Speaking In Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt
This PPT training deck in detail covers the concept of Speaking in Business Communication. It covers the significance, elements, and types of speaking. The PowerPoint module also contains key speaking components, such as business presentations, public speaking, and business meetings, along with techniques to develop effective speaking and the PVLEGS framework poise, voice, life, eye contact, gestures, and speed. The PowerPoint deck also contains key takeaways, case studies, activities, discussion questions, MCQs, and memes to make the training session interactive. It also includes additional slides on about us, vision, mission, goal, 30-60-90 days plan, timeline, roadmap, training completion certificate, energizer activities.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Module on Speaking in Business Communication. This deck comprises of 112 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts and every slide consists of an appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 4
This slide represents the meaning of speaking effectively in the business environment. It is an aspect of communication that encourages the speaker to use language to express the thoughts verbally.
Instructor’s Notes:
The Speaker should consider the below-mentioned tips for speaking in business talks:
· Listen First
· Make Eye Contact
· Use Gestures Appropriately
· Relax
· Keep the conversation simple
· Pause and Pace
· Practice Pronunciation
Slide 5
This slide elaborates on of the importance of speaking effectively in a business environment. Whether we talk about public speaking, presentations, or business meetings, speaking focuses on information conveyed, audience targeted, and the one can transmit to an audience.
Instructor’s Notes:
· To Inform: The focus of effective speaking should be on the ability of a speaker to inform the audience. Speaking to inform is crucial, from presenting to schools to presenting pitch decks to your boss or clients. An informative speech should encourage sharing knowledge of any subject with an audience, enhance their understanding, and make them remember the words of the speaker. For example, a person can be asked to instruct a group of coworkers on using new computer software or address the employees on company happenings. It can be in demonstrations or putting forward an area of expertise. That makes effective speaking an essential skill in today's world
· To Win Over Audience: Mastering speaking skills results in an increased level of confidence. It is always imperative to be knowledgeable about the topic you are presenting. When making a persuasive speech, either a sales pitch to a client or any other investor pitch, the speaker needs to be prepared take questions. For example, to express the exciting features of a product or idea to the editor of a publication, the language used has to be fresh and elicit curiosity. Any compelling and clear pitch will always persuade the consumer to know more. When addressing the public on any issue or idea, speaking is found to be more effective in getting your point across
· To Motivate People: Public speakers inspire the audience to work harder and achieve their targets on time. A speaker should influence listeners and make a way where every person comes out flourished. A speech does not, necessarily, ask the listener to work in a certain way, but it tries to modify a person's approach. Once you internalize the skills of a good speaker, gain credibility. Over time, you may even acquire the rare ability to entertain as you inform through your speeches
Slide 7
The following slide illustrates the critical elements of speaking effectively in the business environment. It includes selecting appropriate words to be used, clarity in voice while speaking, and focusing on Nonverbal aspects like body language, gestures, etc.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Words Used:
· For the choice of words, a speaker should consider the following characteristics/principles:
· Choose words that accurately reflect what you want to convey
· Specific words should be preferred over sentences
· Strong words which indicate clear meaning should be chosen
· Add positive words
· Avoid overused and obsolete words
· Voice Clarity:
· Organizing thoughts in a logical sequence, and picking the correct words, is the basic concept of Clarity. Clarity considers the recognition of significant concepts like projection, pronunciation, and diction. Mere common over language, even if it over English, does not mean that the speaker has strong and good communication skills. Communication must be listener-centric, i.e., it must be concerned about the listener and ensure that they understand the conveyed in exactly the same manner as you want it to be understood
· Common obstacles to Clarity are: Fast Speech Rate, Mumbling, Quiet Voice, and Accent/Use of Slangs
· Nonverbal Aspects:
· Nonverbal aspects constitute a considerable part of the communication. These broadly include body language, eye contact, and facial expressions.
· Body Language: Postures and gestures are the two critical elements of Body Language. Body Language can reflect a positive and negative impression. Negative body language gives the wrong impression and stalls career progress
· Eye Contact: While chatting with someone, making eye contact conveys your interest in the conversation. Eye contact usually conveys confidence and sincerity of a person
· Facial Expressions: Face expressions of a person are incredibly expressive and reveal our emotions or thoughts before they are verbalized. It is crucial, especially in a business conversation, to maintain positive facial expressions
Slide 8
This slide shows the pictorial explanation of why sentences in business communication should be framed using positive words.
Slide 9
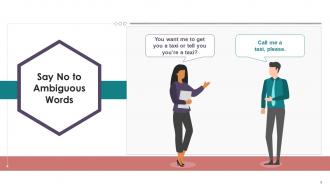
This slide conveys the conversation between two persons, reflecting the misinterpretation of one person due to the use of ambiguous words.
Slide 10
This slide represents the dos and don’ts for the words to be used in communication. A speaker should avoid slang or jargon as they are too informal. Keep the communication easy and understandable.
Instructor’s Notes:
Dos:
· Positive Words: Use respectful dialogue, use positive mannerisms, and be friendly in communication
· Example:
· Don’t say: “The damage to your phone won’t be fixed for a week.”
· Say: “You can collect your phone next week.”
· Don’t say: “I think that is a bad idea.”
· Say: I think the idea can be improved.”
· Specific Words: To make the language easy to understand, the speaker should use specific words
· Example:
· The sentence ‘After this is accomplished” can be rewritten as “then”, and “at an early date” can be replaced with “soon”, etc.
· Confident Words: Avoid using words like “just” or “I can’t”, as it reduces the power of the statements put and presents you as lacking skills. Instead, a person should replace these words with ‘I won’t”, which is an active word showing your boundaries for yourself. Avoid filler words like um, ah, like, you know etc.
Don’ts:
· Ambiguous Words: Words which can be understood differently by different readers should be strictly avoided in business communication.
