Fundamentals Of Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt
This training deck provides a comprehensive Introduction to Business Communication Fundamentals. It covers the elements, process, types internal and external, statistics, and importance of business communication. The PPT module also includes slides on communication styles such as passive, aggressive, passive-aggressive, and assertive. Further, it covers techniques to achieve effective communication along with the models of business communication such as Aristotle, ABC Accuracy, Brevity, and Clarity, AIDA Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action, and PAS problem agitate solution. The PowerPoint deck also contains case studies, activities, discussion questions, MCQs, and memes to make the training session interactive. It also includes additional slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities, detailed client proposal, and training assessment form.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Module on Fundamentals of Business Communication. This deck comprises of 116 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts and every slide consists of an appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
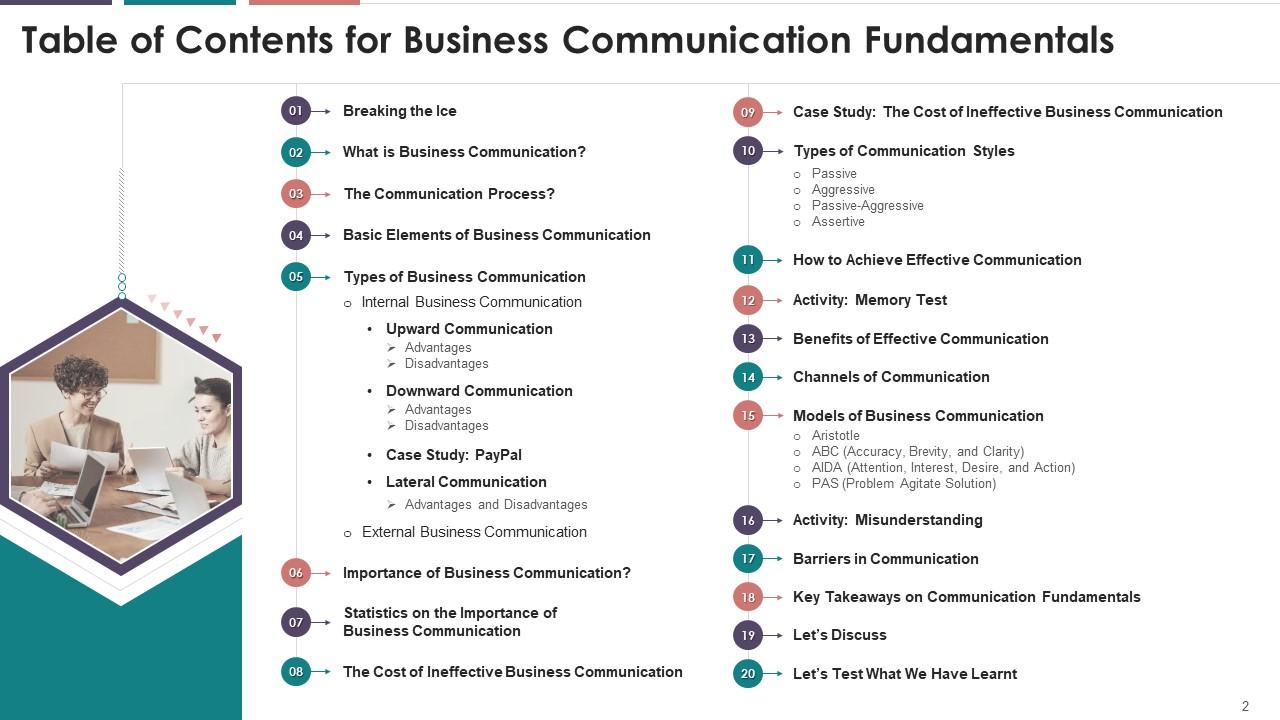
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 7
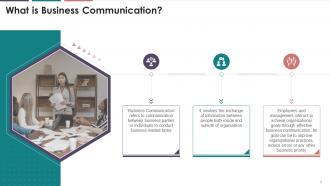
This slide depicts an overview of business
communication. It emphasizes that business communication is communication
between business parties or individuals to carry out business-related tasks. It
also entails exchanging information between individuals both within and outside
the organization.
Instructor’s Notes:
Some examples of business communication
are:
·
A group of employees is having a
brainstorming session
·
Two co-workers sharing information to
collaborate on a project
·
A supervisor providing feedback to a direct
report
·
A leadership team communicating the
company's vision to its employees
·
A client is presented with a deliverable by
an account manager
·
A customer providing feedback on a
deliverable
In addition to sharing information,
effective communication is also required for carrying out day-to-day business
processes and tasks such as:
·
Creating and disseminating plans and
proposals
·
Introducing new concepts to clients,
co-workers, or management
·
Having productive meetings
·
Making decisions as a group or organization
·
Order taking, sending, and fulfilment
Slide 8
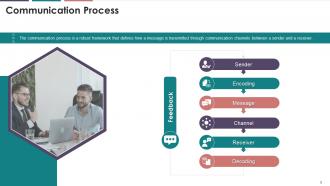
This slide illustrates the communication process. It
mentions that the communication process is a six-stage robust framework that
defines how a message is transmitted through communication channels between a
sender and a receiver. The framework elements are sender, encoding, message,
channel, receiver, and decoding.
Instructor’s Notes:
Key Components of the Communication Process
·
Sender: The
person who came up with the idea and wished it would be delivered to the
recipient
·
Encoding: The
process of describing or translating information into a message
·
Message: The
concept, fact, or opinion that the sender wishes to convey
·
Communication channel: The
method by which the message is delivered for example e-mail, voice message,
telephone etc.
·
Receiver: intended
audience of the message
·
Decoding: the
process of interpretation of the message
·
Feedback: the
response or action taken by a receiver after decoding a message
Slide 9
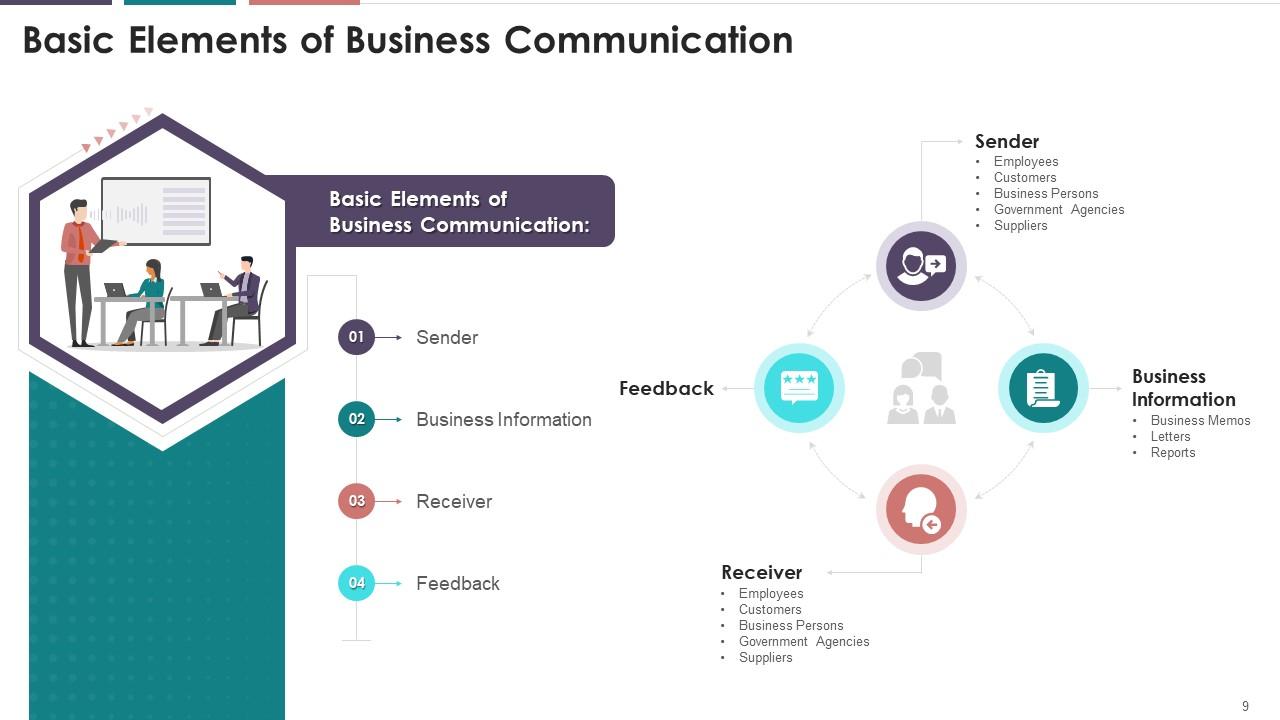
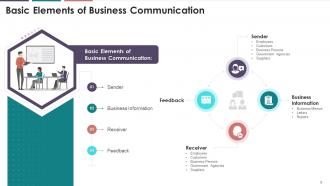
This slide illustrates information on the essential
elements of business communication. The elements are sender, business
information, receiver, and feedback.
