Overview Of Stable Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt
This set of slides in-depth cover the types fiat-collateralized, commodity-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized, real word applications, limitations, risks, and regulations of stablecoins, a type of cryptocurrency coin.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Overview of Stablecoins in Cryptocurrency. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1
This slide introduces the concept of stablecoins. Stablecoins are digital assets linked to the value of another currency, commodity, or financial instrument.
Slide 2
This slide discusses the main aim of stablecoins, which is to ensure that value of cryptocurrency remains stable.
Slide 3
This slide highlights the four types of stablecoins. These are fiat-collateralized, commodity-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized.
Slide 4
This slide discusses Fiat-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Fiat-collateralized stablecoins are backed by sovereign money such as the Pound Sterling or the US Dollar. To issue a specific number of cryptocurrency tokens, the issuer must provide dollar reserves in the same amount as the collateral
Slide 5
This slide discusses Commodity-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Transferable assets like precious metals, oil, real estate etc can back Stablecoins with collateral. Among these, Gold is the most commonly collateralized asset.
Instructor’s Notes: The value of a real-world asset is also, essentially, exposed to the behaviour of holders of commodity-collateralized stablecoins. These assets can appreciate or depreciate over time, which might impact trade incentives.
Slide 6
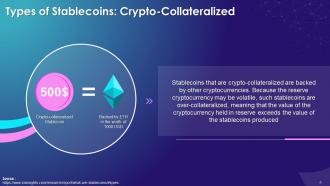
This slide discusses Crypto-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Crypto-collateralized stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies and are over-collateralized.
Instructor’s Notes: For example, to obtain $500 in stablecoins, you must invest $1,000 in Ether (ETH). The stablecoins are now 200 percent collateralized in this situation, and even if the price drops by 25%, the $500 worth of stablecoins is secured by $750 worth of the ETH.
Slide 7
This slide discusses Non-Collateralized Coins which are a type of stablecoins. Non-Collateralized or Algorithmic stablecoins may or may not hold reserve assets. They keep the stablecoin's value stable. This is done through an algorithm, essentially, a computer program that runs a preset formula to control the stablecoin's supply.
Instructor’s Notes: For example, to obtain $500 in stablecoins, you must invest $1,000 in Ether (ETH). The stablecoins are now 200 percent collateralized in this situation, and even if the price drops by 25%, the $500 worth of stablecoins is secured by $750 worth of the ETH.
Slide 8
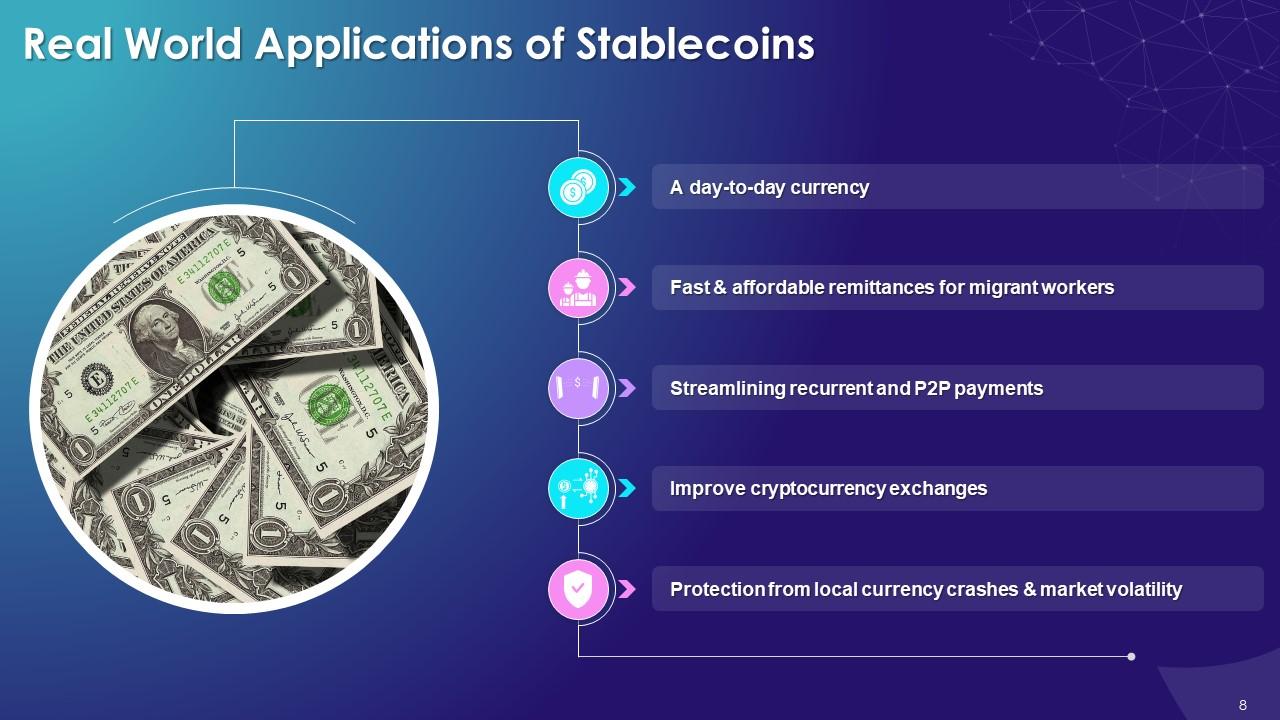
This slide lists applications of stablecoins. These include the use of stablecoins as a day-to-day currency which is fast & affordable, streamlining recurrent and P2P payments, and providing protection from local currency crashes & market volatility.