· Example 1: Consider the short phrase, “I read the book.” This sentence alone could refer to the present or the past, as the word “read” in English is spelled the same way in the present and past tenses. However, if we change the sentence to “I read the book when I was 10,” that clears up the ambiguity and places the context in the past tense.
· Example 2: Well, I’ve indeed never tasted fish cooked that way before! The confusion is whether the fish was good or bad?
· Jargons/Slangs: These are basically technical words that only a target group can understand and are, indeed, meant only for their consumption. These words are unconnected with the conversation and the listener perceives these as a bid to show-off.
· Example 1: “AWOL” which means Absent without leave. It is a military jargon, which is used to refer to a person whose whereabouts are known.
· Example 2: “Stat” is a term used in hospitals or the medical field and means immediately. (Call the doctor, stat!, which means call the doctor immediately).
· Obsolete Words: These are the words which are non-existing or non-active in English language now.
· Example:
· Words like fizzle (meaning to confuse), and
· Twattle (meaning to gossip) are obsolete words which were earlier very much used in English language but have faded away now.
Slide 11
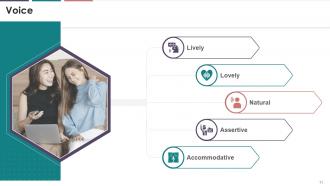
This slide explains the essential elements that should be present in the voice and tone of the speaker while communicating. He/she should seem lively, natural, assertive and accommodative while speaking formally or informally.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Lively: The speaker should sound energetic and enthusiastic. A dull or less active speaker usually fails to engage the audience
· Lovely: The speaker should deliver the message in a polite and soft-spoken manner
· Natural: The voice of the speaker should be natural
· Assertive: Assertiveness in voice requires clear and straightforward communication that grabs the attention of the audience. The speaker must clearly state his/her expectations from the listener
· Accommodative: It refers to the adjustment of the voice or tone by the speaker according to the speech styles of other participants in the communication process
Slide 12
This slide includes the dos and don’ts for the voice aspect of communication. A speaker should work on the speech rate, should be audible and should avoid use of slangs.
Instructor's Notes:
Dos:
· Clarity in Speech: Structuring of thoughts in proper sequence, use of various tools for communicating, and checking effectiveness of such tools. Connectivity of the internet while communicating online, network availability while speaking on telephone etc all need to be checked.
· Good Communication Skills: Make sure that the listener takes home what the speaker tries to deliver. Use of easy words, more straightforward language and additional aids must be prepared to make the communication better and effective
Don’ts:
· Fast Speech Rate: Sputtering might cause shortening of vowel sounds or the wrong pronunciation of words. Speaking at an average speed lead to the proper formation of sounds, and it also helps listeners get time to absorb the information provided
· Mumbling: Mumbling is related to a fast speech rate. When a speaker mumbles, it distorts words and sounds
· Quiet Voice: It causes a lack of clarity as listeners fail to hear and absorb what has been said. To overcome this barrier, a speaker should practice jaw and tongue relaxation as it will encourage openness in sound and formation of words
· Use of Slangs/Accent: Using accents usually makes it difficult for listeners to understand the message conveyed. Confusion results as listeners find such information challenging ang puzzling. A person, even when using an accent, should focus on speaking at a slow speed so that messages are conveyed correctly
Slide 13
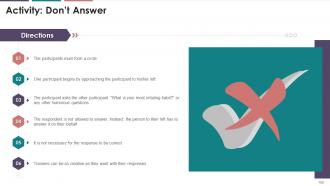
This slide represents a question-based activity where the audience will use its skills and analyze why the image stating the person facing the audience is correct and the other person turning the back towards the audience while presenting is incorrect.
Slide 14
This slide explains the dos and don’ts for nonverbal aspects to be used in communication. It states that the speaker should avoid using expressions that exhibit their nervousness. They should maintain eye contact with the audience and interact with every individual present.
Instructor’s Notes:
Dos:
· Eye Contact: Eye contact has the power to change the way a person thinks or responds to information. It usually indicates a confidence, and also encourages the audience to pay attention, positively influencing listening
· Face your Audience: Speaking while facing your audience and showing them that you are genuinely focused on them. The audience feels more involved and connected in such a communication
· Smile and Relax: A smiling and relaxed speaker indicates openness and friendliness in engaging with the audience. When a speaker smiles, it reduces a his/her anxiety levels. Smiling also indicates a positive attitude
Ø For Example, If a person who is speaking looks arrogant or frustrated, it will put the audience in an anxious position, where he/she might feel neglected or become less interested in listening
· Be Natural in Voice and Expression: The speaker should try to be natural in voice and tone rather than train it in any particular way. Also, he/she should naturally convey the expression not only using words, but the emotions as well
Don’ts:
· Staring at a Particular Person: Looking at a person continuously or staring at a person is usually a sign of aggression. Rather than focusing on one person, the speaker should maintain eye contact with a wider audience
· Hands in Pocket: Keeping hands in your pocket while communicating indicates a lack of professionalism. On occasions, however, one hand in your pocket demonstrates that the speaker is relaxed and comfortable
