Blockchain Technology for Web 3 0 Training Ppt
This PowerPoint training module in detail covers blockchain technology for web 3.0. It covers the evolution, features, and technologies semantic web, blockchain, and artificial intelligence behind web 3.0. It also contains PPT slides on industries that web 3.0 is likely to disrupt DeFi, supply chain, DApps, DeSo, and DAOs. Further, it covers the pros and cons of web 3.0 and the similarities between metaverse and web 3.0. The PowerPoint module also has key takeaways, discussion questions, and MCQs related to the topic to make the training session interactive. It also includes additional slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities, detailed client proposal, and training assessment form.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
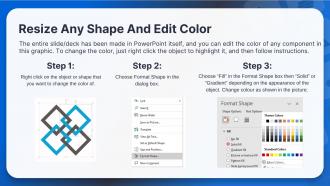
Presenting Training Session on Blockchain Technology for Web 3.0. This presentation deck contains 100 plus well researched and uniquely designed slides. These slides are 100 percent made in PowerPoint and are compatible with all screen types and monitors. They also support Google Slides. Premium Customer Support available. Suitable for use by managers, employees and organizations. These slides are easily customizable. You can edit the color, text, icon and font size to suit your requirements.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
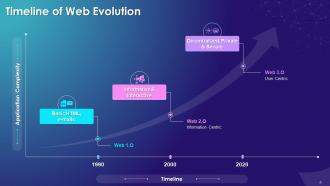
This slide explains the evolution of the Internet from read only internet in Web 1.0 to the latest version of internet called Web 3.0 in which a person can also own assets. In Web 2.0, we could make changes to the internet.
Slide 5
This slide explains the evolution of web from generation 1 to generation 3. Here, we go into the specifics of what has changed from the days of Web 1.0 to Web 3.0 now. The idea is to learn that from a one-way publishing source, the internet is today a place where we will have ownership of data; Now, the platform itself can be used to read, write and even interact with world around. A significant change, indeed.
Slide 6
This slide mentions the graphical representation of the evolution of web from basic network structure involving emails etc. to a decentralized and secure web.
Slide 7
This slide explains the concept of web 3.0. It explains Web 3.0 uses technologies; like Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to facilitate and achieve real-world human communication. Significantly, Web 3.0 not only allows individuals to own data but also get paid for their time spent on the web.
Slide 8
This slide explains the characteristics of Web 3.0 applications. Some of the characteristics are behavioral advertising, ownership of digital assets, portability and personalization, decentralized, and smart applications.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Behavioral Advertising/Improves Advertising with Smarter AI: Web 3.0 ensures that only relevant ads are visible to users, in view of their interests. The Artificial Intelligence technology targets a particular set of people based on their previous interactions and data. It helps to learn about unnecessary ads, and makes only relevant ads visible to the user
- Ownership of your Digital Assets: Web 3.0 provides users with a unique identity to access and control their digital assets, data, and services. It does away with the requirement of logging in or seeking permission from a particular provider. The ownership of the digital assets is vested in the user in different forms like Non-Fungible Tokens and other such mechanisms
- No Permission Required from a Central Authority: Web 3.0 offers a decentralized system, eliminating the need for a central authority. This provides the user with the freedom to post and interact
- Portability and Personalization: Web 3.0 assets are portable. and can be easily transferred, carried or moved. It refers to the ability of an application to move across environments and not only platforms
- Smart Applications: Web 3.0 has given rise to smart applications like Facebook/Meta, Wolfram Alpha (computational knowledge engine collecting information from databases on web to make it available through a suitable user interface), etc. Such applications are enhancing productivity and consumer interactions
Slide 9
This slide illustrates technologies that contribute to the success of Web 3.0. The technologies are Semantic Web, Decentralized Technology, 3D Interactive Web Technology, the Social Web, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
Slide 10
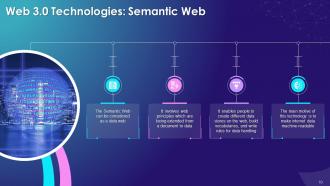
This slide explains the concept of semantic web in web 3.0. It says that semantic web can be thought of as a data web, which involves the principles extended from a document to data. It enables people to create different data stores on the web, build vocabularies, and write rules for data handling.