Slide 11
This slide showcases the information regarding the two
major types of business communication. The two major types of business
communication are internal communication and external communication.
Slide 12
This slide shows information about upward
communication. It emphasizes the use of the bottom-to-top management approach
in internal communication. It also mentions that information flows from
subordinates to managers or anyone higher up in the hierarchy in upward
communication.
Instructor’s Notes:
The following are the characteristics of upward
internal business communication:
·
It includes a bottom-to-top approach, in
which subordinates report to superiors
·
It is participatory
·
The main goal is to provide timely
feedback, suggestions, requests, and escalation of any issues or concerns to
superiors, and so on
·
The information flows from lower to the
upper levels
Slide 13
This slide depicts information regarding the advantages
of upward communication. The benefits are improved relations, knowing employee
attitude, prompt appreciation, decision making, motivation, creativity
development, and favorable organizational environment, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
Following are the advantages of upward business
communication:
·
Improved Relations: Subordinates
express their views through upward communication. As a result, there is a
harmonious relationship between superiors and subordinates
·
Providing Suggestions: Through
upward communication, subordinates can provide constructive feedback to
superiors. These perspectives may be useful in achieving organizational
objectives
·
Favorable Organizational Environment: Upward
communication strengthens the bond between subordinates and superiors. As a
result, the organization achieves continuous growth
·
Knowing Employee Attitude: Every
company offers some kind of employee welfare program. If upward communication
is active, the management will know how satisfied employees are with these
welfare activities
·
Feedback: Subordinates
communicate their reactions to the superiors' decisions via upward
communication. As a result, upper-level management can check to see if
lower-level employees have accepted the message that superiors sent
·
Prompt Appreciation: Subordinates
have the opportunity to praise their boss for any positive or effective action
as a result of upward communication. It eventually leads to a friendly
relationship between superiors and subordinates
·
Decision Making: Before
making decisions, upper management wants to know specific information about the
production, procurement, marketing, and financial matters, among other things.
Subordinates provide relevant information through upward communication, making
decision-making more manageable and faster
·
Development of Creativity: Upward
communication necessitates the development of a creative environment in which
employees can demonstrate their development initiatives
·
Motivation: Lower-level
employees can express their attitudes or opinions to upper-level employees
through upward communication. As a result, subordinates are influenced to work
harder to meet the target
·
Development of Plan: Through
upward communication, upper-level management can gather information from
lower-level management. The evidence gathered from such communication can be
used to create and implement any plan
Slide 14
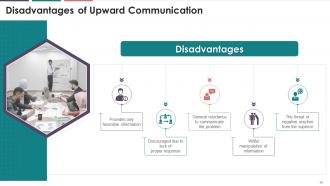
This slide depicts information on the disadvantages of
upward communication. The disadvantages include providing only favorable
information, a general reluctance to communicate the problem, willful
manipulation of information, the threat of negative reaction from the superior,
etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
The following are the disadvantages of upward business
communication:
·
Provides only favorable information: Subordinates
only provide information that is favorable to upper management
·
Discouraged due to lack of proper
response: It may be discouraged as a result of top management's
failure to respond appropriately
·
Takes time to communicate the problem:
It
takes a long time to communicate problems at a higher level due to the various
levels they must pass
·
Willful manipulation of information: There
could be deliberate manipulation of information to achieve personal goals
·
The threat of negative reaction of the
superior: There is a risk that the superior will react negatively
Slide 15
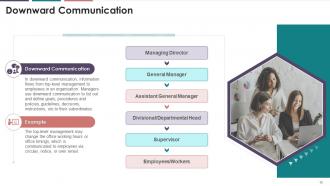
This slide illustrates information regarding downward
communication. In downward communication, the information flows from top-level
management to employees in an organization. It also mentions that managers use
downward communication to list out and define various goals, procedures,
policies, guidelines, decisions, instructions, etc., to their subordinates.
Instructor’s Notes:
The following are the characteristics of downward
internal business communication:
·
It includes a top-down approach, with
superiors communicating with subordinates
·
It is directive in nature
·
The primary goal is to communicate
organizational goals, plans, procedures, and instructions to subordinates
·
The information flows from the upper level
to the lower level
Slide 16
This slide depicts the advantages of downward
communication. The advantages are organizational discipline, efficiency,
effective communication of goals, and ease of delegation.
Instructor’s Notes:
The following are the advantages of downward
communication:
·
Organizational discipline: Downward
communication follows the organization's hierarchy, making organizational
discipline and member compliance much easier to maintain
·
Efficiency: Downward
communication provides efficiencies because instructions and information are
delivered from sources in power who can coordinate activities at the top of the
organization. Employees receive feedback from the managers who supervise them
·
Effective communication of goals: Upper
management can easily communicate goals and delegate responsibilities for
meeting those goals
·
Ease of delegation: Delegation
is much easier if it comes directly from the vertical communication structure
representing the chain of command
Slide 17
This slide illustrates the disadvantages of downward
communication. The disadvantages are time-consuming, distortion of information,
lack of feedback, enthusiasm, and frustration.
Instructor’s Notes:
The disadvantages of downward communication are as
follows:
·
Time consuming: Downward
communication is a time-consuming process, as information flows through
different levels of hierarchy. By the time when information reaches lower-level
employees, it may have lost its significance
·
Distortion of information: People
in downward communication tend to change or manipulate information. As a
result, when information is passed from one level to another, the authenticity
of the information is lost
·
Lack of feedback: Top-level
executives usually give little or no importance to the messages received from
subordinates. Subordinates rarely send feedback as a result of their superiors'
negligence. Communication becomes ineffective as a result
·
Lack of enthusiasm: Managers
use downward communication to send orders, instructions, and advice to
subordinates. As a result, a delay in the downward flow of information harms
employee enthusiasm
·
Creates frustration: Downward
communication makes it difficult for subordinates to discuss any issues with
their superiors. Furthermore, subordinates are forced to follow the orders and
instructions of their superiors, which creates frustration in the minds of
employees
Slide 19
This slide illustrates a case study on PayPal. It
highlights background, approach, outcome, and learning from the case study.
Slide 20
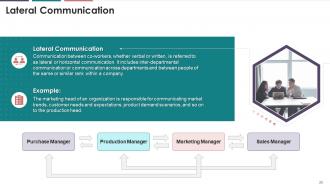
This slide illustrates information about lateral
communication. It emphasizes that lateral communication involves verbal or
written communication between co-workers. It also mentions inter-departmental
communication or communication across departments and between people of the
same or similar rank within a company as lateral communication.
Slide 21
This slide depicts the advantages and disadvantages of
lateral communication. The benefits of lateral communication are better
understanding, improved coordination, increased productivity, end of
misunderstanding, and job satisfaction. The disadvantages include lack of
control, wastage of time, lack of cooperation & coordination, and low
productivity in certain situations.
Slide 22
This slide illustrates information regarding external communication.
It highlights that external business communication refers to interactions with
people outside of the organization. These people can be customers,
shareholders, suppliers, partners, regulatory bodies, etc.
Slide 25
This slide depicts information on the importance of
business communication. The importance is efficient functioning, facilitation
of decision making, minimizing organizational conflicts, job satisfaction and
higher productivity, better labor relations, enhanced motivation and morale,
and increased employee productivity.
