In Depth Guide To Blockchain Nodes Training Ppt
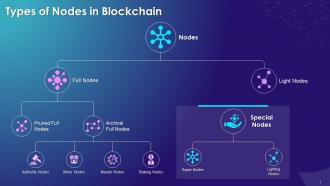
This set of slides, in-detail, cover the types of blockchain nodes, i.e. full nodes and light nodes. It contains full node types, which are pruned nodes and archival full nodes. Further, it has types of archival full nodes that are authority nodes, miner nodes, master nodes, and staking nodes. It also contains PPT slides on super nodes and lighting nodes.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting In Depth Guide to Blockchain Nodes. This slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint specialists. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. You can add or delete the content as per your need.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1
This slide states that there are two sorts of nodes: full nodes and light nodes. Clients, who provide wallet functionalities, are another word for nodes, and full ones store a complete record of the blockchain's history, including all produced blocks. Light nodes, also known as SPV (Simple Payment Verification) nodes, are wallets that download the headers of blocks, saving users' hard-drive space.
Slide 2
This slide describes that full nodes are termed blockchain servers since they keep all transaction records in the blockchain. Full nodes are an integral aspect of the blockchain's governance scheme. While several governance models exist, a blockchain is upgraded or improved only once a majority of full nodes agree to it. As a result, full nodes possess voting power on the blockchain.
Slide 3
This slide states that pruned nodes have a set amount of memory for storing data. There is no limit to the number of blocks that may be added to the blockchain, but there is a limitation on the number of blocks that a pruned full node can store.
Slide 4
This slide describes that archival full nodes are the most frequently found full nodes in a blockchain, and they store the entire blockchain in its database. The only significant difference between an archived full node and a pruned full node is the amount of RAM available.
Slide 5
This slide states that In a public Blockchain, anyone may join the network and then become a node by syncing their system with the blockchain data. However, in many circumstances, data access must be preserved. In such a circumstance, the authorized entities need to regulate the blockchain. This is where authority nodes are used. The name of these nodes derives from the fact that they govern or are responsible for approving additional nodes to join the blockchain network.
Slide 6
This slide describes that some consensus techniques, like Proof-of-Work, require nodes to solve complicated mathematical problems to validate a network transaction. Such validation activities need a substantial amount of computing power and energy usage. As a result, miner nodes are nodes established exclusively to carry out the mining operation.
Slide 7
This slide states that masternodes are full nodes with the ability to maintain the Blockchain ledger and validate transactions but cannot add new blocks to the Blockchain.
Slide 8
This slide describes that staking is the process of choosing a node based on predetermined parameters such as coinage or network time spent. The selected node can complete a transaction and get a reward, and Staking nodes do not require a large amount of processing power.
Slide 9
This slide states that a light node saves and provides only the data required to support daily activities or quicker transactions. They do not validate the blocks and only save the Block headers. Simplified Payment Verification nodes (SPV nodes) are another name for these.
Slide 10
This slide describes that Super Nodes are created to carry out specific activities in Blockchains. A super node, for example, is responsible for applying a blockchain protocol modification or maintaining the rules governing a specific blockchain.
Slide 11
This slide states that Lighting Nodes establish a secondary network with a user and push transactions to the main blockchain. This enables quick transactions, while lowering transaction costs due to reduced network congestion.
In Depth Guide To Blockchain Nodes Training Ppt with all 27 slides:
Use our In Depth Guide To Blockchain Nodes Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
A beautiful, professional design paired with high-quality images and content that is sure to impress. It is a must-use PPT template in my opinion.
-
A perfect platform for all your presentation needs. Unlimited products at an affordable price.