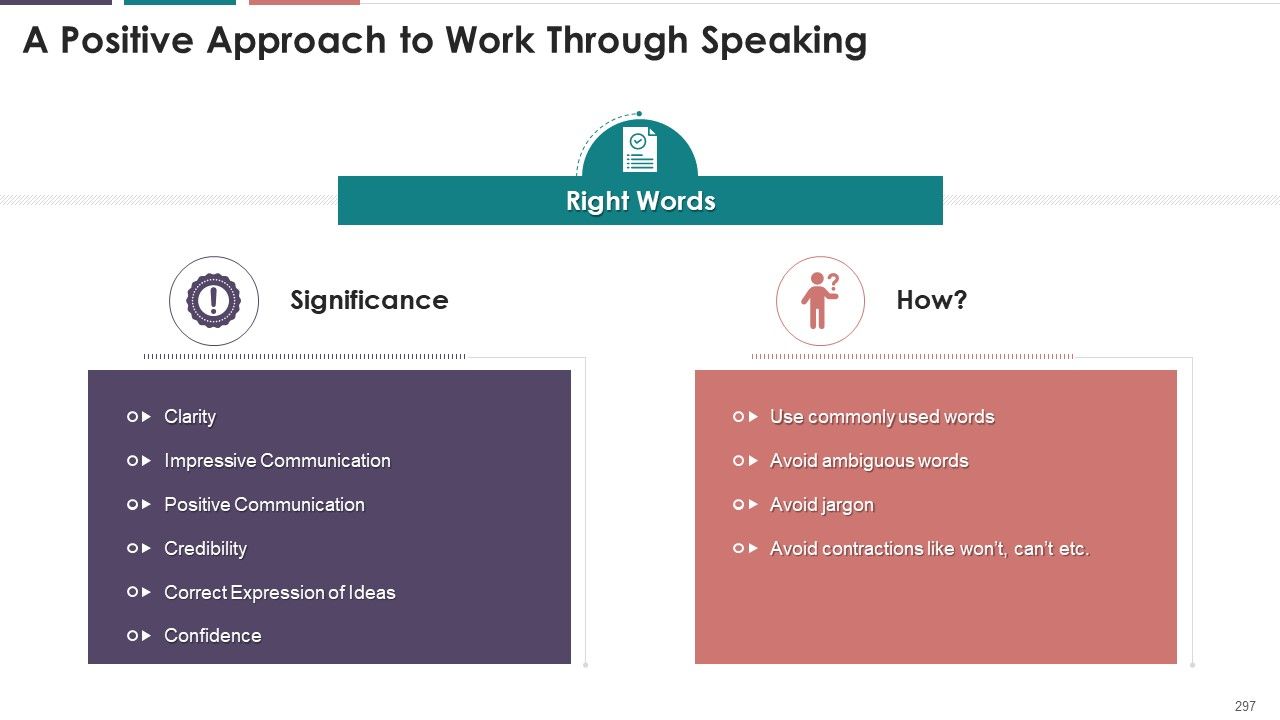
- Choose the Right Words
- Prepare Before the Call
- Right Time and Way to Schedule the Call
- Choose the Right Environment for the Call
- Right Way to Put Someone on Hold
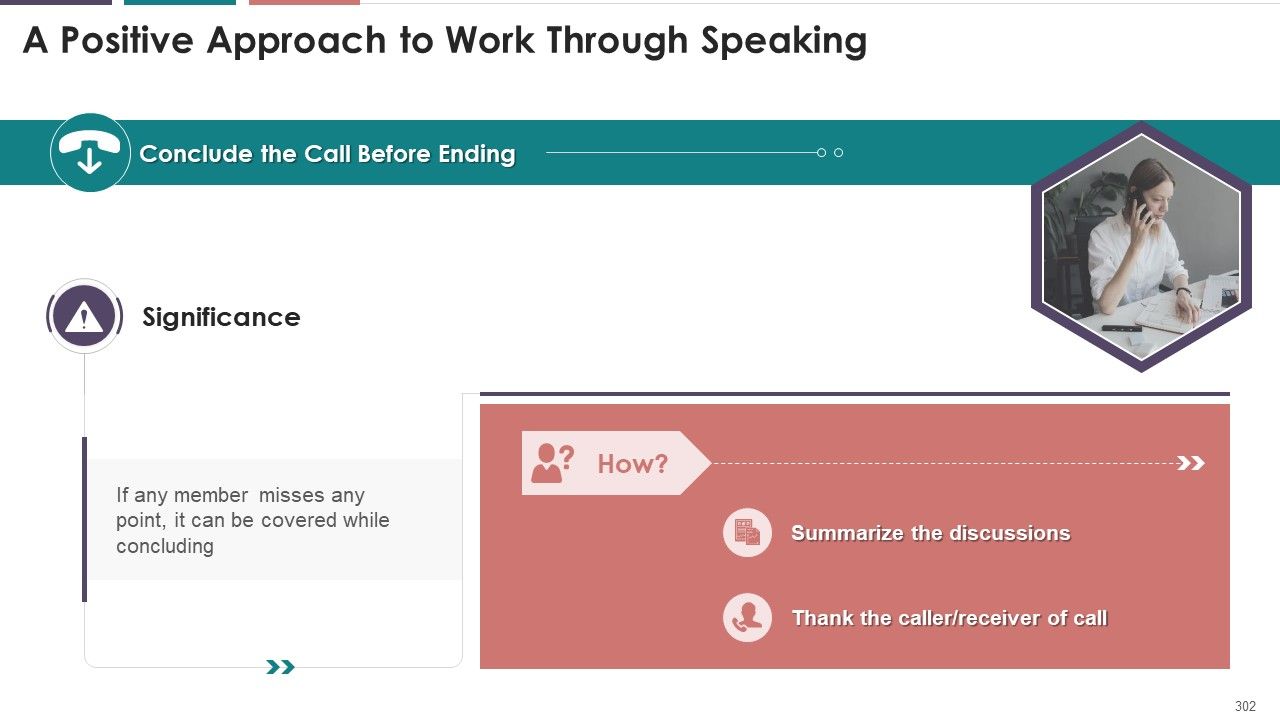
- Conclude the Call Before Ending
- Activity: Speech Monitor
- Barriers to be Reduced in Communication
- External Distractions
- Speaker Distractions
- Body Language
- Message Intent/Semantics
- Personal Perspective
- Activity: Tongue Twisters
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Evaluation Exercises
- Activity: Step into the Difficult Customer’s Shoes
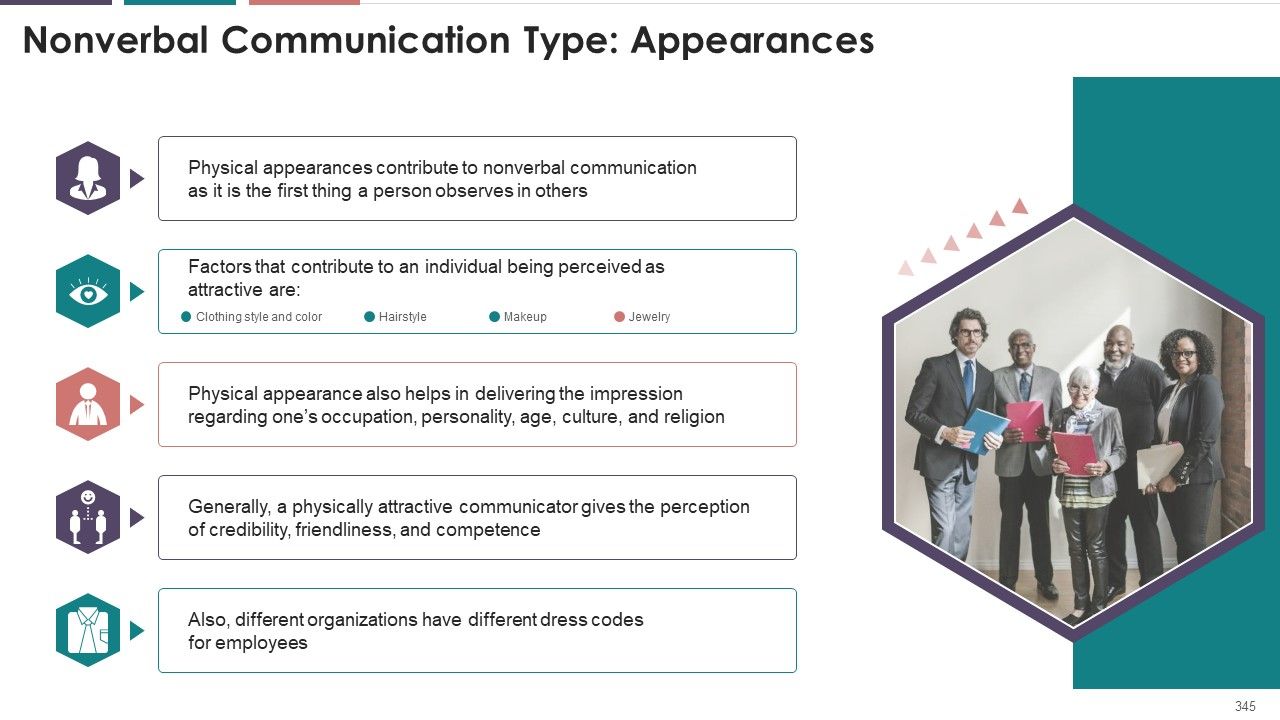
- What is Nonverbal Communication?