· Shuffling of Papers: Many times the speaker has to deliver something vital, which requires keeping flashcards or handy notes. In such a case, he/she should make sure that he/she makes more eye contact with the audience and is not reading most of the time or shuffling papers
· Turning your Back: It is found that when a speaker presents while turning back towards the audience or focuses on reading through the papers, it kills the interest and effectiveness of the communication. The speaker should continuously engage with the audience to grab their attention and make them a participant in the listening-speaking process
Slide 16
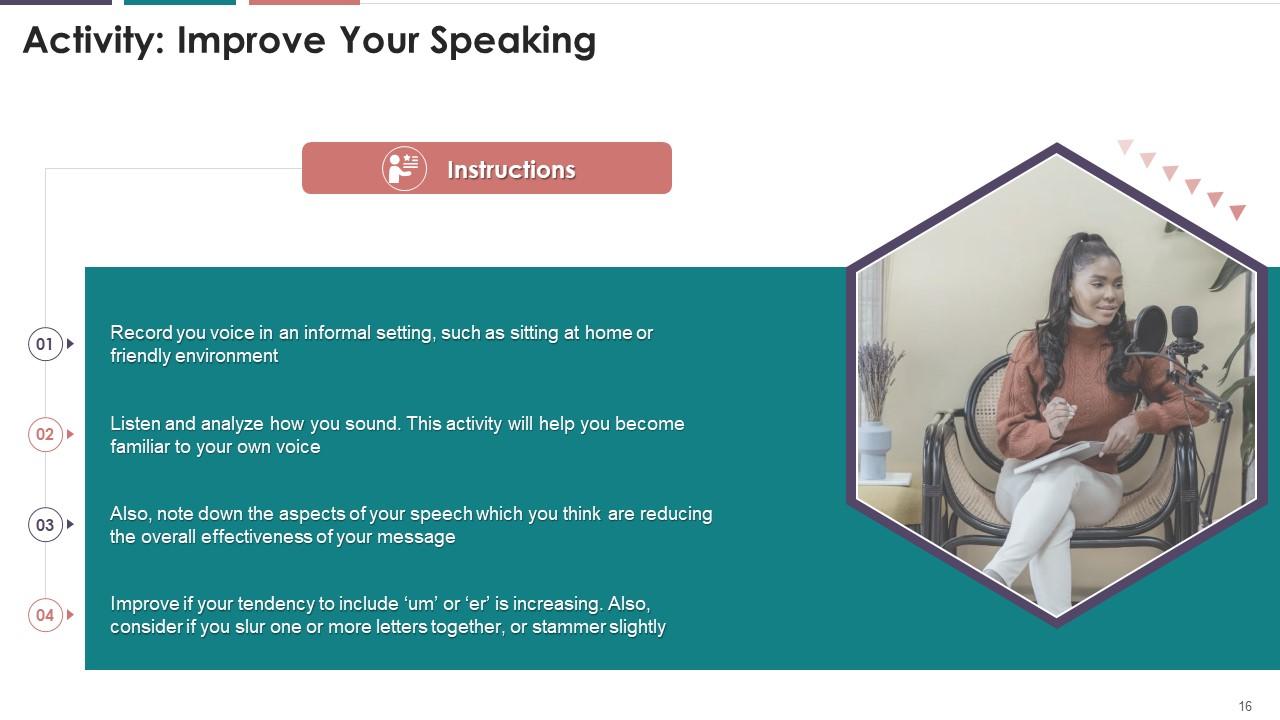
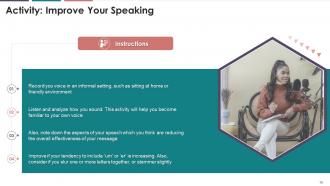
This slide covers an activity planned for the audience, where they will be able to analyze, interpret and improve their speaking skills and pattern, whether in person or over a telephone.
Slide 17
This slide explains the different types of speaking in the business environment, including speaking to inform, speaking to persuade, speaking to motivate, and speaking to entertain the target audience in several ways.
Instructor’s Notes:
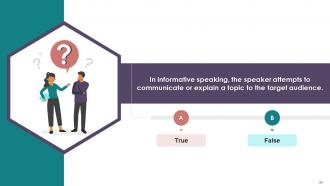
· Speaking to Inform: In informative speaking, the speaker attempts to communicate or explain a topic to the target audience. College lectures, industry conferences, and public speaking reflect informative speaking where vital information is shared. In this speaking, only important aspects are communicated. The speaker is not attempting to persuade others or show them how to do something themselves. Instead, critical information is disseminated
· Speaking to Persuade: Being a glitzy form of communication, it is used mainly by politicians, lawyers, and clergy. This kind of speaking necessitates voice inflections and language nuances for the audience from a particular point of view. Considering a few examples, politicians may use this to seek votes; lawyers may be willing to persuade a jury, whereas clergy members must be trying to win the faith of others. In this kind of speaking, a person may use emotional appeals and forceful/strong words
· Speaking to Motivate: The speeches are highly emotive and can be given in multiple types of settings. Speakers seek to arouse, encourage and stimulate the audience to enrich their personal or professional lives. Various businesses usually hire motivational speakers to encourage their employees to work hard and perhaps take greater pride in their employer and job. Proper guidance is given to the audience to reach specific goals like professional growth and development, better health, and many more. Illustrating examples of how to achieve those goals are presented
· Speaking to Entertain: It is a speech designed to catch the audience’s attention. Entertaining speeches should communicate a clear message in a typically different manner than traditional or other types of speaking. These are often delivered on informal or special events, due to which they are often referred to as special-occasion speeches, for example, raising a toast at a wedding
Slide 19
This slide shows various components of ‘Speaking’ in business communication. Business speaking can be conducted either as business presentations, public speaking, and business meetings.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Business Presentations: Speaking to your target audience includes online business presentations or business talks. The most prominent example is training a virtual team or addressing your team in meetings held online. While speaking in a business meeting using the presentation, the speaker can take the form of a story, keep the content simple, talk naturally, and put minimal content on the slides
· Public Speaking: Public speaking is considered an essential aspect in all the three areas like business, education, and the public arena. It is because the words spoken are more powerful than the written words. When talking from a marketing perspective, it may help the business person to market the offers in a better way
· Business Meetings: Business Meetings involve gathering two or more persons for different purposes like informing or discussing some topic. Business meetings can be either in person or by telephone. These meetings should reflect a clear intent and be conducted in the right tone and atmosphere. It should involve maximum participation of members, making them feel an essential part of decision making and hence the organization
Slide 22
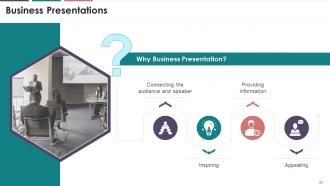
This slide analyses the significance of conducting business presentations in the organization. When performed as presentations, business speaking helps connect the audience with the speaker, provides them valuable information, inspires them to work in a systematic manner and adds appealing content to everybody's vocabulary of presentations.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Connecting the audience and the speaker: Interactive business presentations create camaraderie and connect the audience and the presenter. The delivery of the intended message is effective as audience feel the personal connect
· Providing Information: Every listener wants to know significant pointers of the presentation. These may be in the form of customized solutions or a bagful of tricks to accelerate learning. An excellent presentation leaves the audience with a good piece of information that should be eye-opening and enlightening
· Inspiring: Every business presentation must capture the attention of the audience using story elements, lessons, conflicts, etc. Additionally, a presentation should target capture the audience's attention from the word go. Meandering is a strict no-no
· Appealing: Visual or physical props greatly impact the business presentations and the concerned audience. Most common elements appealing to the target audience in business presentation are the information, infographics, animation, design, along with the body language of the person presenting. How relevant is the information presented is directly related to how the props are being used
Slide 23
This slide explains the meaning of business presentation as a part of speaking in business communication.