Instructor’s Notes:
Importance of business communication:
·
Efficient functioning: Communication
is essential in all types of organizations, whether small or large, public or
private. An organization's employees' efficient performance is dependent on
effective communication within the organization
·
Facilitates decision making: The
desired outcomes of an organization are heavily reliant on making the right
decision at the right time. An efficient communication system is vital to
making sound decisions
·
Minimizes organizational conflicts: Most
business conflicts are not basic but rather a result of misunderstanding and
ignorance of the facts. Proper communication between interested parties reduces
the point of friction and minimizes those that inevitably arise
·
Job satisfaction and higher
productivity: Effective communication leads to improved
performance because people are better able to understand their jobs and roles
·
Establish better labor relations: The
need for industrial peace is crucial. Better management and labor relationships
result from effective communication
·
Enhance motivation and morale: Employee
morale improves as a result of communication because they are aware of their
role in the business. It gives employees a feeling of assurance and motivates
them to work. Employee motivation and morale can be improved through effective
communication
·
Increases employee productivity: Four
out of every five employees believe that effective business communication improves
their job performance. Because of information overload, employees frequently
waste time searching for content they require to do their jobs
Slide 26
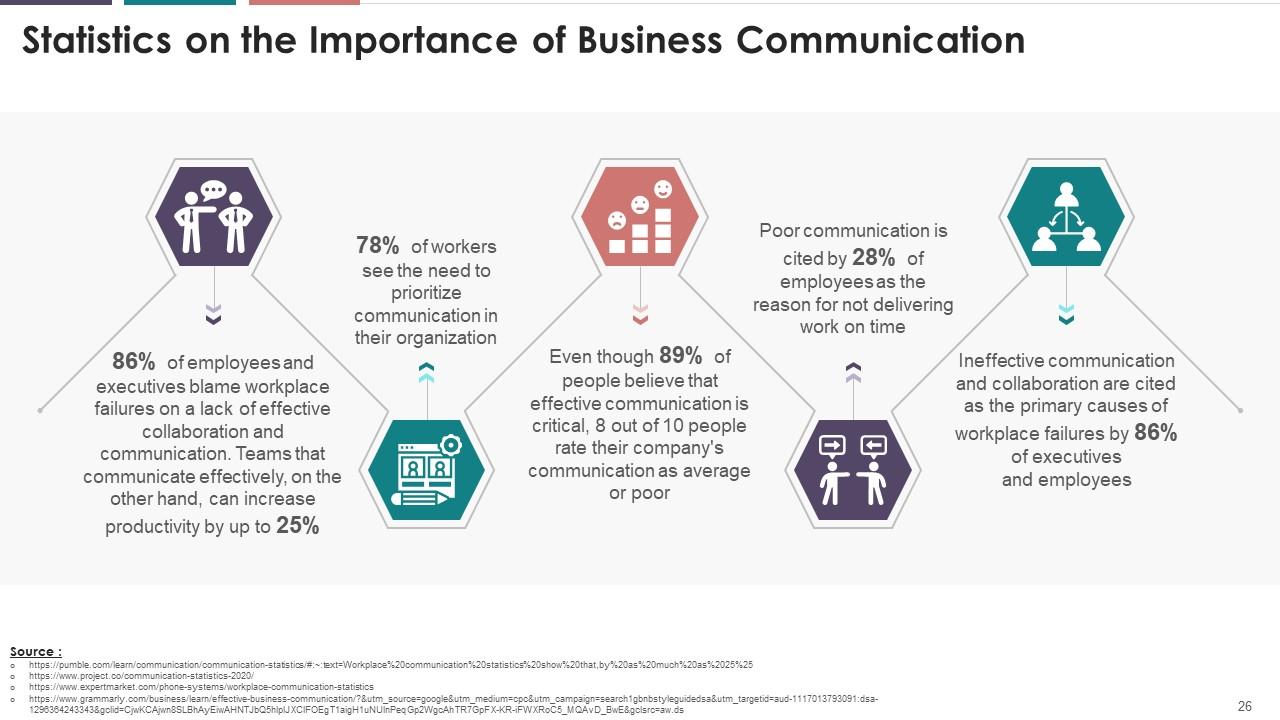
This slide depicts the statistics on the importance of
business communication. It highlights that 86% of employees and executives
blame workplace failures on a lack of effective collaboration and
communication. And teams that communicate effectively, on the other hand, can
increase productivity by up to 25%. It also mentions that 78% of workers see the
need to prioritize communication in their organization, and poor communication
is cited by 28% of employees as the reason for not delivering work on time.
Slide 27
This slide illustrates the statistics on the cost of
ineffective business communication, and it demonstrates that ineffective
communication has resulted in poor financial outcomes for 52% of workers.
Instructor’s Notes:
Poor internal communication can lead to:
·
Strained interpersonal relationships
between team members, which has a negative impact on collaboration
·
Misunderstandings about roles,
responsibilities, or priorities disrupting workflows. This leads to missed
deadlines, poorly executed projects, and other costly oversights
Erode company culture and employee satisfaction, leading
to increased turnover and negative feedback on employer review websites
Poor external communication with other
businesses and customers can:
·
Lower contract renewal rates and
opportunities for upsells and collaboration (for B2B businesses)
·
It will result in dissatisfied customers
and clients, who will be more likely to take their business elsewhere
·
Degrades the public's perception of your
brand, potentially portraying your company as unprofessional, untrustworthy, or
(worst-case scenario) unethical
Slide 29
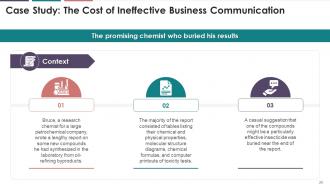
This slide illustrates a case study on the cost of
ineffective business communication. It mentions Bruce, a research chemist for a
large petrochemical company, who wrote a lengthy report on some new compounds
he synthesized in the lab from oil-refining byproducts. The report's main body
consisted of tables listing their chemical and physical properties, molecular
structure diagrams, chemical formulas, and computer printouts of toxicity
tests. It also suggested, in a casual manner and buried at the end of the
report, that one of the compounds might be a particularly effective pesticide.
Slide 30
This slide depicts a case study on the cost of
ineffective business communication. It highlights that after seven years, the
same oil company also launched a major research program to develop more
effective but environmentally friendly insecticides. It also mentions that
someone discovered Bruce's report and toxicity tests after six months. A few
hours of additional testing confirmed that one of Bruce's compounds was the
safe, cost-effective insecticide they were looking for.
Slide 32
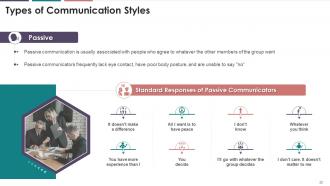
This slide depicts the information regarding passive
communication style. It mentions that passive communication is usually
associated with people who agree to whatever the other group members want. It
also demonstrates that passive communicators frequently lack eye contact, have
poor body posture, and cannot say "no. "
Slide 33
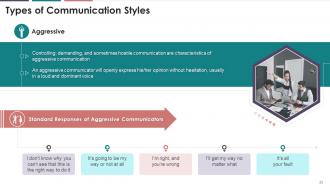
This slide is an introduction to aggressive
communication styles. It depicts that controlling, demanding, and sometimes
hostile communication are characteristics of aggressive communication. It also
mentions that an aggressive communicator will openly express their opinion
without hesitation, usually in a loud and dominant voice.
Slide 34
This slide depicts information regarding
Passive-Aggressive communication style. It highlights that passive-aggressive
communicators are more likely to communicate with another person through body
language.
Slide 35
This slide depicts information about the passive
communication style. It states that assertive communicators can express themselves
politely and respectfully, taking into account other people's opinions and
feelings.
Slide 37
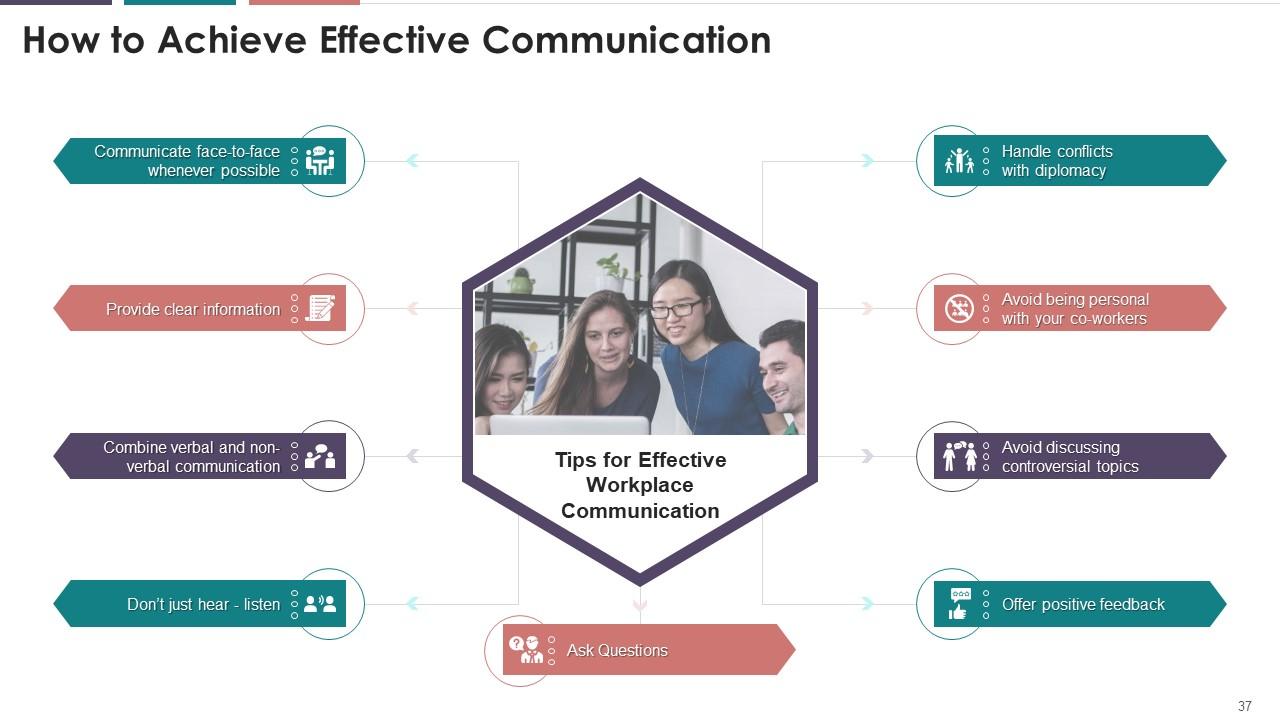
This slide illustrates the tips for effective workplace
communication. The tips are face-to-to-face communication whenever possible,
providing clear information, combining verbal and nonverbal communication, not
just hearing, but listening, handling conflicts with diplomacy, avoiding being
personal with your co-workers, avoiding discussing controversial topics, etc.