Slide 11
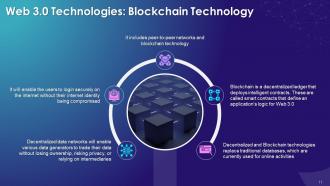
This slide explains the concept of decentralized technology in Web 3.0. It says that decentralized technologies include peer-to-peer networks and blockchain technology. These technologies provide a way forward towards a new decentralized web.
Slide 12
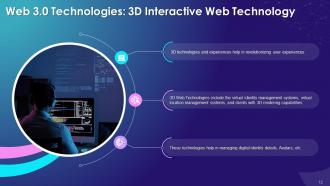
This slide explains the concept of 3D technology in Web 3.0. It says that 3D technologies and experiences help in revolutionizing user experiences. 3D Web Technologies include the virtual identity management systems, virtual location management systems, and clients with 3D rendering capabilities.
Slide 13
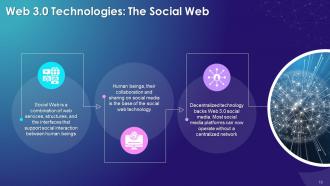
This slide explains the concept of social web in Web 3.0. It says that social web is a combination of web services, structures, and the interfaces that support social interaction between human beings. Decentralized technology backs Web 3.0 social media. Most social media platforms can now operate without a centralized network.
Slide 14
This slide explains how AI and ML are contributing to the improvement of web technology. AI has multiple use cases for Web 3.0, one of which is it helps web technology to learn how to make valuable decisions, and discriminate between genuine and fraudulent data to deliver accuracy to the users. Web 3.0 also uses AI and ML to copy the ways human beings learn and improve their accuracy. After a length of time, it can evaluate any available information and extract out relevant results.
Slide 15
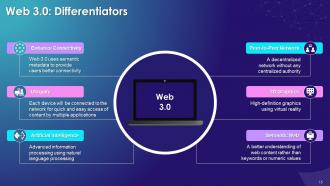
This slide explains the Web 3.0 and its uniqueness is studied here. It says that, Semantic Web, AI, Ubiquity, Enhanced Connectivity, Peer-to-Peer networks and 3D Graphics are what makes Web 3.0 a generational concept.
Slide 16
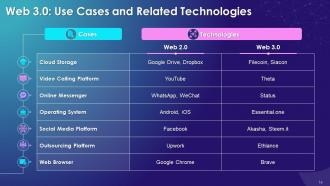
This slide explains that in a useful visualization, we get to learn on how technologies prevailing under Web 3.0 are different from that we are still using as part of Web 2.0. We are able to know about the use cases of web like cloud storage, video interactions, online messaging, operation system, outsourcing, browser, etc. All of these will have a different interface in Web 3.0, and some of these are already on the verge of being mainstream
Slide 18
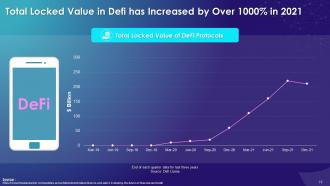
This slide illustrates information regarding Decentralized Finance (DeFi) in Web 3.0. It emphasizes that DeFi (Decentralized Finance) is a component of Web 3.0 that's gaining steam. It entails executing real-world financial transactions on the blockchain without the help of banks or the government. Instead, DeFi uses smart contracts, which are blockchain-based programs that execute actions automatically when certain conditions are met. It also mentions that Metaverse tokens can be easily purchased or sold using smart contracts, peer-to-peer transactions, and other methods via DeFi networks.
Slide 20
This slide illustrates the significance and benefits that Decentralized Finance (DeFi) provides to users. It states that DeFi eliminates the need for a central bank or government agency (or any third party) to approve financial transactions. It is designed to solve problems like inefficiency in financial transactions, limited access, opacity, and centralized control.