Slide 24
This slide depicts tips for successful conduct of business presentations. Business presentations have to be very precise in terms of content, visual elements and should add value to the existing knowledge base of the listener.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Limited Text: The presenter should include limited text in the presentation, maybe pointers, bullet points, or short notes
· Inclusion of Visual Elements: Text added on slides should be accompanied by relatable and relevant photos, images, or videos, making it more lively, engaging, and practical
· Voice Modulation: The speaker should make sure that there is effective voice modulation in a presentation to make it more influential, persuasive, and commanding
· Value Addition: The main goal of presentation should be to add value to the existing knowledge base of the listener
Slide 25
This slide explains the most common errors that mar a presentation. The major mistakes are inappropriate content, boring presentation, verbose presentation, and the failure to address audience concern.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Too Much Text: A presentation has to be minimalist and has to say more with less. Clutter is unacceptable, as it makes the slide boring and bulky
· Solution: Always scrutinize before adding information and evaluate the reason why this information is included
· Inappropriate Content: The presenter should make sure that the content added on the slide is relevant. Try to put yourself in the shoes of others to get a clearer idea about their needs and motivation
· Solution: Asking questions about what the individual is needs will help make the presentation more relevant for the audience
· Lack of Preparation: Every presentation which looks highly inspiring or motivating takes almost weeks of preparation. The common error which a speaker should avoid is avoiding preparation
· Solution: Proper preparation beforehand, practicing words, running through all the slides, and checking equipment well in advance, will help you overcome the fear and plan the projects and events properly
· Monotone Voice: Voice is considered the primary means of communication. It is found that even if you have unique content but a monotone voice, you will anyhow lose your audience
· Solution: Along with the content, an effective voice should be vital, audible, and clear. People should learn and master the art of making the voice more effective by learning aspects like voice production, when and how to pause while speaking, vocal exercises, and voice care
· Failure to Address Audience’s Concerns: Many times the information which is presented does not match the needs and requirements of the audience. In such a case, the audience loses interest in the communication process
· Solution: The speaker should focus on bringing tailored content and information matching the audience's needs. He/she should not seem over-occupied with the delivery of content and ignorant of the concerns of the audience; instead, he/she should make the audience clear on what is the agenda of the presentation and what is expected
· Too Wordy or Too Much Jargon: The presentation should not be too wordy, meaning it should be to the point and concise. The presenter should not rush the process and not delay the procedure unnecessarily, like using up an hour for a 20 minutes process. Also, the use of jargon or highly technical terms should be avoided
· Solution: If any technical term is used, be sure to introduce to the audience what it means. Also, the presentation should be made short and informative
Slide 28
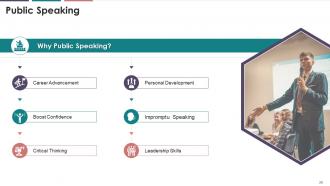
This slide represents the significance of speaking in publicly. Public speaking helps boost the confidence of the speaker, enhance leadership skills, encourage critical thinking, contribute towards personal development, assist in career advancement, and helps an individual get over the fear of impromptu speaking.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Career Advancement: Effective public speaking skills help with career advancement, as they indicate creativity, critical thinking skills, leadership abilities, poise, and professionalism. These qualities are always in high demand in the job market. Public speaking skills improves the effectiveness of what you say, making you the star in office meetings; your ideas and suggestions are accepted. Speaking skills also help you excel in job interviews
· Boost Confidence: Public speaking can significantly boost your confidence. The nervousness and the butterflies in stomach that result from just stepping up on stage and facing a huge crowd never really goes way. With practice and rehearsal, however, this just fades away
· Critical Thinking: Public speaking is considered the best way to develop and enhance critical thinking skills. After careful thought from all aspects, the message which needs to be delivered has to be tailored to the requirements, needs and even expectations of the target audience
· Personal Development: Public speaking equips the person with skills required to analyze and interpret any topic. Improved confidence and ability to speak in a crowd contributes to the personal development of an individual
· Impromptu Speaking: When called over a stage at the wedding to speak a few words, at a performance award ceremony, or on any other special occasion, you might not get the words immediately to convey. If you acquire public speaking skills, however, you will always find yourself graciously accepting the opportunity in such a situation. Public speaking skills helps you let go of constant worrying and tackling the fear of being asked to say something, especially at formal events
· Leadership Skills: Leaders need to have the capability to drive change. Public speaking skills are vital in being effective at that. Speaking powerfully, you can change people’s minds about an issue. If you master this skill of bringing a change and encouraging individuals, you can hop to leadership positions. You already have command over a significant aspect of leadership
Slide 29
This slide explains the meaning of public speaking as a component of business communication.
Slide 30
This slide illustrates various verbal and Nonverbal skills that are considered absolutely essential to public speaking.