- Verbal vs Nonverbal Communication
- Activity: Nonverbal Communication Assessment
- Nonverbal Communication Significance
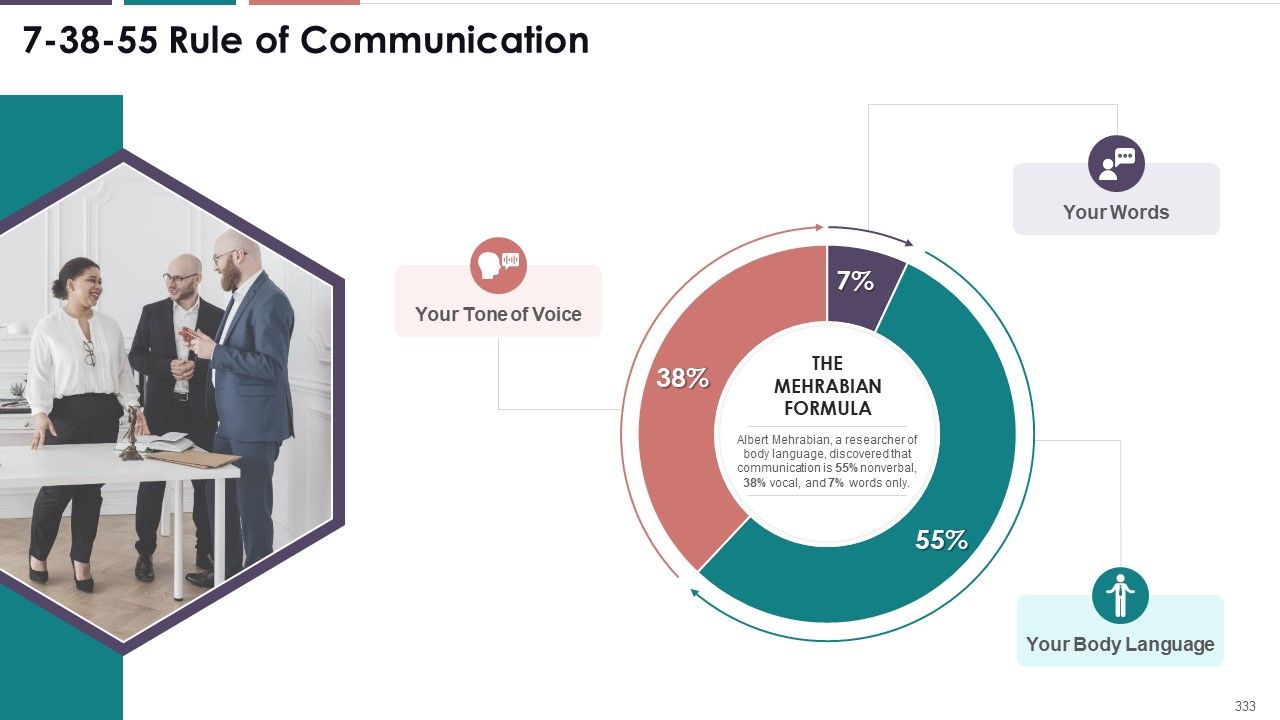
- 7-38-55 Rule of Communication
- Importance of Nonverbal Communication
- Facets of Nonverbal Communication in Workplace
- Repetition
- Contradiction
- Substitution
- Complement
- Accent
- Activity: Observation
- Types of Nonverbal Communication
- Facial Expressions
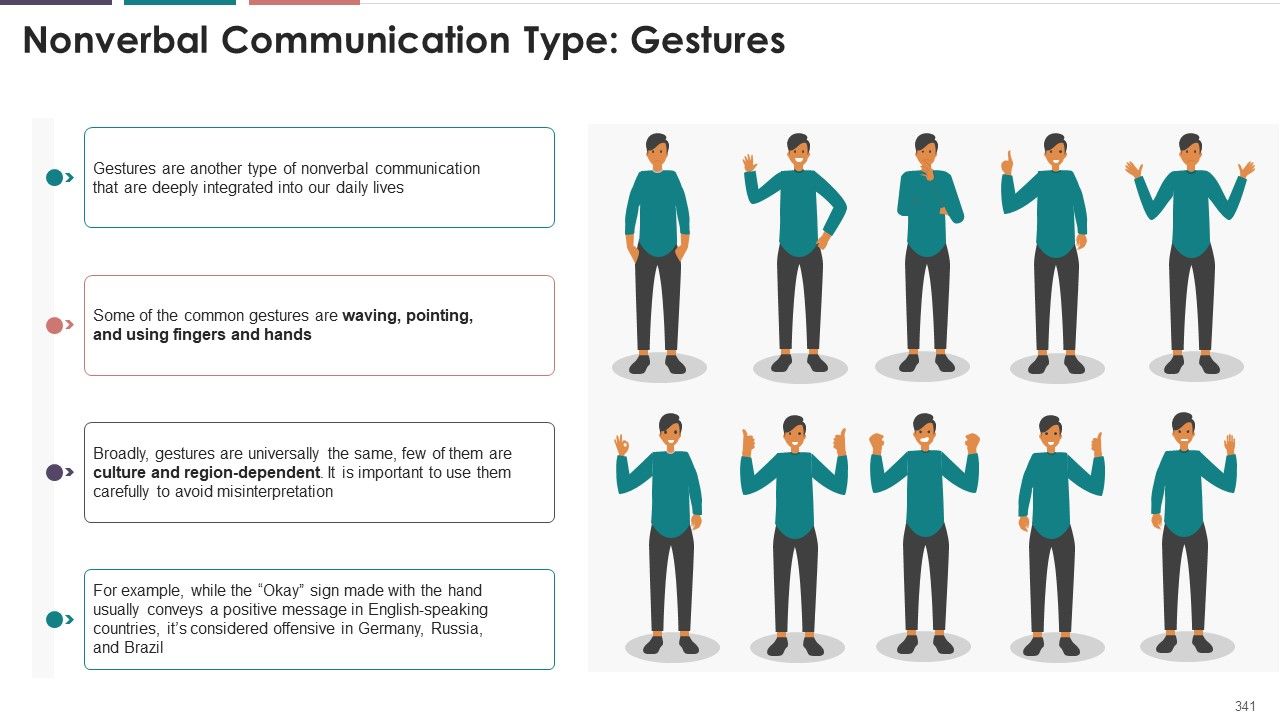
- Gestures
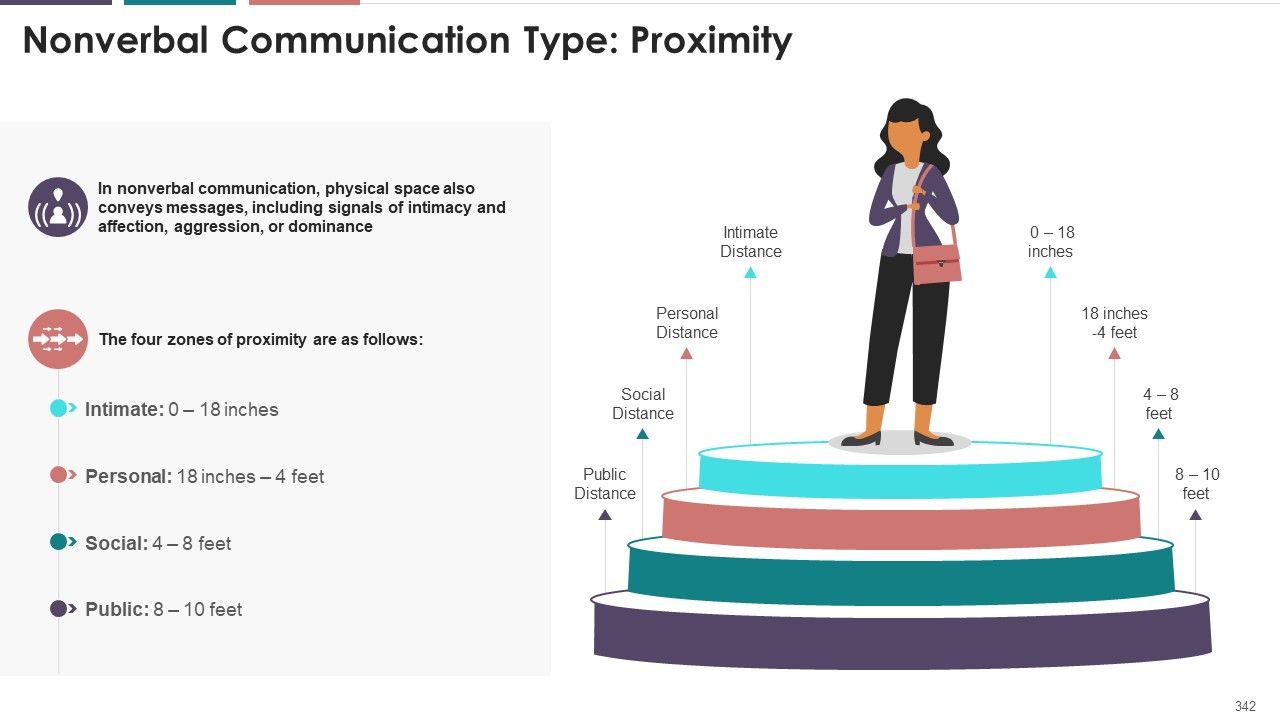
- Proximity
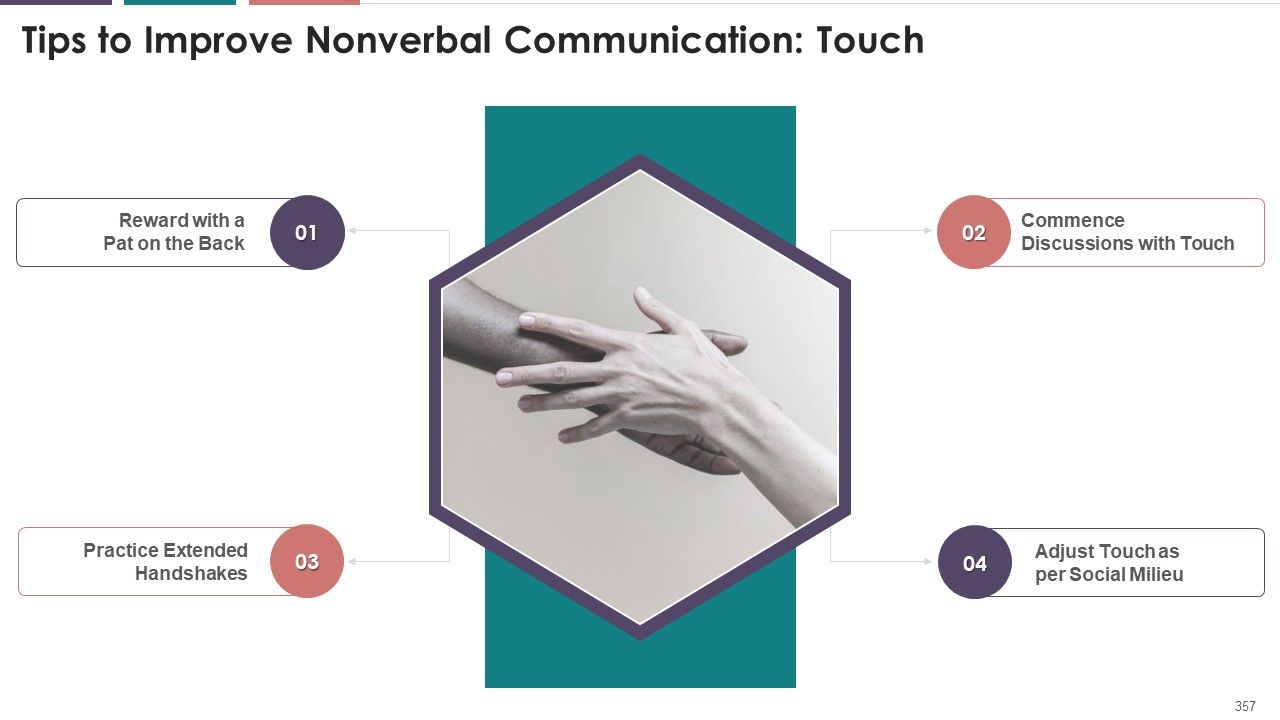
- Touch
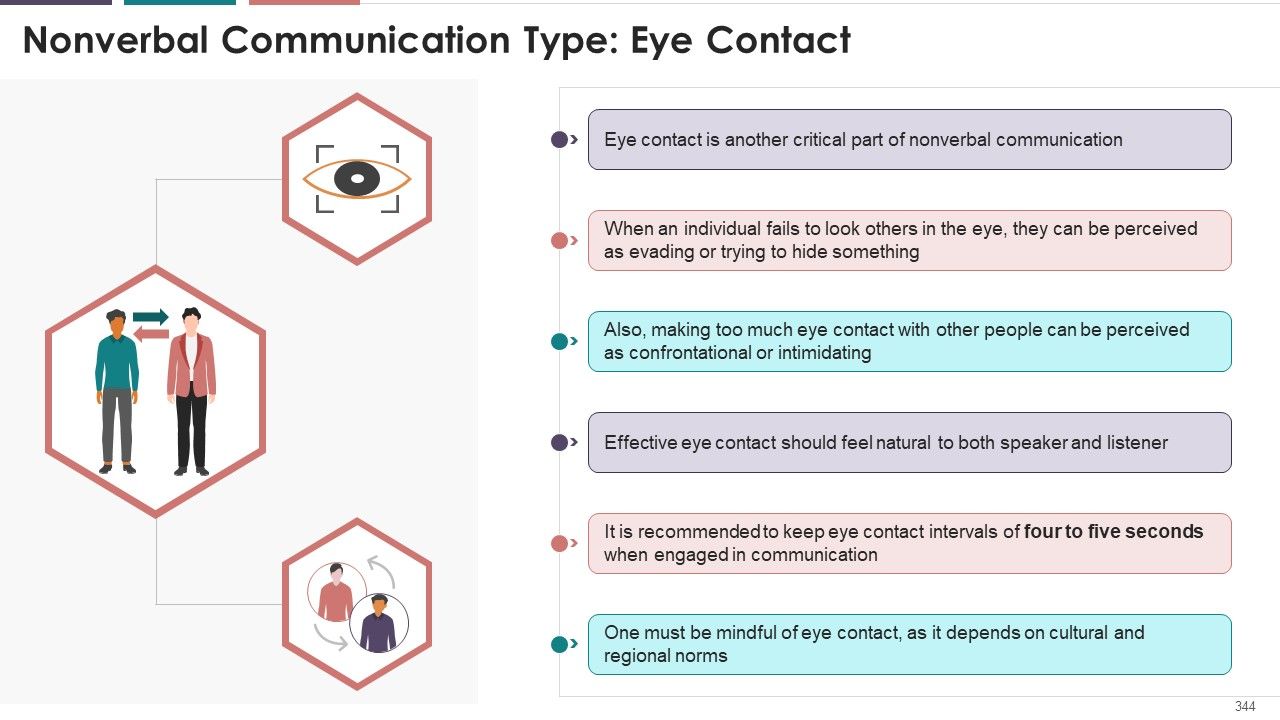
- Eye Contact
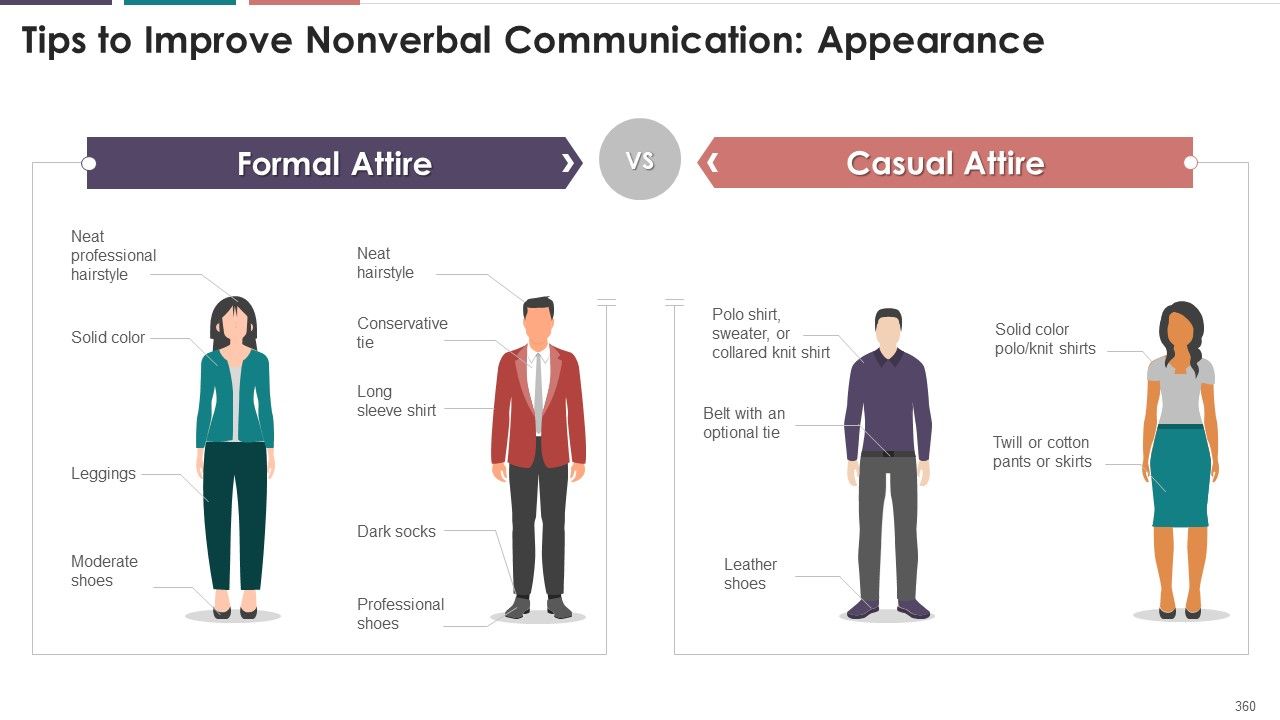
- Appearance
- Activity: Guess the Initial Mood
- Factors that Impact Nonverbal Communication
- Culture
- Environment
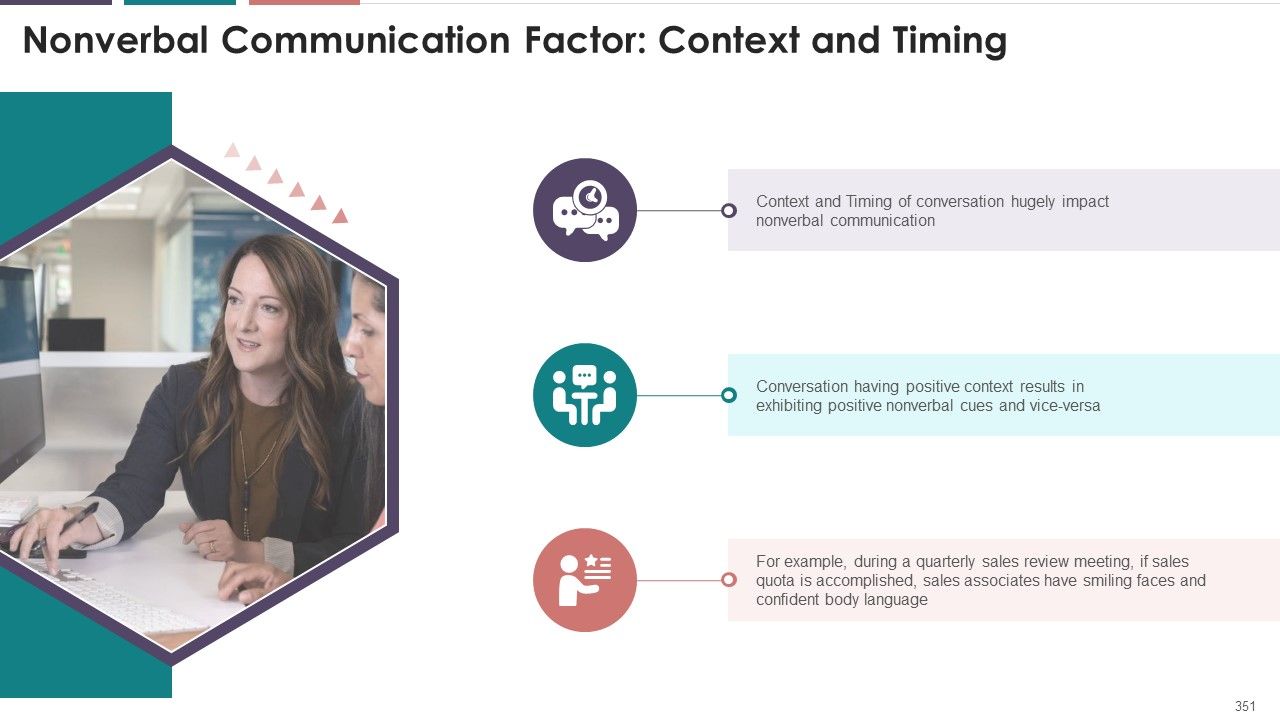
- Context
- Timings
- Activity: One Talker/One Not
- Techniques to Improve Nonverbal Communication