Instructor’s note:
The tips for effective workplace
communication are as follows:
·
Communicate face-to-face whenever
possible: Electronic communication can be potentially harmful to
a relationship, particularly with co-workers. Electronic communication is often
misunderstood. Prefer phone call or pay a visit to a coworker when you have
something important to say
·
Provide clear information: When
you fail to communicate clearly and accurately, it can lead to confusion rather
than clarity. To avoid miscommunication, avoid sending emails written in haste
and always plan what you want to say before speaking
·
Combine verbal and nonverbal
communication: Only 7% of the message is conveyed by the
words we choose. One must make sure that verbal and nonverbal messages are in
sync. For example, if you're trying to obtain approval for your business
proposal, make your nonverbal gestures positive and confident
·
Don’t just hear – listen: The
majority of conflict arises as a result of poor listening skills. To improve
listening skills, paraphrase what is said to confirm that you were paying
attention and ensure accuracy. This will lessen the likelihood of a conflict
and will assist you in becoming a more effective communicator
·
Ask questions:
In addition to demonstrating that you were listening, asking questions confirms
that you have understood the other person. A person can also use questions to
elicit additional information and better comprehend the conversation
·
Handle conflict with diplomacy: If
you believe someone misunderstood something that you said, speak with him/her
as soon as possible to avoid unnecessary resentment and productivity loss.
Handle minor misunderstandings as quickly as possible to prevent a conflict
·
Avoid being personal with your
co-workers: Too much personal information must not be
disclosed to co-workers. Aim to be friendly while remaining professional. If an
employee gets too personal with co-workers, the risk of being perceived as less
credible while communicating something important increases
·
Avoid discussing controversial topics:
To
avoid offending anyone, refrain from discussing politics or religion or other
controversial topics in office. While it's a good idea to talk to and get to
know your co-workers, it's best to avoid controversial topics
·
Offer positive feedback: Appreciate
your coworker if they do an excellent job on a task. Positive feedback is a
perfect way to improve workplace communication
Slide 38
This slide depicts an activity on a memory test that
the trainees can perform. It demonstrates the steps of the activity. The steps
are that the participants have to carefully listen to a list of words and not
write down any of the words.
Instructor’s Notes:
·
Read out a list of words to test the
participant’s memory
·
Instruct the participants to listen
carefully
·
Repeat each of the words slowly. Give a
pause between each words. The words could be-
·
Dream
·
Surgeon
·
Mattress
·
Flower
·
Nod
·
Chair
·
Truck
·
Snore
·
Parrot
·
Insomnia
·
Alarm
·
When you've finished reading the list of
words, divert your audience's attention by talking about something else for at
least one minute
·
After you've finished speaking, have each
participant write down as many words from the list as they can remember
Takeaway: The
participants will discover that remembering a list of somewhat random words is
extremely difficult, especially when there is a time-lapse and another
discussion between hearing them and recalling them. Connect this to real-life
listening situation by emphasizing the importance of paying attention to people
when they speak to you, especially if the conversation is crucial.
Slide 39
This slide depicts the benefits of effective
communication in an organization. The benefits are less misunderstanding,
healthy workspace culture, non-threatening environment, team spirit, clear
direction, stronger teamwork, higher employee job satisfaction, and business
success.
Slide 40
This slide categorizes communication channels based on
formality and means of communication. It highlights that based on formality,
the channels are divided into formal and informal and based on means of
communication into digital, face-to-face, and written communication.
Instructor’s Notes:
Communication channels by formality
·
Formal communication entails
the exchange of information such as an organization's goals, policies, and
procedures
Example: Business plans,
strategy, goals, annual reports, agreements, workplace safety guidelines and
procedures, board presentations, etc.
·
Informal communication channels,
on the other hand, are used to deliver official business messages in a more
relaxed manner
Examples: Lunch
time discussions and ongoing collaboration among team members
Communication channels by means of
communication
·
Digital communication channels: Electronic
means of communication include a variety of online tools that employees use to
stay in touch with one another and stay up to date on company news and updates
Examples: email,
internal communication platforms, and intranets
·
Face-to-face communication: Although
electronic means of communication in the workplace are taking over,
face-to-face communication is still essential. It is much more personal, as it
has a more human touch to it
·
Written communication: Written
communication refers to any message that uses the written word. Written
communication is the most critical and effective mode of business communication
The various types of written communications
used internally for business communication are:
·
Memos\Reports
·
Bulletins
·
Employee manuals
·
Emails
·
Instant Messages
Examples of written communications commonly
used with clients or other businesses are:
·
Emails
·
Letters
·
Proposals
·
Telegrams\Faxes
·
Postcards
·
Contracts\Advertisements
·
Brochures
·
Publications
Slide 42
This slide depicts the information regarding
Aristotle's communication model. It demonstrates that Aristotle's communication
model is primarily speaker-centered in which the speaker, and speech is
essential. The major component of the model is Speaker, Speech, Occasion,
Audience, and Effect.
Instructor’s Notes:
The five primary elements of Aristotle Model of
Communication are used in this example: speaker, speech, occasion, audience,
and effect.
·
Speaker- The Leader
·
Speech - About war and victory
·
Occasion- Battlefield
·
Audience - Soldiers and other army
personnel
·
Effect – Defeat the enemy and end the
battle
Slide 43
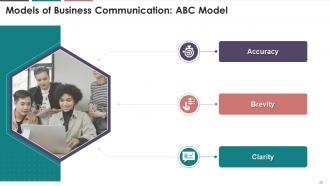
This slide depicts the ABC model of business
communication, and it highlights the elements of the ABC Model that are
accuracy, brevity, and clarity.
Instructor’s Notes:
The ABC Model of Communication is as follows:
Accuracy: It
is a critical aspect of communication. It includes correct information matching
expression. The information must be accurate and well-expressed. Overwriting,
misspellings and grammatically incorrect structures are all causes of
misunderstanding. Accuracy of expression necessitates the absence of spelling,
punctuation, grammar, or usage errors
Brevity: The quality of
being brief is referred to as brevity. It's an eye-catching feature of written
communication. Brevity means conveying as much information as possible in the
fewest words. It is possible to achieve this by avoiding wordiness and
repetition
Ways to achieve brevity in writing:
·
Replace several vague words with more
powerful and specific ones
·
Join sentences
·
Eliminate redundant wording
·
Remove words that state the obvious or go
into excessive detail
·
Begin each sentence with the subject
·
Eliminate redundancy
·
Long phrases and sentences are a big no
·
As far as possible, use the active voice
Clarity: The message should
be clear, well-planned, and logically expressed. There should be no ambiguity.
Clearly written messages reduce misunderstandings and save time. Expressions
that are vague or ambiguous must be avoided. Readability is made possible by
clarity. Clear, simple, familiar, precise, specific words, phrases, and
expressions should improve readability.