Slide 31
This slide explains the most common errors that must be avoided. It is suggested that the speaker must refrain from using filler words, speaking at a normal rate, make constant eye contact with different members of the audience, and pre-plan start and finish time of their speech.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Neglecting to Prepare: One of the most common mistakes in public speaking is not giving enough time to preparation. This is the root cause of ineffective and inefficient public speaking
· Solution: Before presentation or speech, a person must set some time aside to make sure that work has been completed in all aspects and proper time has been given to preparation
· Using Filler Words: Filler words in speaking refer to ‘um’ and ‘uhs’ that mark out the public speaker as unprofessional and unprepared. The audience will perceive information delivered with frequent use of such filler words with skepticism.
· Solution: To avoid this, the speaker should make sure that he devotes enough time for practice and preparation before delivering the speech
· Talking Too Fast or Soft: Whenever an individual presents publicly, he/she gets nervous and makes another common mistake: Speaking too fast, which confuses the audience. The other end of the spectrum is talking too softly. The audience might not understand and hear what you have said if you will speak too softly
· Solution: To avoid speaking too fast, the speaker should practice the delivery and speed before the actual delivery and allow the audience enough time to grasp the information shared. Also, to improve talking too slowly, the speaker should make sure that his voice is audible to all and avoid mumbling
· Eye Dart: In most cases, speakers fail to maintain constant eye contact with the target audience, reflecting insincerity and disinterest
· Solution: The speaker must maintain eye contact for at least 2-3 seconds with every person present before to engage and connect with them
· Overshooting Time: Overshooting time refers to overutilizing the time than the actual requirement, i.e., taking 1 hour for a 30-minutes planned task. Extended time will disturb the schedule and make it challenging to engage the audience for long
· Solution: The speaker should always pre-plan and formulate the best-suited content according to the time allotted
· Lack of Pauses: Rushing through the content while speaking is considered a negative sign in business communication. It is believed that the person is either anxious or nervous if he/she is too fast, does not pause in the conversation, and rushes throughout the conversation
· Solution: The speaker should take short breaks and pause before and after sentences. It simplifies the understanding process for the audience
Slide 32
This slide mentions an exercise for trainees to improve their speaking skills.
Instructor’s Notes:
Sample topics for practicing impromptu speaking:
· Goals are good for you
· Intelligence is not enough
· Beauty is always in the eyes of the beholder
· Youth is wasted on the young
· Does money make the world go round?
Slide 35
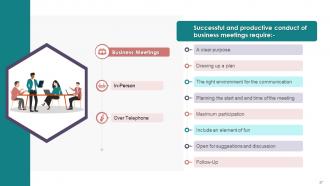
This slide illustrates the significance of business meetings. Business Meetings can help in taking better decisions, resolving conflicts, making the employee feel important or recognized in the organization, information exchange, and appraise performance of employees at regular intervals.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Better Decisions: The main objective behind any meeting is taking essential decisions on current and predetermined issues. The meeting for decision-making should be a regular activity and based on collective opinion. All decisions, whether of routine or non-routine nature, should be discussed in such meetings
· Resolving Conflicts: Conflicts are common in all organizations. If the conflict is healthy and competitive, it will increase productivity. An unhealthy or ugly conflict needs immediate resolution. Conducting meetings regularly help individuals arrive at a compromise and resolve the conflict on a positive note
· Employee Engagement: Organization goals, objectives, and the success rate is always discussed in meetings. Explaining and motivating the team for their contribution towards the organization's success rate motivates employees. Updating them on their targets and goals helps them perform better
· Announcing Changes: Business meetings should convey the existing and upcoming changes related to the policies, benefits, hierarchy, etc, to the target audience in meetings conducted. This will make people understand and accept the changes with minimal resistance
· Information Exchange: Meetings are arranged to exchange or provide valuable information to members
· Performance Review: Meetings are also called upon to review performance and convey the progress of any ongoing or completed project. Members can also discuss and gain valuable opinions from other members present on ongoing projects and issues
Slide 36
This slide explains the meaning and types of business meetings as a component of business communication.
Instructor’s Notes:
· Informative Meetings: The meetings whose purpose is to inform the target audience about new schemes, products, policies, members, etc.
· Consultative Meetings: These are the meetings where the members of the organization are consulted, and their opinions are taken for solving an existing or expected problem
· Executive Meetings: In executive meetings, authorized or competent persons take or implement significant decisions. The authorized individuals persons may include top-level officials, professionals hired, etc.
Slide 37
This slide shows various elements that help conduct a business meeting effectively and efficiently, along with the different ways in which a meeting can be conducted, i.e., in person or by telephone.
Instructor’s Notes:
In Person Speaking- In-Person Speaking can also be referred to as face-to-face communication, where both the speaker and receiver are physically present.
Advantages:
· Allows the use of both of verbal and Nonverbal aspects
· Discussion of visual elements or real-life situations becomes easy
· The conversation remains interactive and allows the participants to clear confusion, then and there
Disadvantages:
· Face-to-face communication can be expensive and has a added layer of complexity when the subject under discussion is likely to hurt one of the parties
· This kind of conversation is difficult to be delayed to re-directed
By Telephone- It is a type of communication where the speaker and the receiver connect via a device known as ‘telephone’ or ‘cell phone.’ They are not physically present and interact from two different places.
Advantages:
· It is a cheaper and convenient form of communication
· People find it easy to collect notes in the telephonic form of communication
Disadvantages:
· Only the most obvious of nonverbal communication is transmitted
· Difficulty in presenting visual objects
· The voice quality of a person may sometimes seem to be of higher pitch, rude or non-serious
Slide 39
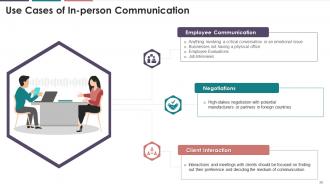
This slide mentions the areas of application of in-person communication.
Slide 40
This slide explains the points that needs to be considered communicating at the workplace.