- Facial Expressions
- Gestures
- Proximity
- Touch
- Eye Contact
- Appearance
- Key Barriers to Nonverbal Communication
- Impactful First Impression with Nonverbal Communication
- Mirroring in Nonverbal Communication
- Trust and Rapport Building in Nonverbal Communication
- Effective Online Business Conversations using Nonverbal Communication
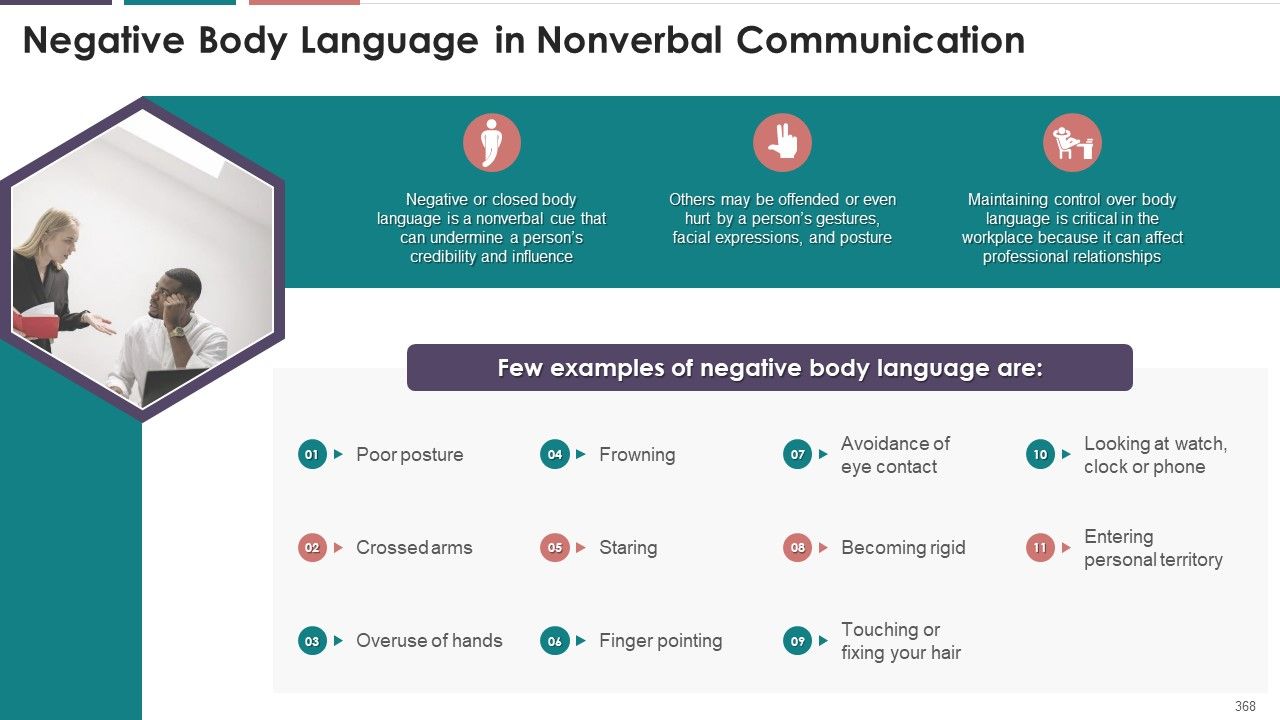
- Negative Body Language in Nonverbal Communication
- Tips for Spotting Nonverbal Deception
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Purpose of Online Meeting
- Importance of Online Meeting
- Statistics for Online Meeting
- Online Meeting: Pros and Cons
- Software for Online Meeting
- Online Communication Improvement Tips
- Before Meeting
- During Meeting
- After Meeting
- Online Meeting: Dos and Don’ts
- Barriers for Online Meeting
- Activities for Online Meeting
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- Memes