The factors that influence clarity are as follows:
·
Always use words that are simple, common,
and meaningful. Avoid using technical terms and jargon
·
Use short, simple sentences since long
sentences can be confusing to the reader
·
While writing, use proper punctuation it
aids comprehension
·
Provide definite and concrete details with
facts and figures
Slide 44
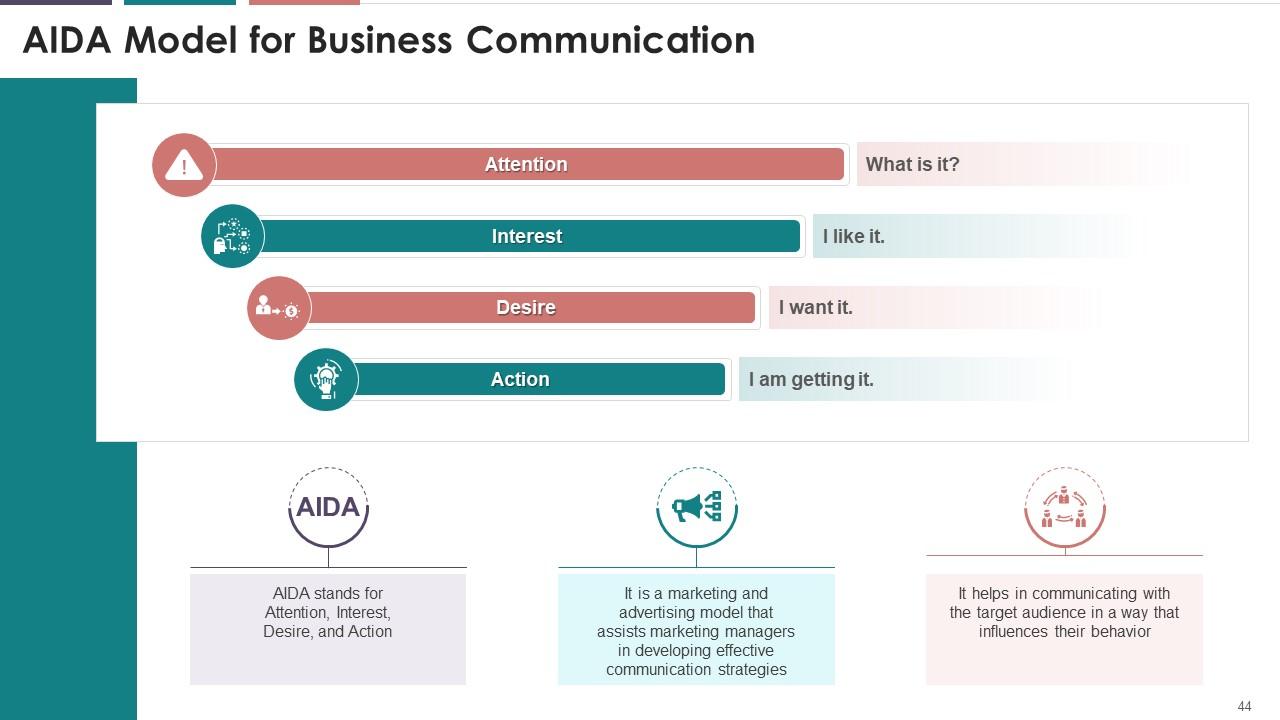
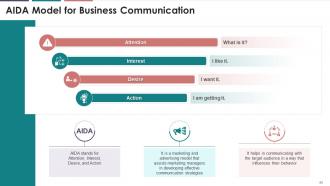
This slide illustrates the AIDA model of communication
with the respective letters standing for Attention, Interest, Desire, and
Action. It is a marketing and advertising model that assists marketing managers
in developing effective communication strategies.
Instructor’s Notes:
Here's what you can do to implement AIDA
·
Attention: Your
target audience will become curious about what your company does if your
content can capture their attention and deeply engage them. At this point, the
consumer is wondering, "What is it? “ You must first get your content in
front of them to get to this stage. This is accomplished through increased
brand awareness and effective messaging
·
Interest: Once
your target audience is interested in your product or service, they will want
to learn more about your brand, the benefits of your solution, and how you
might fit with them. The goal at this point is to get them to say, "I like
it“
·
Desire: Create
desire for your product or service by making an 'emotional connection' and
displaying your brand's personality. Change the consumer's opinion from
"liking" to "wanting" it
·
Action: Encourage
the buyer to interact with your company and take the next step, such as
downloading a brochure, making a phone call, signing up for your newsletter, or
engaging in live chat, etc.
Slide 45
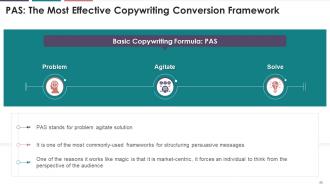
This slide depicts an effective copywriting conversion
framework, i.e., PAS (Problem, Agitate, Solution). It highlights that PAS is
one of the most commonly-used frameworks for structuring persuasive messages.
It mentions that PAS is a market-centric model, and it forces an individual to
think from the perspective of its audience.
Instructor’s Notes:
How PAS works:
·
Problem - Describe
the issue that your prospect is experiencing
·
Agitation - Entails
poking at a problem until it becomes emotive
·
Solution - Present
your solution to the agitated problem
Example:
·
Problem: Finding
the ideal hotel can be difficult. It's almost too stressful to bother with
·
Agitate: Researching
all of your options, determining how far away the local hotspots are, and
reading reviews from previous 'guests.' Then there's the matter of cost
·
Solution: xyzhotels.com
makes it simple to find the best hotel deals. We compare hundreds of travel
websites for you to ensure that you get the best hotel deal possible
Slide 47
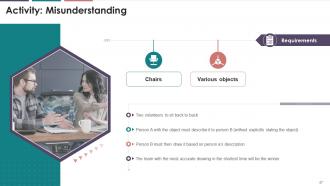
This slide depicts an activity that trainees can
perform during their training session to aid in the development of
problem-solving skills and effective communication strategies. It mentions the
requirements and the instructions of the activity.
Instructor’s Notes:
·
This game will help in discovering new ways
to communicate in the face of barriers
·
It also aids in the development of
problem-solving skills and effective communication strategies
·
Make it competition for larger groups by
determining which team produced the most accurate drawing in the shortest
amount of time
Slide 48
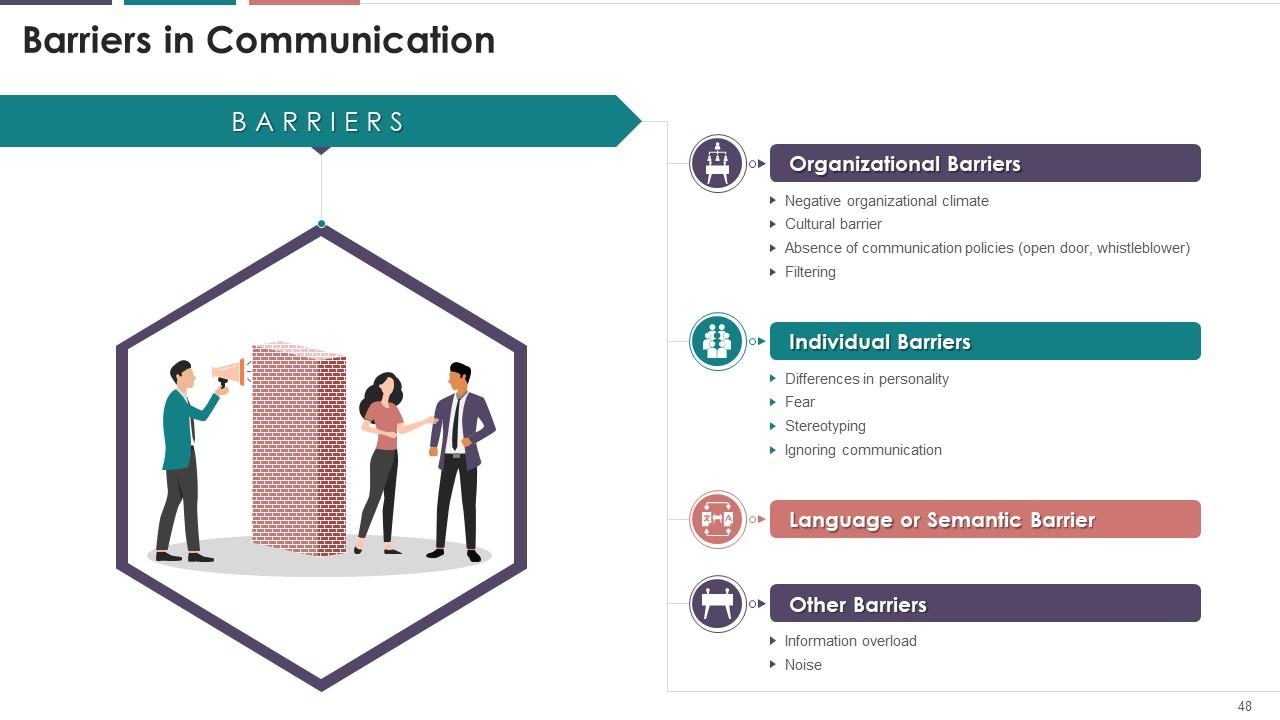
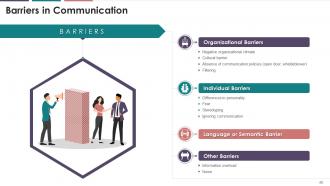
This slide illustrates the types of communication
barriers. The barriers are organizational, individual, language or semantic
barriers, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
Organizational Barriers
·
Negative organizational climate: The
main aspect of organizational climate that acts as a communication barrier is
top management's negative attitude. The negative attitude of top management
discourages communication initiative of the employees
·
Cultural barrier: Employees
who do not understand each other's culture or background may encounter these
types of organizational barriers. These types of barriers are becoming more
common as organizations become more global
·
Absence of communication policies: A
well-designed communication policy promotes communication throughout the
organization. Employees fail or are hesitant to communicate in the absence of
such policies
·
Filtering: It implies the intentional distortion of
information. Filtering is a common issue in upward communication. Employees
tend to pass only those messages that create a positive impression about them
Individual Barriers
·
Differences in personality: Every
individual has a distinct personality. This uniqueness of character creates a
barrier to communication. For example, if this attitude is unfavorable, there
is a greater chance that messages will not be sent from or to superiors on time
·
Fear: Fear
of attack or being criticized for knowing very little can cause communication
problems
·
Stereotyping: Stereotyping
is generalizing about a group of people or events that are held widely by a
particular culture. People develop common statements and mindsets about others
when they engage in stereotyping
·
Ignoring communication: Superiors
may intentionally and consciously ignore communication from their subordinates
in order to maintain their significance. This works against subordinates'
eagerness to communicate
Language or Semantic Barrier: The
semantic barrier in communication is defined as the misunderstanding (or
different interpretation) of meaning that impedes effective communication. It
can take the form of language, sign, or symbol e.g. swastika in India is a holy
symbol while in Europe it symbolizes Nazism
Other Barriers
·
Information overload: Managers
are flooded with information from a variety of sources. They may not always be
able to keep the flow of information under control. As a result, communication
effectiveness suffers
·
Noise: it
refers to a barrier that slows or reduces the effectiveness of communication.