Slide 21
This slide provides information about the definition of supply chain and how it is managed. It is a network that connects a company's suppliers in order to manufacture and distribute a certain product or service. The management of a supply chain entails the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventories and finished goods between enterprises and locations.
Slide 22
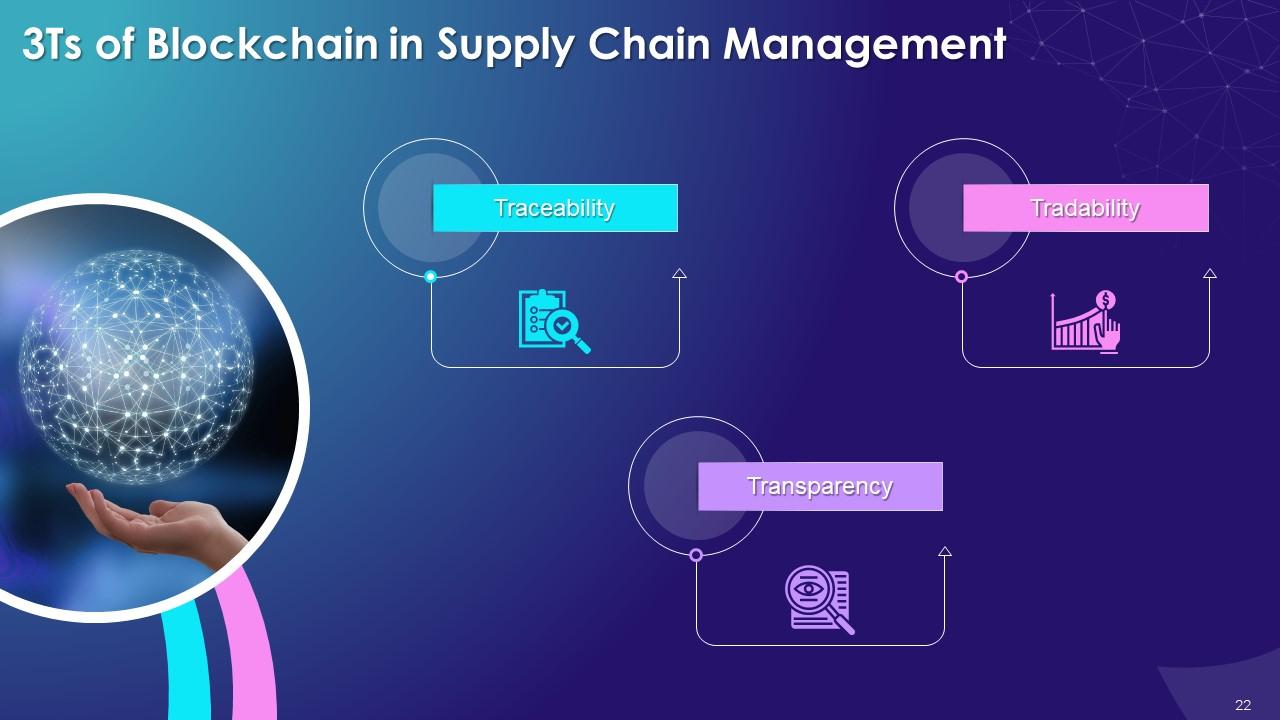
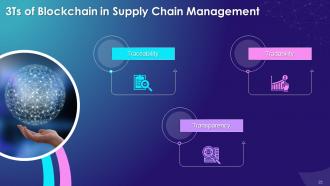
This slide depicts the three foundation pillars of blockchain in supply chain management. These are Traceability, Transparency and Tradability.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Traceability: Global supply networks need to be equipped with the capacity to handle any business situation, be it damage to consumer-packaged goods or product recalls. At times, companies are forced to recall consumer items or raw materials to prevent diseases or injuries. Consumer product recalls, on the other hand, can have a detrimental impact on millions of people all over the world. The supply chain's traceability enables quicker and more efficient recalls. Blockchain aids in the verification of a product's accurate and ethical sourcing, reducing the risk of counterfeiting. The blockchain's immutability allows for a transparent verification of certifications, legal papers, and other data
- Transparency: Process tracking, as well as reporting and regulatory compliances, are possible with blockchain. According to estimations, replacing traditional methods with blockchain could increase transaction volumes. Blockchain technology allows you to track digital or physical products throughout their existence
- Blockchain adds transparency to process tracking, giving manufacturers a bird's-eye view of their whole value chain. It can assist in asset tracking and record and display past asset records. Improved regulatory compliances and reporting are other prospective benefits. Providing stakeholders with reliable, relevant, and unedited information in real-time could improve corporate governance. It can also ensure that data is delivered to the right people at the right time
- Tradability: In addition to supply chain management, blockchain’s use in ownership and licensing could boost efficiency. Verifying previous ownership through established licensing procedures is important in many sectors of the economy. Furthermore, Blockchain might be used to automate smart contract payments for accurate service, software, and product licensing. One of the most notable advantages is the ability to reach consensus. Every entity on the blockchain has access to the same version of the ledger, making it easier to monitor ownership
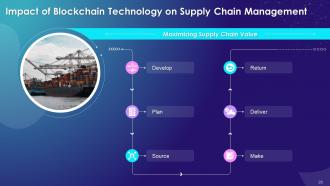
Slide 23
This slide covers the multi-step process of blending the blockchain technology into the supply chain network. The major steps highlighted are develop, plan, source, make, deliver and return.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Develop: Obtain greater access to source material data to better advise material selection in research and development and the design of a closed loop
- Plan: Increase chances for suppliers and customers to collaborate on planning, leading to the lowering of forecast and inventory risk