- What is a Story?
- Significance of Storytelling
- In General Communication
- Grab Attention
- Make it Personal, Emotionally Connect People, and Create Loyalty
- Challenge Current Perspective
- Create Empathy
- Likely to be Revisited
- In Business Communication
- Business Development
- Competitive Advantage
- Marketing and Advertising
- Decision Making
- Increase Employee Engagement and Efficiency
- In General Communication
- Characteristics of a Good Story
- Audience Specific
- Contextualize the Story
- Humanize the Story
- Make the Story Action Oriented
- Keep it Humble
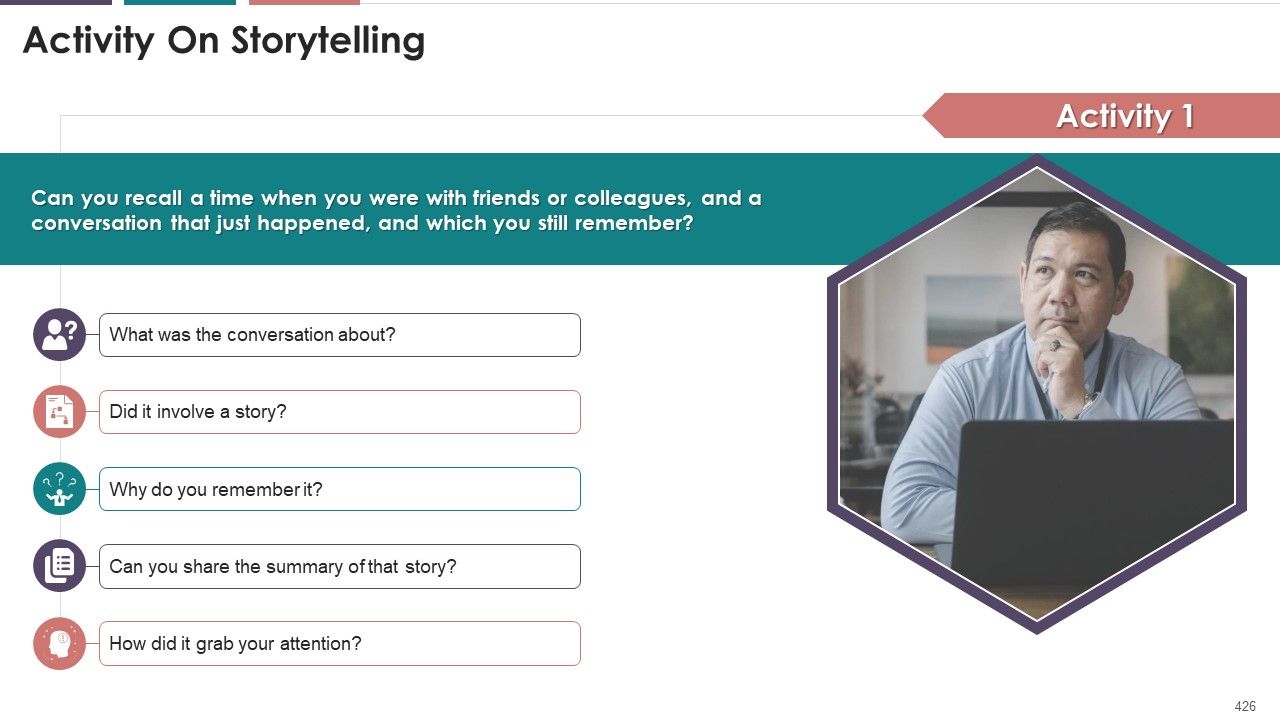
- Activity on Storytelling
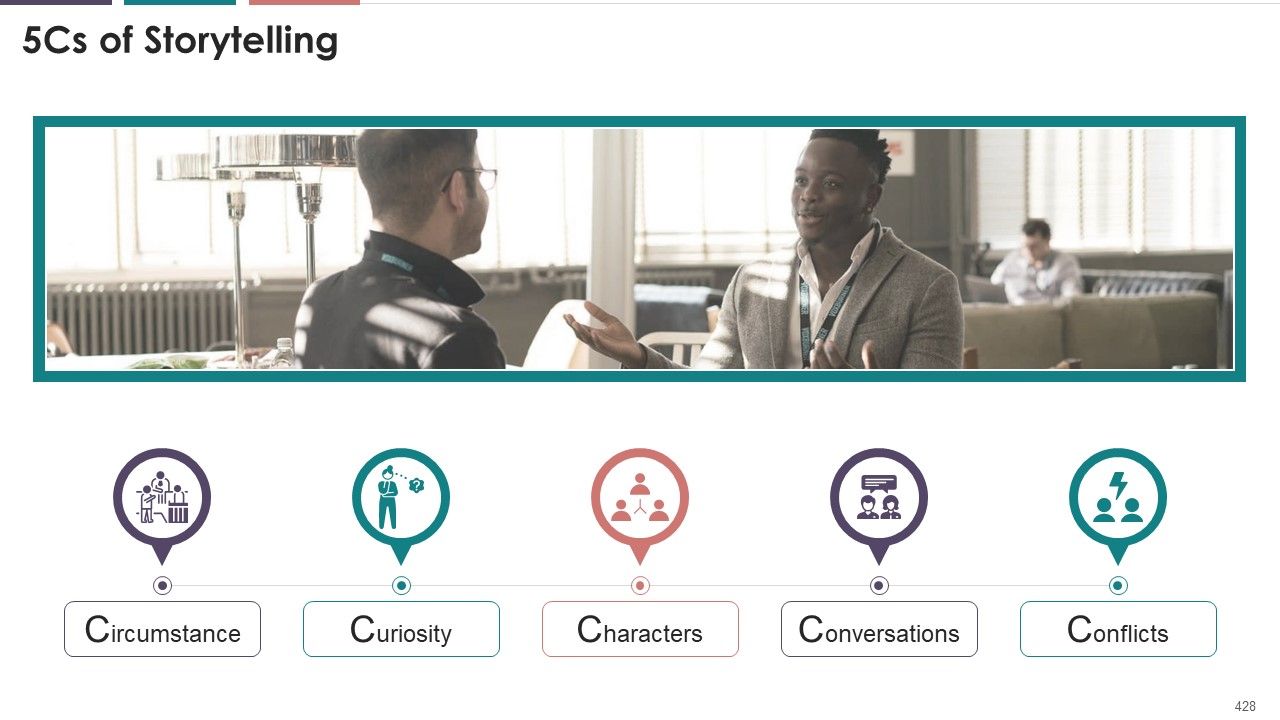
- 5Cs of Storytelling
- Circumstance
- Curiosity
- Characters
- Conversations
- Conflict
- Business and Personal Storytelling
- Activity on Storytelling
- Techniques to Make your Story Captivating
- Immerse your Audience in a Story