Noise on the sender's end can interfere with their ability to transmit the
message to the receiver. Noise can also occur at the receiver's end,
influencing how they interpret the message
Slide 50
This slide showcases the summary or key takeaways on
communication fundamentals.
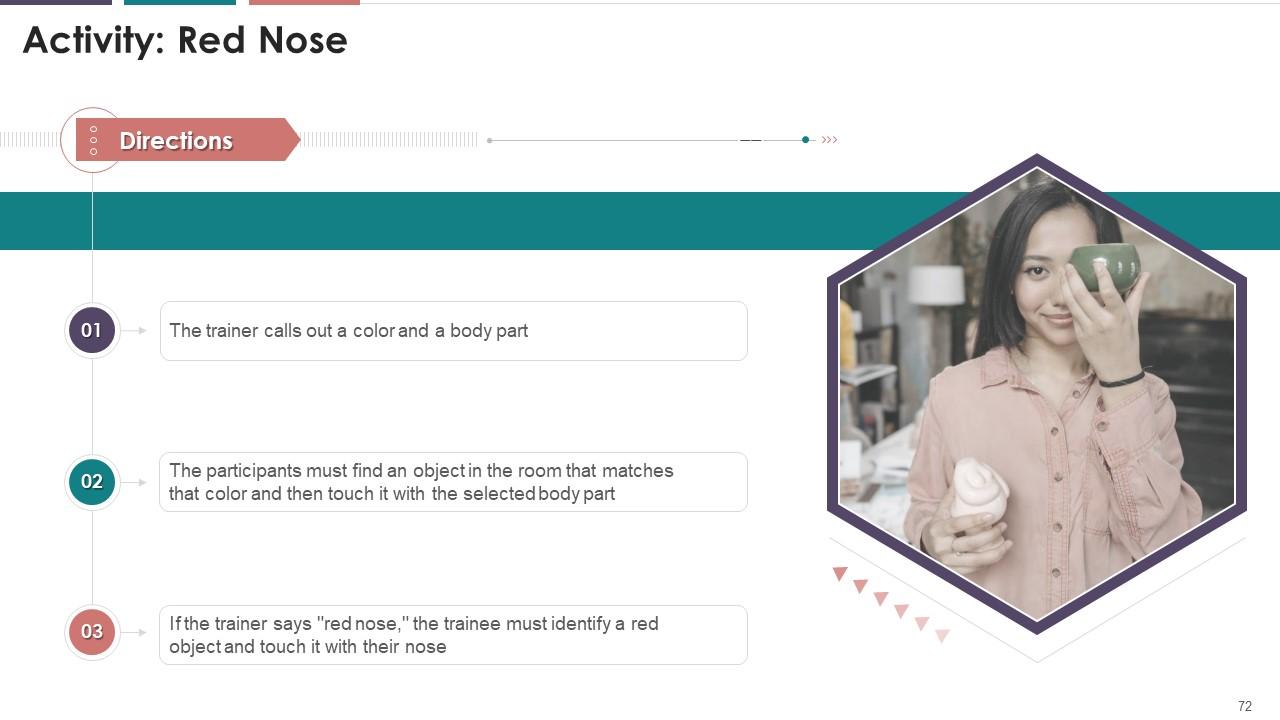
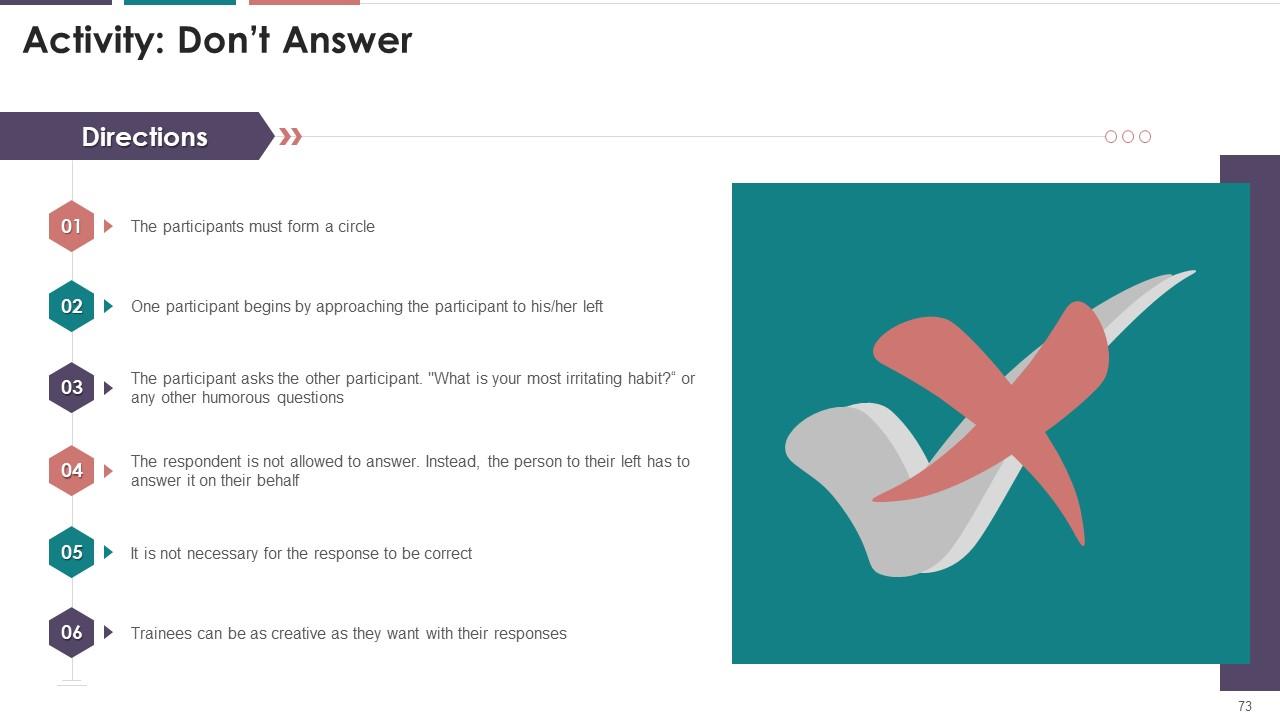
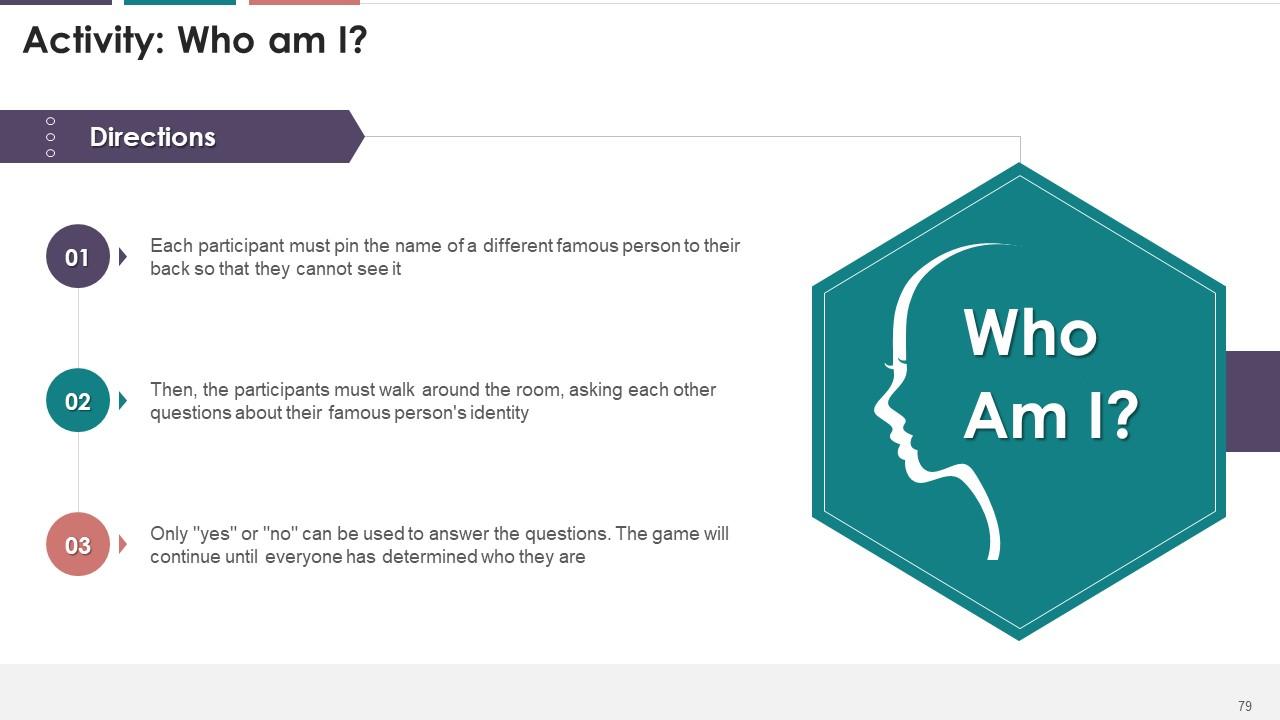