Slide 42
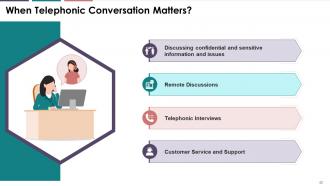
This slide mentions the areas of application of telephonic communication.
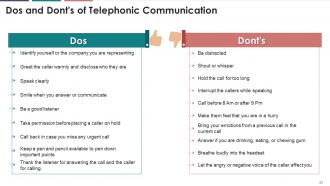
Slide 43
This slide explains the etiquette that needs to be kept in mind while answering the phone call. These are usually applicable to both formal and informal communication, being an integral part of telephone conversations.
Slide 44
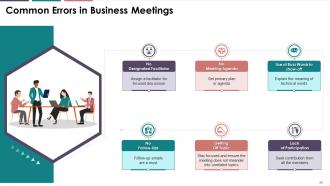
This slide covers the prevailing errors which creep into business meetings, reducing the effectiveness of the communication. Errors like frequent use of jargon and technical terms, lack of participation, delayed follow-ups, distracting conversations, etc., can turn the meetings ineffective.
Instructor’s Notes:
· No Designated Facilitator: A meeting without a designated facilitator usually ends in informal and unnecessary discussions. When no one is given charge of a meeting, it can easily run off-track
· Solution: It is always advised to have someone as a facilitator to ensure that off-topic and unnecessary discussions are reduced, and the discussion remains focused and positive.
· No Meeting Agenda: Meeting without any agenda is usually taken as unimportant by the members. Business meetings need a thoughtful structure to be efficient
· Solution: The meeting, whether on-call or in person, should always have some set or primary plan.
· Use of Buzz Words: Buzz Words are words with heavy and deep meanings. These can be technical terms or phrases which are not commonly understood by the audience and should be avoided in business documents
· Solution: In case the speaker makes use of any technical or heavy word, he should make sure that the audience is clear about what it means.
· Lack of Participation: The meeting facilitator should ensure active participation from all members, or the meeting will be a huge waste of time and effort. When only one or two persons participate in the process, it becomes difficult for others to pay attention or feel part of the discussion
· Solution: Contribution from all members helps the speaker in getting across his/her message with a lot more flair.
· Getting Off Topic: It is common for the members to get distracted from the original objective of the meeting. It usually happens when the meeting is conducted in a blended mode, i.e., few people are present virtually and few physically. The speaker of the meeting should make sure that the members stick to the agenda
· Solution: The Speaker can say, That’s an excellent topic to discuss. Let's talk about this once the meeting is over
· No Follow-Ups: Not following-up regularly after the meetings can mean that important issues remain unaddressed
· Solution: Immediately after the meeting is over, the facilitator should send a follow-up email mentioning the key takeaways from the meeting. He/she can also add the meeting results like discussions held, decisions made, etc.
Slide 45
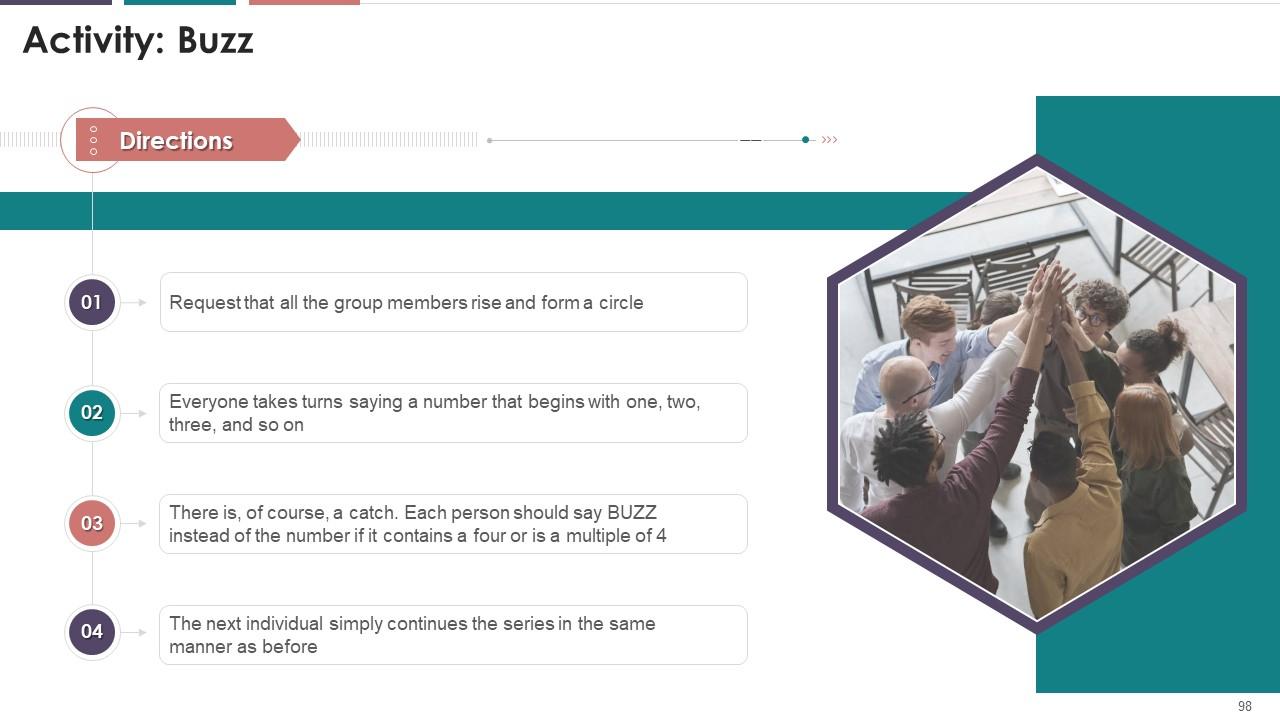
This slide can be used by the trainer to conduct a group activity with the target audience and develop effective speaking skills.