- Tell a Personal Story
- Create Suspense
- Bring Characters to Life
- Don’t Tell
- Build up to a S.T.A.R. Moment (Something they’ll always remember)
- End with a Positive Takeaway
- How to tell a story effectively: 7 Tips
- Choose a Clear Central Message
- Embrace Conflict
- Have a Clear Structure
- Mine your Personal Experiences
- Engage your Audience
- Observe Good Storytellers
- Narrow the Scope of your Story
- Activity on Storytelling
- Key Takeaways
- Meaning of Culture
- Six patterns of Cultural Differences
- Case Study: Cross- Cultural Communication
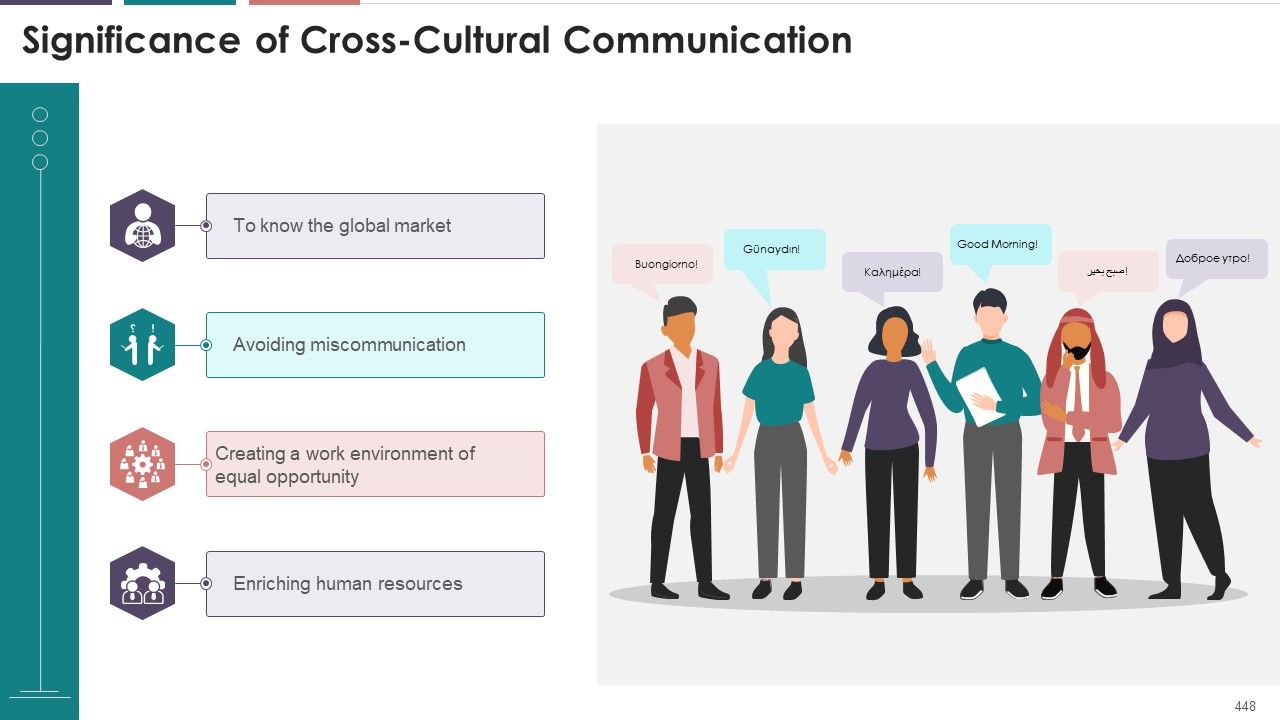
- Cross-Cultural communication
- Why is cross-cultural communication significant?
- Sources of miscommunication in cross-cultural communication
- Factors affecting cross-cultural communication
- Case Study: Intercultural Perception Checking
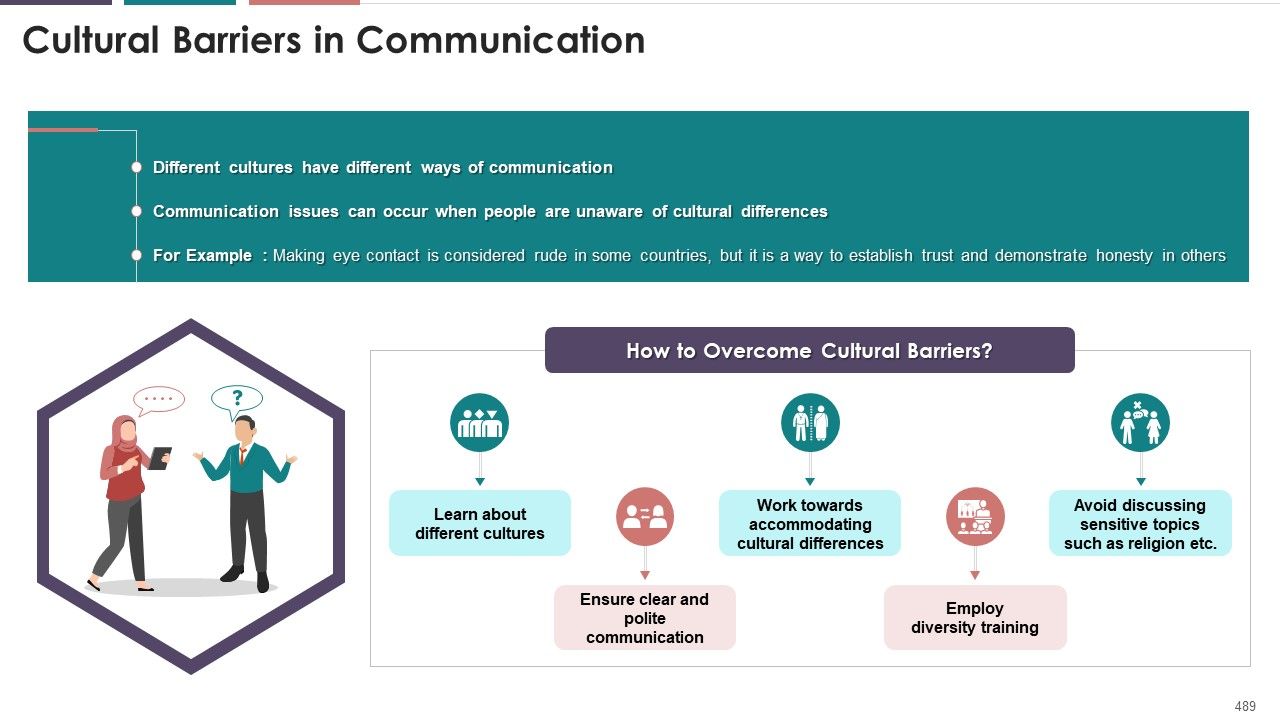
- How should cross-cultural communication be improved?