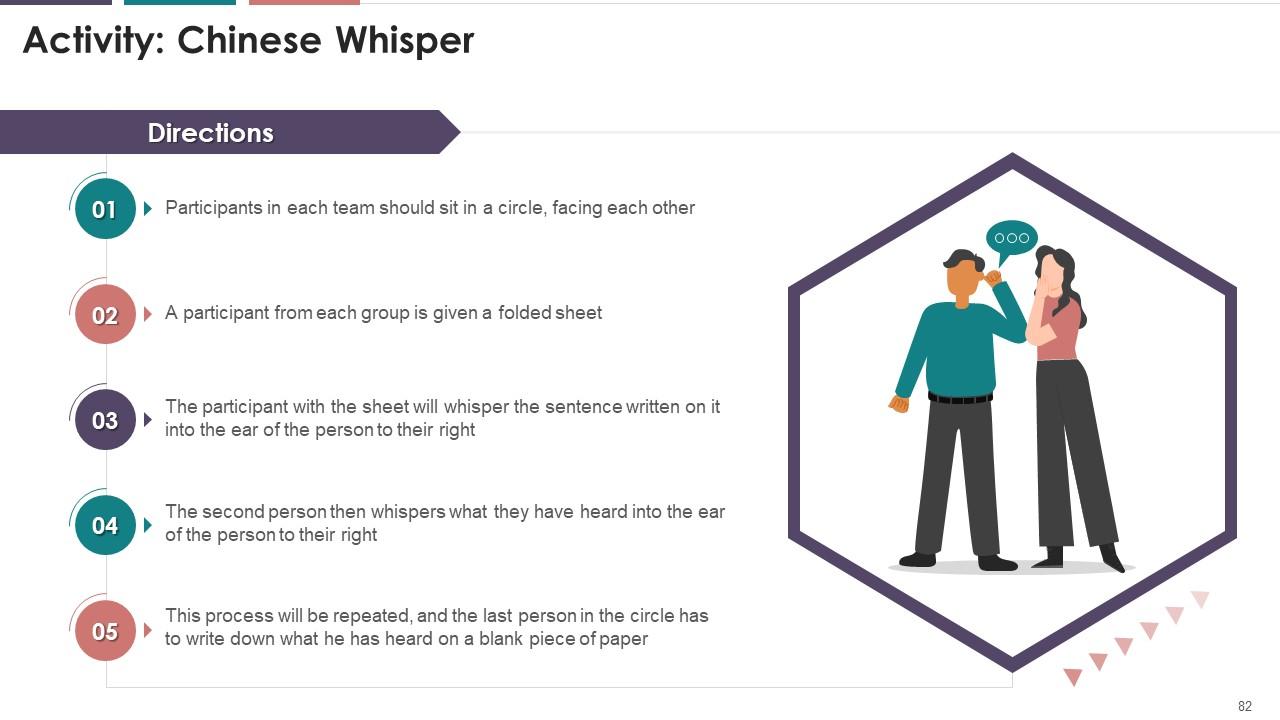
Slide 71 to 82
These slides depict an energizer activity to engage the
audience of the training session.
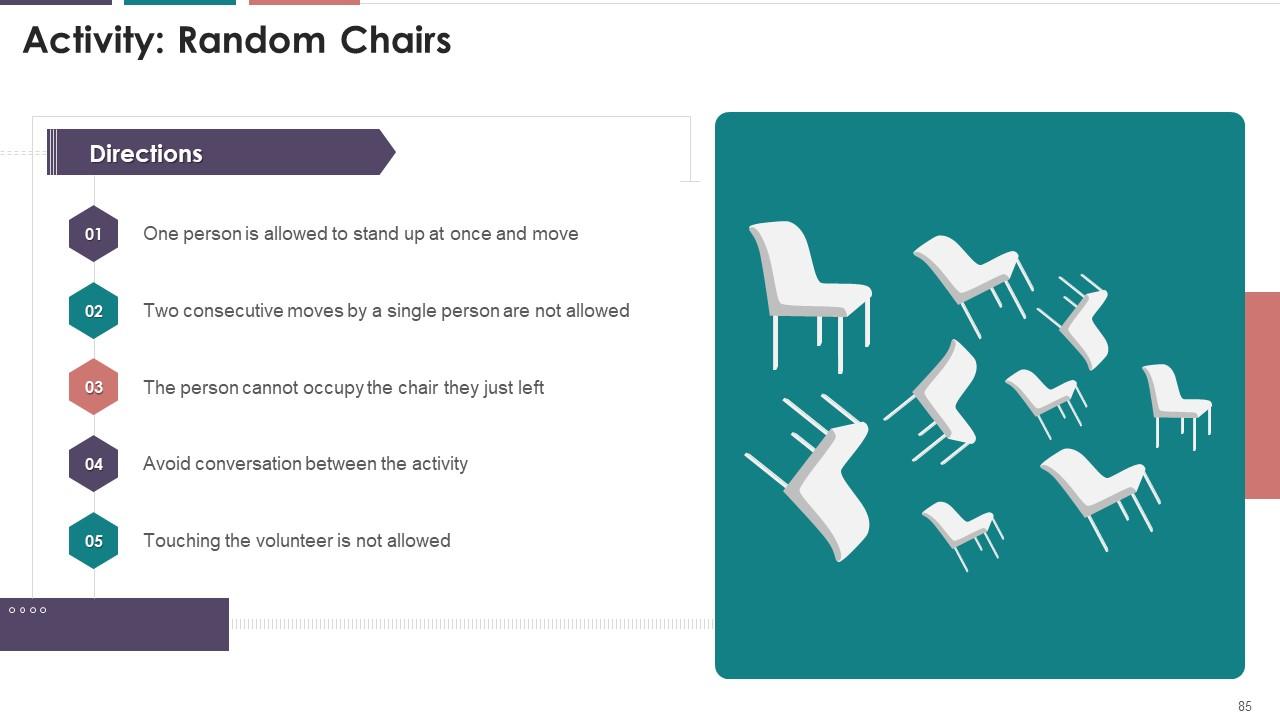
Slide 85
The above slide displays the activity for the team
members found less energetic and enthusiastic. It will ensure an increase in
energy levels and the productivity of employees at the workplace.