Instructor’s Notes:
- A day-to-day currency: Well-designed stablecoins have the potential to be used in commerce just like any other currency. Since no conversion of multiple fiat currencies is required, stablecoins might be used for international money transfers
- Fast & affordable remittances for migrant workers: Many migrant workers currently rely on businesses to transfer money back to their families, which is time-consuming and expensive. Stablecoins can be a better alternative. Workers and their families can use digital wallets to receive stablecoins almost instantaneously from anywhere globally, with low fees and no price volatility
- Streamlining recurrent and P2P payments: Enforcement of smart contracts is also possible with stablecoins. An employer, for example, may set up a smart contract that automatically transfers stablecoins to its employees at the end of each month
- Improve cryptocurrency exchanges: Due to rigorous rules, only a few cryptocurrency exchanges presently offer fiat currencies. However, by simply employing a USD-backed stablecoin instead of actual dollars, exchanges can get past this obstacle and provide crypto-fiat trading pairings. This encourages the general acceptance of cryptocurrency trading since it simplifies the process and allows them to continue thinking in terms of dollars or euros rather than fluctuating bitcoin values
- Protection from local currency crashes & market volatility: Local citizens may instantly trade their crashing currency for comparatively safe USD-backed, EUR-backed, or even gold-backed stablecoins, shielding themselves from further value erosion
Slide 9
This slide highlights the limitations of Stablecoins. The major ones are people’s trust in the solvency of the organisation backing the stablecoin, lower probability of making gains by trading in stablecoins etc
Slide 10
This slide discusses risks and regulations associated with Stablecoins. These are: systematic risk & loss of value, threat to market integrity & investor protection, illicit activity, and tighter regulations.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Systematic risk & loss of value: Economic power would be excessively concentrated in a single entity with centralized coins, such as thosethose having fiat backing and that private entities produce. Tether, for example, with its current market share of more than 50%, poses such a threat. Tether's failure could jeopardize an entire ecosystem of apps, businesses, and users who rely on it. Investors may try to cash out their stablecoins if the economy overheats and the value of Tether's non-cash collateral plummets, only to discover that the issuer is unable to return the entire money invested (referred to as 1:1 ratio)
- Threats to market integrity & investor protection: According to the US Treasury Department, the ease and speed of transacting with stablecoins encourage speculative trading of digital assets, endangering market integrity and investor protection
- Illicit activity: Stablecoins could be misused to break laws on Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-terrorist Financing Legislation (CFT). The increased use of stablecoins for cross-border transactions, the lack of international standards for stablecoin providers, the irregular implementation of AML/CFT standards among different countries, and the possibility of anonymity while transacting in stablecoin are all factors that contribute to the risk of the currency being misused for illicit activity
- Tighter regulation: To address the prudential risks of stablecoins, the US Treasury advocated stricter regulation in 2021. These recommendations included that the stablecoin issuers must be insured depository institutions, custodial wallet providers must be subject to "appropriate federal oversight," and interoperability standards must be implemented across stablecoins, among other requirements
Overview Of Stable Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt with all 26 slides:
Use our Overview Of Stable Coins In Cryptocurrency Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Making a presentation has never been this easy for me. Thank you SlideTeam for offering a splendid template library.
-
Commendable slides with attractive designs. Extremely pleased with the fact that they are easy to modify. Great work!