- Tips for effective Cross-Cultural communication
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s test what we have learnt
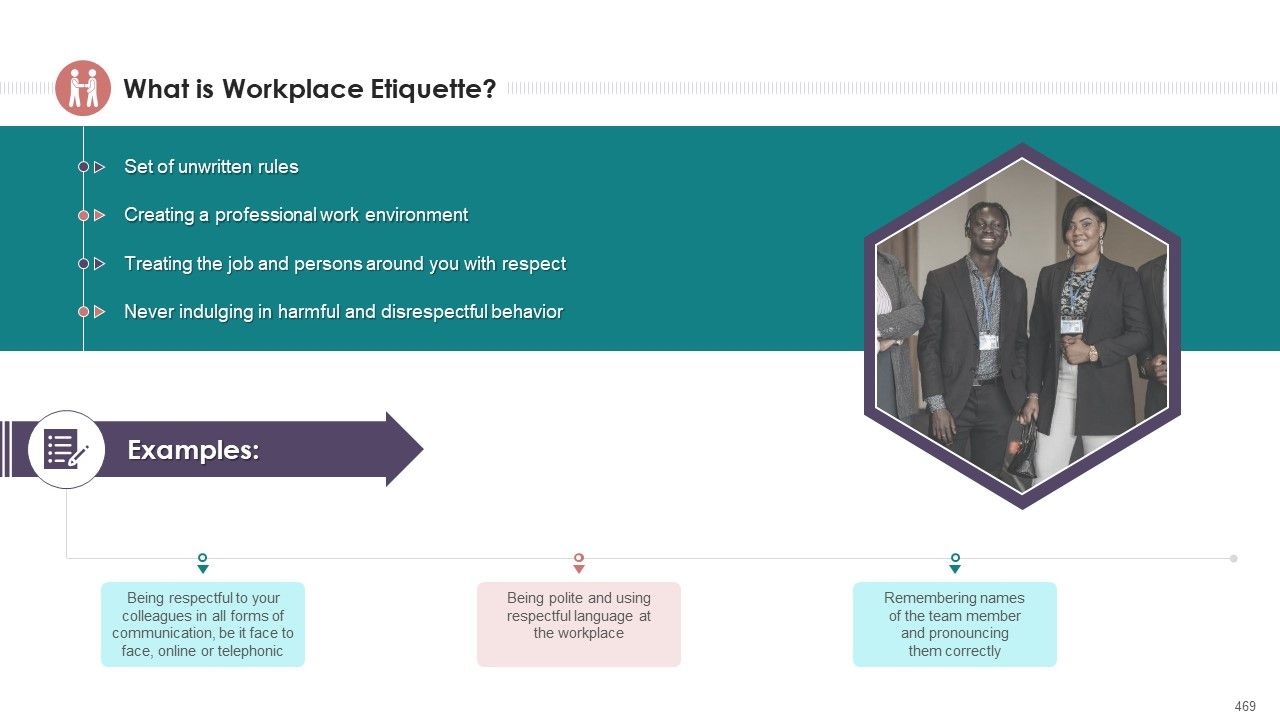
- Workplace Etiquette Meaning
- Workplace Etiquette Significance
- Enhance Workplace Relations
- Enriches Impression
- Promotes Business Growth
- Enhances Kindness and Confidence
- Consequences of Lack of Workplace Etiquette
- Anger or Irritation
- Stress
- Strained Relationships
- Case study on Workplace Etiquette
- Principles of Workplace Etiquettes
- Respectful to Coworkers
- Shake Hands
- Remember Names
- Maintain Eye Contact
- Knock Before You Enter
- Avoid Using Mobile and Internet for Matters Other Than Official
- Be on Time
- Avoid Gossip
- Communication Balance and Build Friendships
- Know When You Are Called
- Be Serious with Emails
- Know What to Keep Confidential
- Know What to Wear
- Filter Your Speech/Words
- Handling Sensitive Matters
- Case Study: Remembering Names
- Dos and Don’ts of Workplace Etiquette
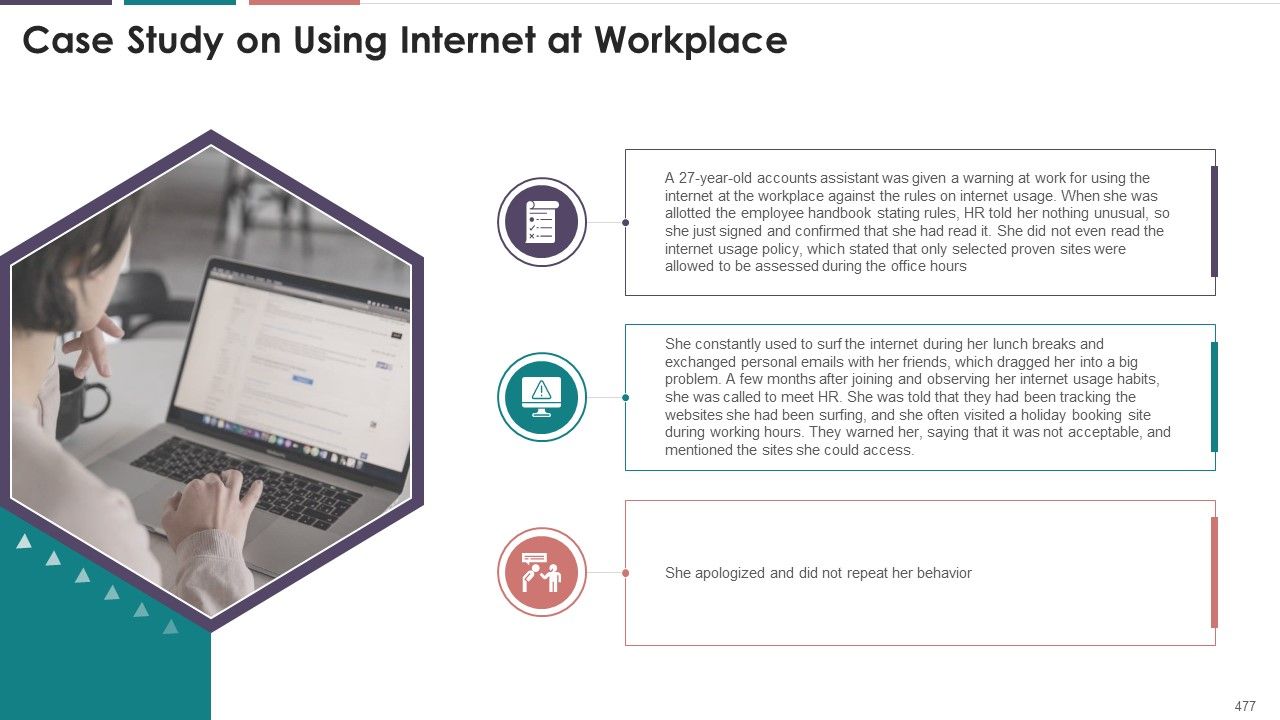
- Case Study: Using Internet at Workplace
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Barriers in Communication
- Physical Barriers
- Cultural Barriers
- Language Barriers
- Perceptual Barriers
- Interpersonal Barriers
- Gender Barriers
- Emotional Barriers
- Activity: Guess the Emotion
- Activity: Tell a Story
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
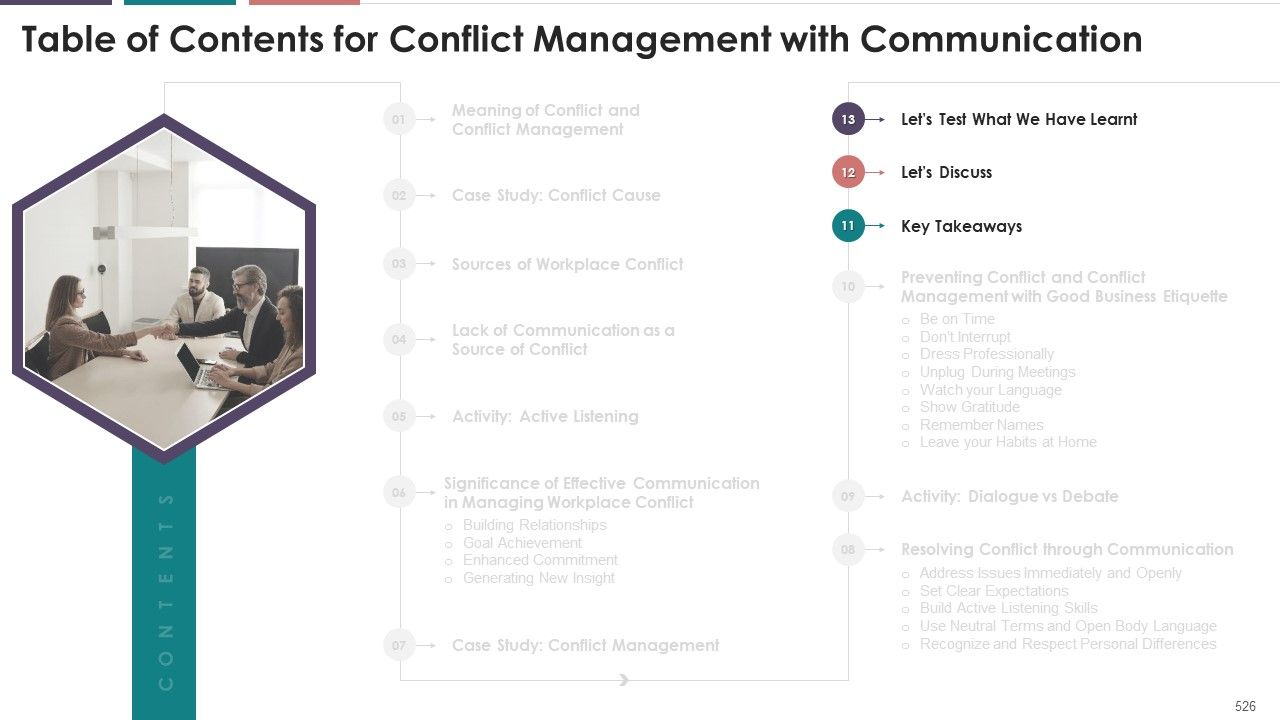
- Meaning of Conflict and Conflict Management
- Case Study: Conflict Cause
- Sources of Workplace Conflict
- Lack of Communication as a Source of Conflict
- Activity: Active Listening
- Significance of Effective Communication in Managing Workplace Conflict
- Building Relationships
- Goal Achievement
- Enhanced Commitment
- Generating New Insight
- Case Study: Conflict Management
- Resolving Conflict through Communication
- Address Issues Immediately and Openly
- Set Clear Expectations
- Build Active Listening Skills
- Use Neutral Terms and Open Body Language
- Recognize and Respect Personal Differences