- Source: Replacing the use of paper with smart contracts and blockchain transactions reduces sourcing and operational costs; support business efforts by providing transparent sourcing
- Make: Make outsourced production more visible and compliant
- Deliver: Offer a comprehensive image of all product phases along the supply chain path to regulators and end-customers
- Return: Based on information capability, choose which batch to recall
Slide 24
This slide highlights the key features of a blockchain-based supply chain that solves the problems being that plagues traditional supply chain management. The listed benefits are cost reduction, improved security, making the supply chain ethical, global compatibility, accelerated process, and provenance.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Transactional cost reduction: At its most basic level, the capacity of blockchain-based cryptocurrencies to facilitate cross-border cash transfers without the use of banks means that blockchain technology can accelerate supply chain payments while cutting expenses
- Enhanced security: Blockchain technology is made up of secure "blocks." These are clones of the document preserved chronologically and linked to preceding blocks. This makes them highly secure and difficult to forge. A hacker would have to make changes to hundreds of copies at once, which is practically impossible to do without the software noticing. Blockchain is an excellent method for protecting your supply chain information from cyber threats
- Making supply chain ethical: Ethical sourcing is a big concern for consumers because of global awareness around blood diamonds and sweat-shops. Consumers want to know more about the origins of their goods and operational details of firms that make these. This has prompted interest in developing an ethical supply chain
- Global compatibility: Raw materials and final products flow through more third-party hands than ever before as the global supply chain expands. As a result of items moving through so many third-party providers, safety risks may arise that are hard to identify and track. As a product travels through the global supply chain to its end destination, blockchain delivers real-time updates to address this issue
- Accelerated process: Blockchain technology, in principle, ensures the integrity of data and transactions. There are fewer errors and disagreements. The necessity for product recalls, or order refills are decreased, which speeds up the process. The use of smart contracts minimizes the necessity for intermediaries or third parties
- Provenance: Provenance is the verified history of ownership, custody, and origin of a specific product such as a lot, a batch, or a serial number in the realm of the supply chain. The transparent structure of blockchain enables an audit of a work of art's provenance and ownership history
Slide 25
This slide tabulates a comparison between the traditional supply chain and a blockchain-based supply chain with the major parameters being data integrity, data security, data verification and government regulations.
Slide 26
This slide explains the concept of DApps, which is decentralized applications. It refers to an application that does not rely on any centralized infrastructure. As it relies on decentralized storage and communication, most DApps execute their backend code on a decentralized peer-to-peer network, such as a blockchain.