Slide 47
This slide covers various techniques that can be used for effective speaking in business communication, such as identification and focus on the topic. The purpose of the speech must be disclosed at the outset, with a start that arouses audience interest. The speech rate has to be just right, with the content structure being planned for results to be achieved, if any. The importance of follow-up sessions cannot be overemphasized.
Slide 48
This slide illustrates “Identification and focus on the audience” as a technique of effective speaking. Identifying the correct audience and speaking as per the needs of the audience is the right approach to be followed.
Slide 49
This slide illustrates “Effective beginning of the speech with a pre-decided purpose” as an effective speaking technique. The speaker should identify the goal behind speaking publicly or presenting to the audience.
Slide 50
This slide explains the importance of “Narrating a Story” while communicating with the audience. Sharing a story leads to higher audience engagement, as each listener relates the situation to his/her own life as they start relating the situation to the real-life scenarios.
Slide 51
This slide states that the speaker should always focus on including topic-related content and structuring the content in the best manner to deliver the message as planned. He/she should try to list real-life examples of each scenario to highlight the relevance of every concept.
Slide 52
This slide explains the relevance of speech rate as the most common issue which arises while speaking is the delivery of messages at a fast pace, making it difficult for the audience to retain and understand the conveyed message.
Slide 53
This slide explains the significance of feedback and follow-up sessions with the audience. Conducting regular follow-up sessions helps both the speaker and the audience analyze the communication process in great depth.
Slide 54
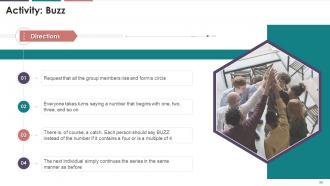
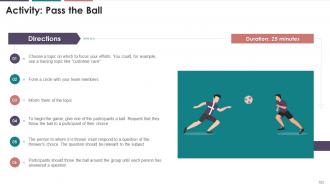
This slide illustrates an exercise that the target audience can perform during their training session to improve listening skills.
Instructor’s Notes:
· While participants are busy passing the message along to the next person in line, play music, or engage them in conversation to create some noise. This will make it a bit more complicated, but it will mimic real-life conditions where distractions abound
Slide 56
This slide shows the various elements of PVLEGS framework of speaking, where P stands for poise, V for voice, L for life, E for eye contact, G for gestures, and S for speed.
Slide 57
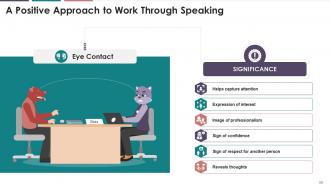
This slide is about spreading a positive approach to work through speaking and lists eight simple, but often ignored actions to really make it happen. These are eye contact, confidence, choosing the right word etc.
Slide 58
This slide covers the basic points on why eye contact is important in speaking.
Slide 59
This slide covers the basic points on why eye contact is important in speaking. Few essentials of maintaining eye contact while speaking include maintaining a neutral smile while having your gaze meet members of the audience, looking positive, keeping eyes on person’s face and giving remaining impassive.
Slide 60
This slide covers the basic points on why being groomed and confident is important in speaking. The speaker should be careful and speak confidently to show assertiveness, invite higher audience engagement and effectiveness.
Slide 61
This slide mentions the importance of using right words in communication. The words chosen should be clear and must be aimed at enhancing clarity in communication. Right words enhance the speaker's confidence, give an accurate expression of ideas, and add to the credibility of the conversation
Slide 62
This slide highlights the importance of conducting meetings, presentations and conversations in a non-distracting environment. It is suggested that conducting calls in a quiet and comfortable environment adds to the productivity of the call.
Slide 63
This slide covers how a good call should be scheduled and conducted, and what will be its significance in the communication process. It includes proper structuring of the call, conducting research before the call, figuring out the objectives of the call, and planning it well in view of the connectivity glitches, if any. The planned call will result in effective exchange of ideas, save time and ensure communication gaps are non-existent.
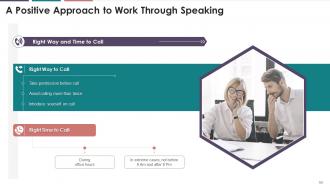
Slide 64
This slide illustrates the basic rules to conduct a professional call and the right time to call. It suggests that an individual should prefer conducting a call during working hours with the prior permission of the receiver.
Slide 65
This slide covers the right way to put a person on hold during a telephonic conversation. An individual should state the reason for placing the call on hold, wrap up shortly and thank the person for cooperating.