- Activity: Dialogue vs Debate
- Preventing Conflict and Conflict Management with Good Business Etiquette
- Be on Time
- Don’t Interrupt
- Dress Professionally
- Unplug During Meetings
- Watch your Language
- Show Gratitude
- Remember Names
- Leave your Habits at Home
- Key Takeaways
- Let’s Discuss
- Let’s Test What We Have Learnt
- First Time Communication
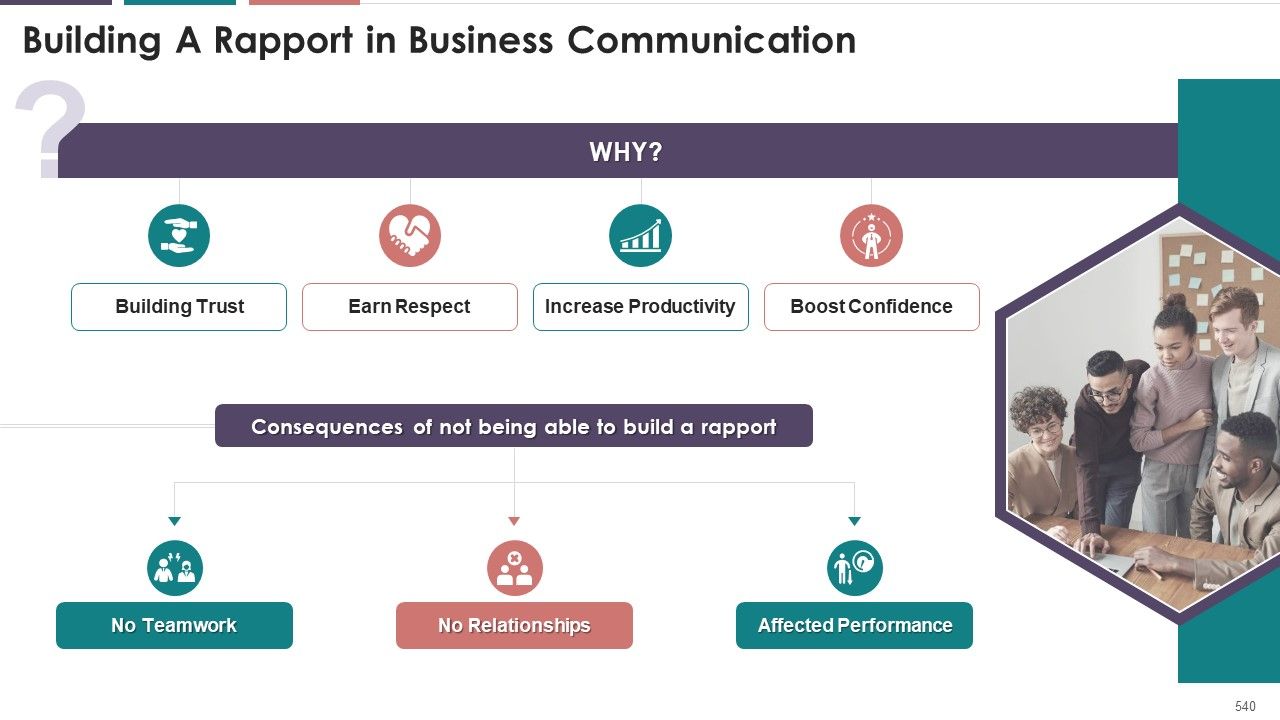
- Building A Rapport
- Professional Way to Ask Questions
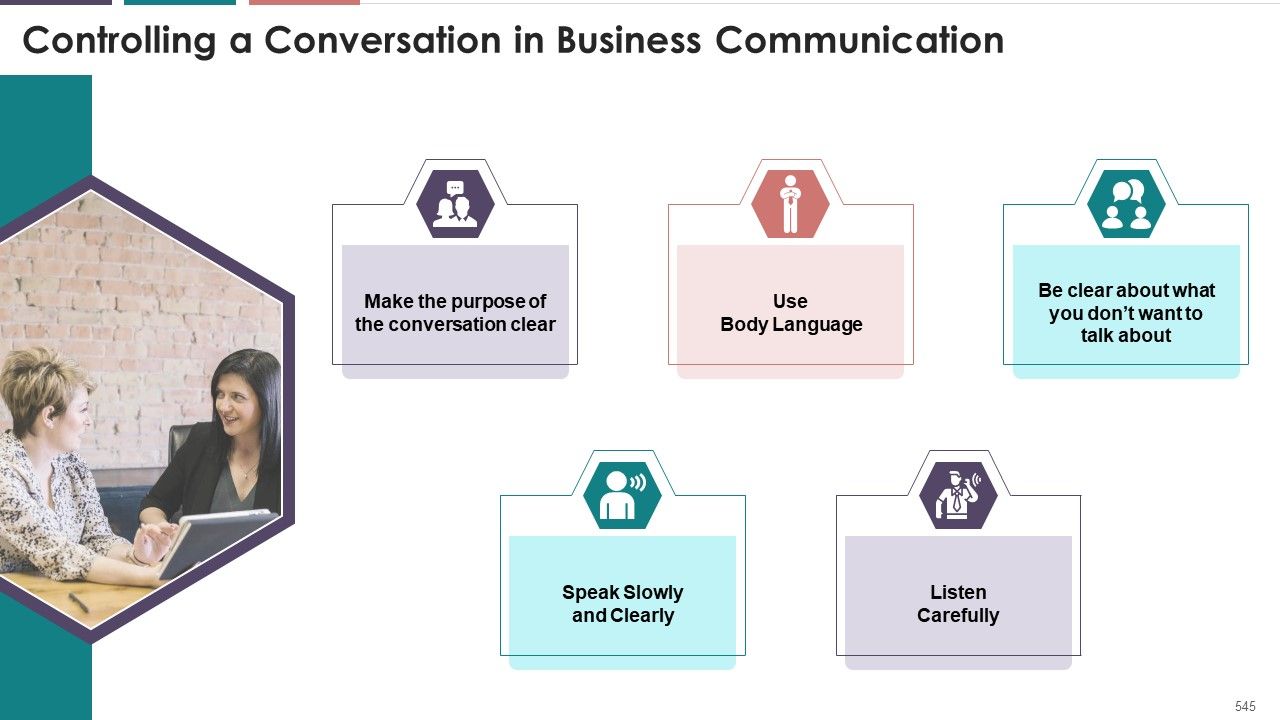
- Controlling A Conversation
Sample Instructor Notes
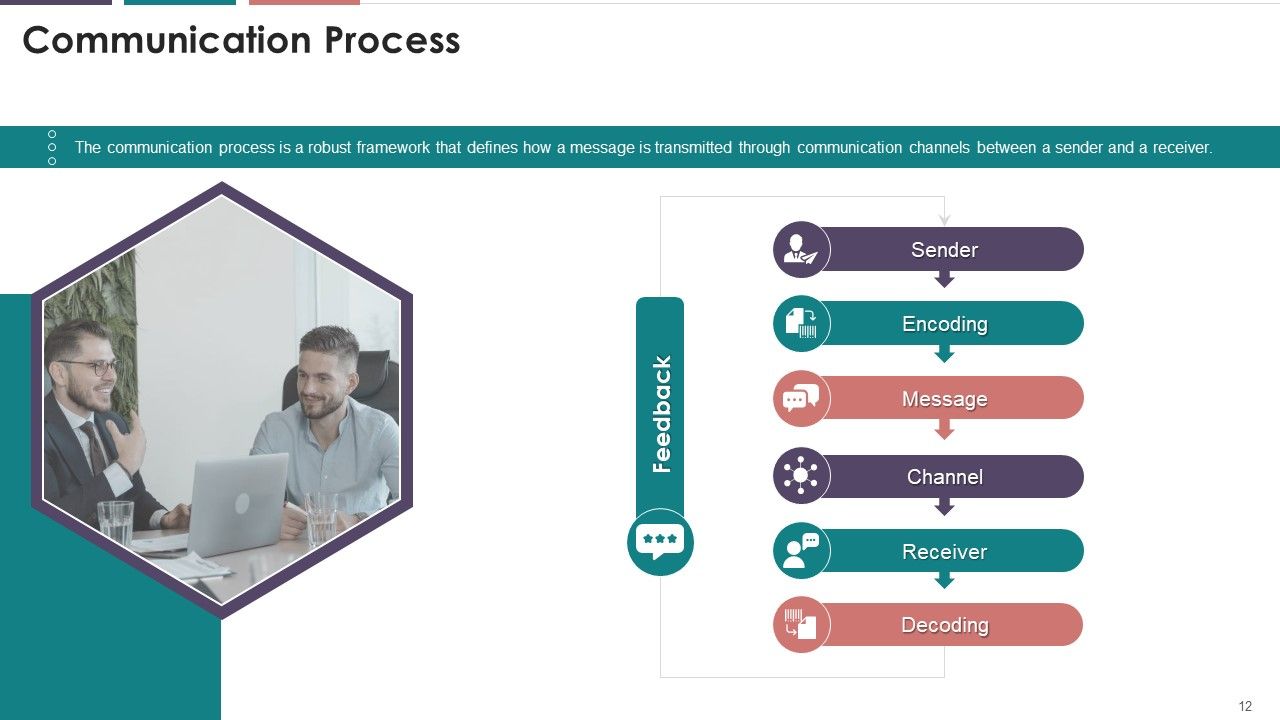
What is this slide for: Introduction to Communication Process Framework
This slide covers: This slide illustrates the communication process. It mentions that the communication process is a six-stage robust framework that defines how a message is transmitted through communication channels between a sender and a receiver. The framework elements are sender, encoding, message, channel, receiver, and decoding.
Instructor’s Notes:
Key components of the communication process are as follows:
- Sender: The person who came up with the idea and wished it would be delivered to the recipient
- Encoding: The process of describing or translating information into a message
- Message: The concept, fact, or opinion that the sender wishes to convey
- Communication Channel: The method by which the message is delivered for example e-mail, voice message, telephone etc.
- Receiver: intended audience of the message
- Decoding: the process of interpretation of the message
- Feedback: the response or action taken by a receiver after decoding a message
What is this slide for: Importance of Business Communication in Organizations
This slide covers: This slide depicts information on the importance of business communication. The importance is efficient functioning, facilitation of decision making, minimizing organizational conflicts, job satisfaction and higher productivity, better labor relations, enhanced motivation and morale, and increased employee productivity.