Slide 27
This slide explains the importance of DApps. They run over blockchain to provide some form of valuable assets like tokens that act as cash and enable applications to exchange value. Being decentralized, DApps are free from control and authority and provide the users with privacy of actions.
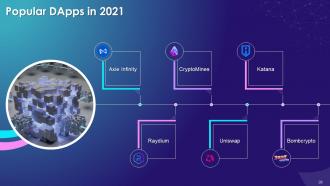
Slide 28
This slide illustrates some popular DApps in 2021. These are Axie Infinity, CryptoMines, Raydium, Uniswap, Katana, and Bomb Crypto.
Instructor’s Notes:
Axie Infinity: Built on Ronin and Ethereum (RONIN, ETH)
- It is a platform for playing games and earning money using crypto tokens. It has different characters (Avatars) known as Axies
- In this game, players purchase NFTs of cute monsters and then pit them against each other in battles. Players then earn tokens during gameplay and trade them for money in an exchange
CryptoMines: Built on Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
- It is a SciFi game where people play to earn and have a fun experience
- A person can collect workers and spaceships to travel through the universe searching for a $Eternal, which allows them to live for another day and make profits
Raydium: Built on SOLANA
- It is an Automated Market Maker AMM. It enables fast trades, shared liquidity, and new features of earning yield
- It leverages the central order book of the Serum Decentralized Exchange (DEX) to offer advantages and to enable faster transactions and trade
Uniswap: Built on Ethereum Platform (ETH)
- It is a protocol on Ethereum for swapping ERC20 tokens
- Uniswap does it using an equation that automatically sets and balances the value based on the demand
Katana: Built on Ronin Blockchain (RONIN)
- It is an Automated Market Maker, that is AMM Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- It is built on Ronin
- The key features of Katana are swap (Users can swap between ERC 20 assets), Pool (Can provide liquidity to DEX and earn swap fees), and farm (Stake their liquidity pool tokens to earn RON)
Bomb Crypto: Built on Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
- This game is a play-to-earn concept
- It is a game where players manage a group of bomb heroes of cyborgs and fight monsters
- It helps you to learn the basics surrounding gameplay and earn through the website of Bomb Crypto
Slide 29
This slide explains DeSo, as part of industries that Web 3.0 has disrupted.
Instructor’s Notes:
How does DeSo work?
- Token-based structure: DeSo uses a token-based structure which is based on the Ethereum (ETH) blockchain and which means that DeSo tokens can be traded between peers and used to pay for network microservices like content creation, tagging other users, commenting, and liking
- Token Curated Registries: These are the foundation of the DeSo Network. TCRs are lists that differ from ordinary lists in one crucial way. They give list members the ability to curate items that to be made into the Token-based structure
Slide 30
This slide explains the importance of DeSo (Decentralized Social). It mentions that DeSo network emphasizes on creation of a social media-specific blockchain will help expedite Decentralized Social movements. Decentralized social gives users with more control and foster independence, removing the central authority. Few benefits of DeSo are censorship resistance, data ownership, improved control over the user-generated content.
Slide 32
This slide highlights the concept of a DAO. It explains the use of smart contract in making rules for DAO. It is a transparent process that members of the organization control.
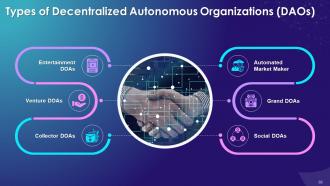
Slide 33
This slide highlights types of DAOs such as automated Market Maker DAOs, grant DAOs, social DAOs, collector DAOs, venture DAOs, and entertainment DAOs.