Slide 66
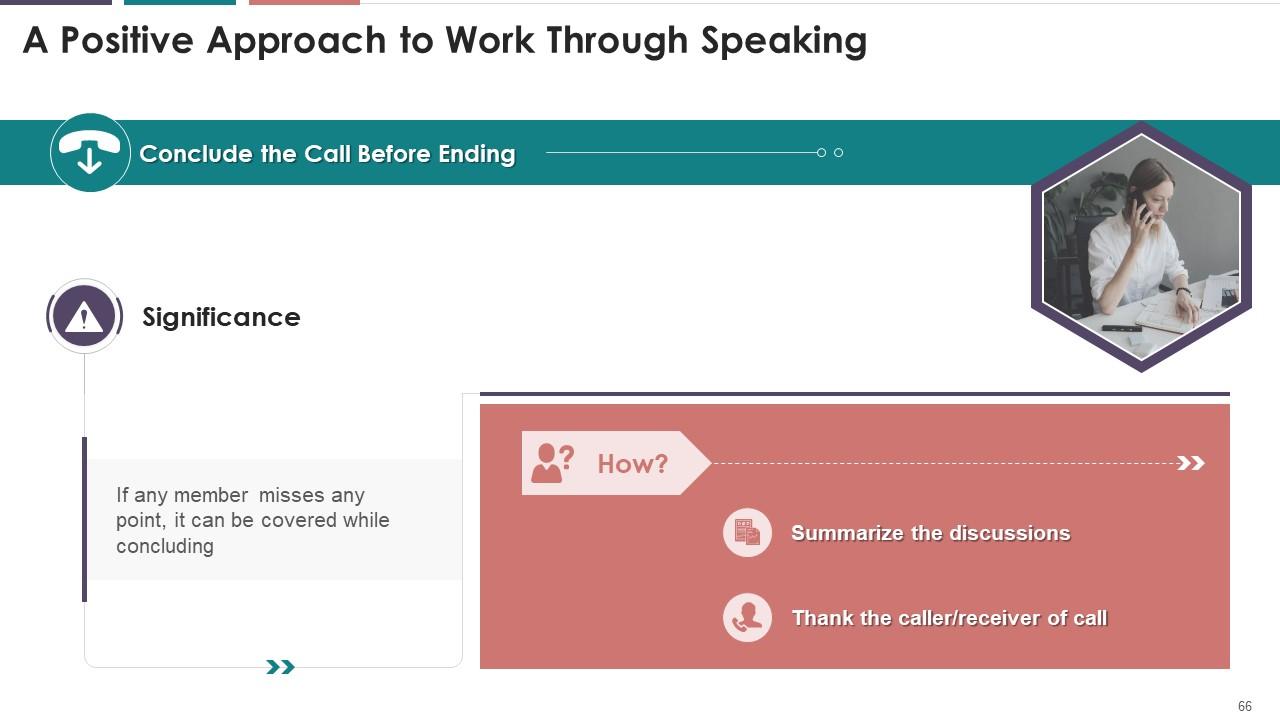
This slide explains the professional way to end a call. It is suggested that an individual should always conclude the discussion before ending the call.
Slide 67
This slide mentions an exercise on improving speaking skills that trainees will be recommended to do and come back with feedback.
Slide 69
Instructor’s Notes:
Answer: A (Listening)
Slide 70
This slide explains the common hurdles that mar effective speaking. These hurdles can be in the form of external distractions like noise, distracted speakers, Nonverbal barriers, wrong interpretation of words or sentences, and different perspectives.
Instructor’s Notes:
· External Distractions: Disturbance or Noise in your work environment, which causes diversion of attention while communicating. External Distractions can be in the form of noisy workplace, cell phones ringing, noisy equipment, etc.
· Solution: Find a peaceful place to sit, away from vehicular and people traffic
· Speaker Distractions: Sometimes, the listeners may not even hear a message due to largely intangible, but significant variables. These may include perceptions by the listener of the speaker such as culture, gender, age, communication style, and job role. For example, a technical person may find it difficult to explain his point to a marketing person, who has a different perspective
· Solution: Make sure that no distraction or perception can scuttle the communication process
· Nonverbal Barriers: Nonverbal communication has a much greater impact than the actual words. In figures, the effect is between 65% and 83% more. Nonverbal communication, like body language and gestures, play a very significant role in making communication effective. A person delivering a message should be aware of not emitting the wrong nonverbal cues to avoid causing offence to anyone
· Solution: The speaker and the listener's body language and gestures should be paid attention to before interpreting their communicated words
· Message Intent/Semantics: Individuals sometime interpret unclear words or words reflecting different meanings differently. Also, people use abbreviations or content without explanation, causing misunderstanding
· Solution: Ambiguous content can always be questioned. The listener is encouraged to say “what do you mean?” to avoid misinterpretation of words or sentences
· Personal Perspective: Personal perspective refers to the already established mindset of a person for something such as stereotypes or preconceived notions. Such a mindset will impede healthy listening and understanding
· Solution: The best solution to such a barrier is clearing the mind before indulging in the communication process. A person should always listen with a fresh and active mind, without any preconceived notions
Slide 71
This slide covers the tongue twisters as a practice exercise for speaking and enunciating correctly. The trainees can practice speed, pronunciation, and clarity of words.
Slide 73
This slide summarizes points for the detailed content covered in the module. The trainer can use this to conclude the speaking portion before ending.
Slide 98 to 109
These slides depict energizer activities to engage the audience of the training session.
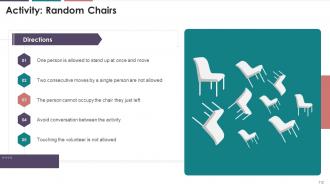
Slide 112
The above slide displays the activity for the team members found less energetic and enthusiastic. It will ensure an increase in energy levels and the productivity of employees at the workplace.
Instructor's Notes:
· Multiple chairs are to be adjusted in the empty and spacious room in a random order
· The chairs should be put in a manner that every chair points in a different direction and all the chairs are occupied
Now,
· Ask for a volunteer from the batch. (Batch may include a maximum of 15 people for a regular size room)
· The volunteer is supposed to walk slowly and approach his/her empty chair and sit down. If the chair is already occupied, then he/she is expected to occupy the other/next alternative empty chair available
· All other members will try to stop the person from approaching the relevant chair
Strategy Formulation:
· Multiple teams can be made to conduct the activity
· Each team can be allotted 2 minutes for planning
· Each round is to be reviewed for the outcomes achieved from the activity
· Each team should have a different volunteer, preferably the person with the lowest energy levels from the batch
· The volunteer should move cautiously so as to not bump into any of the props or persons in the room
Activity Review/Outcomes:
· How did the activity influence the teamwork and engagement skills of all the participants?
· How was the experience while planning and working with 15-20 members at a time?
· Was everybody clear about the purpose and conduct of the respective activity?
· Did you observe any flaws that you wish to improve? Or any other instructions you want to include to make the activity conduct easier?
Speaking In Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt with all 117 slides:
Use our Speaking In Business Communication Training Module On Business Communication Edu Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
Thrilled to see several customizable templates catering various verticals and industries.
-
Making a presentation has never been this easy for me. Thank you SlideTeam for offering a splendid template library.