Instructor's Notes:
·
Multiple chairs are to be adjusted in the
empty and spacious room in a random order
·
The chairs should be put in a manner that
every chair points in a different direction and all the chairs are occupied
Now,
·
Ask for a volunteer from the batch. (Batch
may include a maximum of 15 people for a regular size room)
·
The volunteer is supposed to walk slowly
and approach his/her empty chair and sit down. If the chair is already
occupied, then he/she is expected to occupy the other/next alternative empty
chair available
·
All other members will try to stop the
person from approaching the relevant chair
Strategy Formulation:
·
Multiple teams can be made to conduct the
activity
·
Each team can be allotted 2 minutes for
planning
·
Each round is to be reviewed for the
outcomes achieved from the activity
·
Each team should have a different
volunteer, preferably the person with the lowest energy levels from the batch
·
The volunteer should move cautiously so as
to not bump into any of the props or persons in the room
Activity Review/Outcomes:
·
How did the activity influence the teamwork
and engagement skills of all the participants?
·
How was the experience while planning and
working with 15-20 members at a time?
·
Was everybody clear about the purpose and
conduct of the respective activity?
·
Did you observe any flaws that you wish to
improve? Or any other instructions you want to include to make the activity
conduct easier?
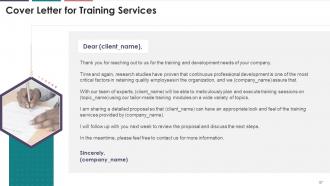
Slide 87
This slide highlights the cover letter for the training
proposal. It includes details regarding what the company providing corporate
training can accomplish for the client.
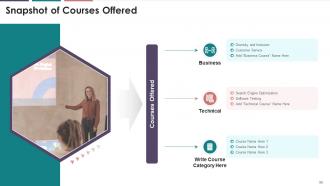
Slide 90
The purpose of this slide is to showcase the multiple
types of courses offered by the training company.
Slide 92
This slide indicates the major deliverables that the
corporate training firm will provide to the client. The key deliverables
highlighted are session plans, PowerPoint deck, evaluation material, and
training handouts.
Slide 94
This slide represents the multiple additional services
offered by the training firm to the client, such as webinars, planning
journals, and e-learning design solutions.
Slide 96
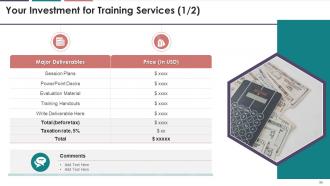
This slide tabulates the major deliverables offered by
the training company to the client along with their associated costs.
Slide 97
The purpose of this slide is to highlight the multiple
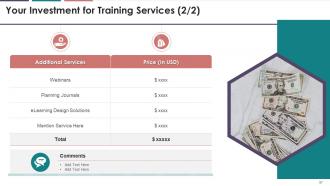
additional services offered by the training firm along with their cost details.
Slide 99
This slide provides an overview of the corporate
training firm's vision and mission statements, core values, and key clients.
Slide 101
This slide highlights the major awards and recognition
won by the training firm for their exceptional service to clients.
Slide 103
The slide provides information regarding the team
members that would be providing the training services to the client. It
includes details of the trainer and their respective designations
Slide 104
The slide provides information regarding the team
members that would be providing the training services to the client. It
includes details of the employees names and their respective designations.
Slide 106
This slide provides information pertaining to
testimonials given by satisfied clients of the training firm.
Slide 107
This slide highlights the testimonials from multiple
satisfied clients of the training firm providing information regarding
congratulatory messages, client name, and company details.
Slide 109
This slide showcases the case study for the training
proposal. It includes information regarding the problem faced by the client and
solutions offered by the training firm. It also covers details of the results
and client testimonial.
Slide 111
This slide provides information regarding the contract
terms and conditions of the training proposal. It also includes details of
deliverables that the training company will provide to the client.
Slide 113
The purpose of this slide is to provide the contact
information of the corporate training firm. It includes the firm’s official
address, contact number, and email address.
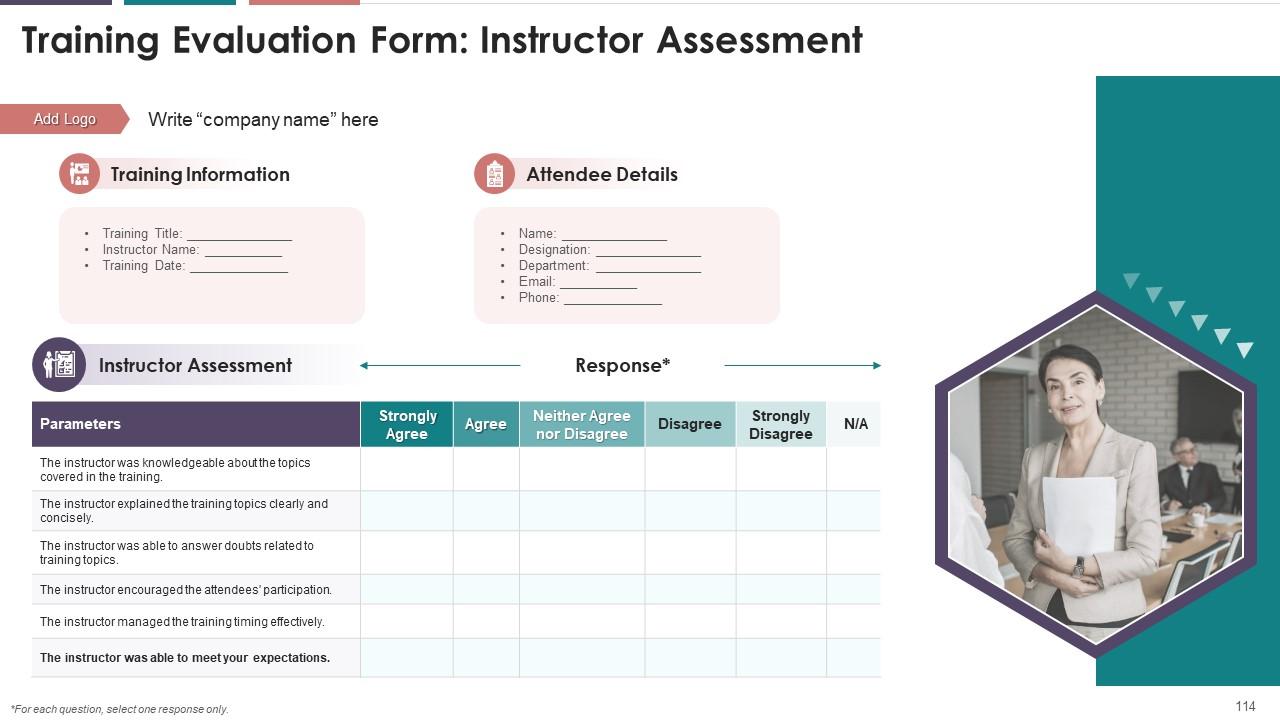
Slide 114
This slide highlights the training evaluation form for
instructor assessment. It also includes sections to fill details of training
information and attendee details.
Slide 115
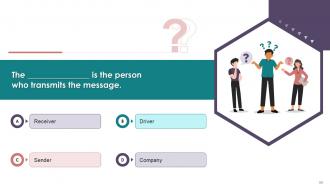
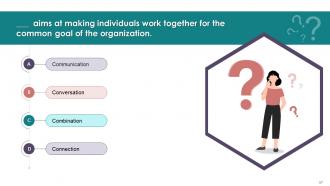
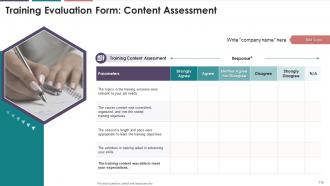
This slide showcases the questions for the assessment
of the training content by the attendees.
Slide 116
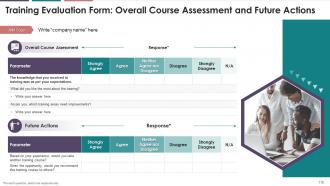
The slide indicates the evaluation form for course
assessment. It also includes questions pertaining to the future actions of the
attendees.
Fundamentals Of Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt with all 121 slides:
Use our Fundamentals Of Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
“I really like the convenient operation and professionalism I saw on the SlideTeam website. I want to express my regards and appreciation to the team.”
-
Visually stunning presentation, love the content.