Instructor’s Notes:
The multiple types of DAOs are as follows:
Automated Market maker:
- Automated Market Maker (AMM) uses smart contracts to provide decentralized financial services to its users
- Maker DAO is one of the most successful and innovative apps on Ethereum
- Maker helps users actively participate in the global financial system
Grant DAOs:
- The earliest use case of DAO is Grants
- The community donates funds and receives tokens in return
- Donors, collectively vote on the allocation and distribution of funds
- The purpose of using DAO is to fund innovative DeFi projects and other organizations submitting applications for a research grant
- The development of grant-based DAOs are practical examples that show that decentralized communities are more flexible in funding distribution than traditional institutions
- Aave protocol is a well-known DAO using grant infrastructure to nurture and build a community of DeFi projects
Social DAOs:
- This form of DAO community is built to focus on particular objectives such as preserving arts and culture
- It helps to unite artists and cultural thinkers with a shared set of values and incentives, allowing them to connect and collaborate
Collector DAOs:
- In collector DAOs, the aim is to acquire cultural collectables for the community
- It also distributes the ownership of high-ticket digital assets equally among members of the community
- It also falls under the category of investment DAOs
Venture DAOs:
- Venture DAOs, also known as investment DAOs, are transparent, inclusive and often open to anyone anywhere
- This is considered as a response to the fact that many investment firms are elitist and non-inclusive
- DAO removes all barriers and lets regular people invest in extraordinary projects
- When thousands of people invest in this type of DAO, it becomes possible to invest in projects that were earlier reserved for the upper echelon of traditional investors
Entertainment DAOs:
- Entertainment DAOs creates an outlet for the artists within us
- It can bring together creative minds from around the world to collaborate on exciting, creative projects
Slide 34
This slide illustrates the working of DAO. It explains that smart contracts are used to establish DAO. It also shows that raising funds and bestowing governance rights are major challenges in operationalizing the DAO.
Slide 35
This slide compares the structure of traditional organization with that of a DAO. It explains that in a traditional organization, senior management takes all decisions, and lower-level employees are not included in such decisions. On the other hand, in a DAO, there is no hierarchy, and all the decisions are taken by the voting process, Members of DAO vote based on their contribution.
Slide 36
This slide highlights benefits of DAOs such as resolving management issues, its nature of being community-based, low percentage of error in operations, transparency, and decentralized.
Instructor’s Notes:
The advantages of DAOs are:
Resolve Management Issues:
- DAO can help improve the management of many traditional organizations by implementing an autonomous structure
- The problem with such organizations is that they run in a top-down structure that works to invalidate the contribution from anyone that is not at the top of the pyramid
- Every investor in DAO has the opportunity to shape how the investment should run
Community-based:
- DAO has a flat structure with little to no management structure in place
- All decision-making powers are given to the token holders in the system
Low Percentage of Error:
- With the help of smart contracts, once the rules of DAO are in place, all decisions are enforced automatically without the requirement of any human input
- It also helps to reduce the risk of errors as human factor is eliminated
Transparency:
- DAO is considered as a decentralized governance structure
- With the help of DAO, one can get rid of managerial staff through system automation
- In DAO, information is publicly available
Decentralized:
- DAO is decentralized as no single person or entity has complete control over it
- It does not have any central point of failure
- It eliminates uncertainty and helps increase participation and security because all members of the DAO share the ledger
Slide 38
This slide explains the various pros and cons of Web 3.0. Web 3.0 provides Data Privacy, Control, Seamless Services, Transparency, Open Accessibility to Data, Enhanced Data Processing, etc. Along with these advantages, there are few shortcomings of Web 3.0 like Complicated Functionality, not quite ready for widespread adoption yet, requirement of advanced devices, etc.
Slide 39
This slide mentions similarities between Metaverse and Web 3.0. It says that both Metaverse and Web 3.0 rely on next-generation internet technologies and transforming ways of online material sharing. They are open and permissionless networks which provide free access to the virtual world and, in general, are open to the public.
Slide 40
This slide mentions the key highlights from the training deck on blockchain for web 3.0.
Slide 55 to 69
These slides depict energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
Slide 71 to 97
These slides consist of a client training proposal highlighting what the company providing corporate training can accomplish for the client.
Slide 98 to 100
These slides highlight the training evaluation form for instructor, content, and course assessment.
Blockchain Technology for Web 3 0 Training Ppt with all 105 slides:
Use our Blockchain Technology for Web 3 0 Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Love how there are no boring templates here! The design is fresh and creative, just the way I like it. Can't wait to edit and use them for my extended projects!
-
Requested a complete pitch deck. Delivered immediately and with high quality well researched content.