Instructor’s Notes:
Importance of business communication are as follows:
- Efficient Functioning: Communication is essential in all types of organizations, whether small or large, public or private. An organization's employees' efficient performance is dependent on effective communication within the organization
- Facilitates Decision Making: The desired outcomes of an organization are heavily reliant on making the right decision at the right time. An efficient communication system is vital to making sound decisions
- Minimizes Organizational Conflicts: Most business conflicts are not basic but rather a result of misunderstanding and ignorance of the facts. Proper communication between interested parties reduces the point of friction and minimizes those that inevitably arise
- Job Satisfaction and Higher Productivity: Effective communication leads to improved performance because people are better able to understand their jobs and roles
- Establish Better Labor Relations: The need for industrial peace is crucial. Better management and labor relationships result from effective communication
- Enhance Motivation and Morale: Employee morale improves as a result of communication because they are aware of their role in the business. It gives employees a feeling of assurance and motivates them to work. Employee motivation and morale can be improved through effective communication
- Increases Employee Productivity: Four out of every five employees believe that effective business communication improves their job performance. Because of information overload, employees frequently waste time searching for content they require to do their jobs
What is this slide for: Principles of Good Business Writing
This slide covers: This slide depicts the principles of good business writing in business communication. The principles are clarity of purpose, clarity of thought, avoiding jargon, reading and revising avoid verbosity, correct grammar and sentence structure, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
The principles of effective business writing are as follows:
- Clarity of Purpose: Before beginning a business document, memo, or email, two primary questions should be considered:
Who exactly is the reader?
What message do I want to send to the reader through my writing?
Clarity of purpose directs the writing and shapes its tone, structure, and flow
- Clarity of Thought: Business writing necessitates the ability to summarize long, scattered sentences into concise, clear ones. To write clearly, one must extract what is essential
- Convey Accurate and Relevant Information: The purpose of business writing is to deliver critical information. The objective of the document gets jeopardized by inaccurate or irrelevant content
- Avoid Jargon: A straightforward and uncluttered writing style goes a long way toward conveying the message to the reader. Writing with industry-specific buzzwords and acronyms should be avoided to the extent possible. Otherwise, the reader may be unable to understand or lose interest in the document
- Read and Revise: Reading the document aloud after it has been completed can reveal flaws and gaps. Constructive feedback from colleagues should be welcome
- Be Direct: When it comes to business writing, presenting the passage's main point in the first 150 words is a good idea as it saves the reader's time
- Avoid Verbosity: If the meaning can be expressed in three words, never use five. Verbosity hinders the reader's ability to engage with the writing
- Correct Grammar and Sentence Structure: A grammatical error appears unprofessional, good grammar demonstrates attention to detail and skill, which are highly valued in business
- Easy to Scan: Business executives value a document that can communicate its message through an executive summary. Business documents can be improved by using numbered or bulleted lists, clear headings, concise paragraphs, and thoughtfully-used bold formatting to highlight keywords
What is this slide for: 3 As of Active Listening
This slide covers: This slide provides information regarding the definition of active listening. It also includes details of three As of active listening which are attitude, attention, and adjustment.
Instructor's Notes:
The three As of active listening are:
- Attention: Listener must be in the present moment entirely and should be highly attentive towards the speaker, disregarding any other anxieties of the day
- Attitude: Listener must listen to the speaker with a positive and open mind
- Adjustment: The listener must be willing to change and adapt their mannerisms according to the speaker’s train of thought until the end of the conversation
What is this slide for: Components of Speaking in Business Communication
This slide covers: This slide shows various components of ‘Speaking’ in business communication. Business speaking can be conducted either as business presentations, public speaking, and business meetings.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Business Presentations: Speaking to your target audience includes online business presentations or business talks. The most prominent example is training a virtual team or addressing your team in meetings held online. While speaking in a business meeting using the presentation, the speaker can take the form of a story, keep the content simple, talk naturally, and put minimal content on the slides
- Public Speaking: Public speaking is considered an essential aspect in all the three areas like business, education, and the public arena. It is because the words spoken are more powerful than the written words. When talking from a marketing perspective, it may help the business person to market the offers in a better way
- Business Meetings: Business Meetings involve gathering two or more persons for different purposes like informing or discussing some topic. Business meetings can be either in person or by telephone. These meetings should reflect a clear intent and be conducted in the right tone and atmosphere. It should involve maximum participation of members, making them feel an essential part of decision making and hence the organization
What is this slide for: Tips to Maintain Effective Eye Contact in Nonverbal Communication
This slide covers: This slide showcases the multiple recommendations to improve nonverbal communication using eye contact. The numerous tips listed are applying the 50/70 rule, keeping eyes on the face, and using the triangle method.
Instructor’s Notes:
Tips to improve eye contact skills are as follows:
- Make Eye Contact Right Away: Always establish eye contact first before starting conversation with someone
- Apply 50/70 Rule: Maintain eye contact in the following proportion while communicating
When Speaking: 50% of the time
When Listening: 70% of the time
- Limit Duration 4–5 Seconds: While gazing into someone's eyes during conversation, don't go beyond five seconds, as it then turns into staring
- Use Triangle Method: Imagine an inverted triangle on the face of another person connecting eyes and mouth. Post five seconds, change the gazing point of the triangle
- Keep Eyes on Face: To avoid constant looking into eyes, look at the multiple spots on the face such as nose, lips, and chin
- Make a Gesture: Avoid abrupt break in eye contact with a gesture such as the nodding of head
- Turn Away Slowly: Avoid darting eyes as another person may perceive it as a sign of nervousness and shyness
What is this slide for: 5Cs of Storytelling
This slide covers: This slide illustrates the 5Cs of storytelling that are circumstance, curiosity, characters, conversations, and conflicts.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Circumstance: The circumstance is one of the core elements of storytelling. While crafting a story, the speaker has to introduce the circumstances in which the action in the story happens. It is equivalent to the context. The circumstance helps the speaker establish the scene and provide the audience with all the required information to better understand the story. The circumstance clarifies the when, where and why of the story. This improves audience engagement and adds a compelling reason to be the story
- Curiosity: A brilliant introduction is crucial for a story's success, but it does not mean that the whole task is done. Once you gain the audience's attention, your next concern should be to stimulate the listener to be consistent throughout the story. Creating suspense makes them curious to know about what will happen next. Eventually, this builds interest and encourages the audience to learn more
- Characters: The speaker needs to be very particular while choosing the characters featured in the story. The characters, roles, emotions, characteristics, etc., play a considerable role in storytelling as people want connection. The characters become the basis that people can relate to or want to be like. Choose your characters carefully to make it easier for the audience to visualize or relate to them
- Conversations: People these days are more likely to engage with and pay attention to the conversation between multiple characters involved. Conversations refer to the dialogues involved in your story, which drive real engagement on the part of the audience. A dull story without any exchanges involved may lead to a lack of interest, so the success of storytelling depends upon human-interest element. The speaker should consider factors like: Will my story get people talking? Will they revisit my story and reshare it with their peers? The true success of the story lies in answers to all these questions
- Conflicts: Every story must include a conflict. The conflict here refers to a problem followed by corresponding solution. Conflict is the key to grabbing audience's attention as it encourages them to invest time in making efforts to unfold. Most successful business stories deeply connect with their target audiences. These leveraging the power of relevant conflicts, adding value to them. While crafting a story related to business or otherwise, the speaker should carefully consider the problems and challenges that it wants to highlight. Then, it must showcase how the business can help resolve the issues highlighted
FAQs
We provide training decks on a wide variety of business and technical topics such as Diversity & Inclusion, Customer Service, Search Engine Optimization, Blockchain Technology, and many more. These are ready-to-present decks that can be downloaded and presented in their current form. These decks are carefully created by industry experts, designed by professionals to deliver a power packed training session.
We want our training decks to evoke curiosity and inspire passion for learning. Each training deck consists of multiple sessions with impeccably designed slides to explain concepts in-depth, key takeaways to summarize sessions, discussions, and multiple-choice questions to assess trainees’ learning. The deck also contains activities and memes to break the monotony and make the training more interactive. Each training deck comes with an assessment form and editable proposal to help pitch your training to clients with success.
It depends on the trainer's content delivery pace, but each deck is created to ensure that training content is for a minimum of 16 hours.
Yes. A significant segment of our customers are professional mentors, coaches and teachers. You can create presentations with our content and distribute these to your trainees. The only caveat is that you cannot share your subscription to our content with others; the license is not transferable. Also, you cannot resell SlideTeam content to others.
Each slide is 100% editable in PowerPoint. Every element of the slide – text, icons, images, vectors, color scheme, etc. can be modified to build an effective PowerPoint presentation. Simply DOWNLOAD, EDIT, and PRESENT!
All PPT slides are compatible with PowerPoint 2007 and above. Some diagrams will not show up correctly with older versions of PowerPoint, like PowerPoint 2003 or lower, because of rendering issues. Yes, they work with PowerPoint for MAC, and decks are compatible with Google Slides too.
Absolutely yes! Our decks are yours to keep and build upon even after your subscription expires. You will not be able to download any additional decks once your subscription expires, but the ones you've downloaded are yours to keep forever.
Our entire website is HTTPS secure, and our payment system is managed by PayPal and Stripe, two of the world's leaders in credit card payment systems and very respected companies in online payments. This makes our systems 100% secure. We do not store or have access to any credit card information ourselves. We direct you to these third-party secure sites with 100% secure SSL connections where you can safely purchase a subscription and then direct you back to our site to download products.
You are allowed to log in and download content from 3 computers. Our website keeps track of login IP addresses, MAC Address Usage, and Browser and Computer Operating System fingerprinting, and you will not be able to log in from more than three computers.