Art Of Leadership Training Ppt
The Art of Leadership PowerPoint Module is an insightful exploration into the multifaceted nature of leadership within contemporary organizational contexts. It kicks off with a foundational definition of leadership, emphasizing its critical role in modern organizations and its impact on achieving organizational goals. It highlights how effective leadership positively influences employee morale and motivation and its intrinsic link to company culture. The PPT Deck delves deep into various leadership theories, including transactional, contingency, transformational, situational, and several others, providing a broad perspective on leadership styles from authoritative to bureaucratic, including their implications and effectiveness in different scenarios. It further explores effective leaders key traits, offering self-assessment tools such as reflective journaling and feedback techniques. Concluding with practical does and does not, activities, and case studies, this PPT equips aspiring leaders with a comprehensive understanding and tools to refine their leadership skills, fostering a transformative impact in their organizations.
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
 Impress your
Impress your audience
Editable
of Time
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting Training Deck on Art of Leadership. This deck comprises of 116 slides. Each slide is well crafted and designed by our PowerPoint experts. This PPT presentation is thoroughly researched by the experts, and every slide consists of appropriate content. All slides are customizable. You can add or delete the content as per your need. Not just this, you can also make the required changes in the charts and graphs. Download this professionally designed business presentation, add your content, and present it with confidence.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 3
This slide gives the definition of leadership. The act of motivating and directing a group or an individual to accomplish a task is known as leadership. Leaders nurture skills of individuals and motivate them to take the steps necessary for success.
Slide 4
This slide talks about the importance of leadership. Effective leadership plays a vital role in making an organization successful, and is the art of encouraging people to perform assigned tasks willingly and efficiently.
Slide 5
This slide discusses the role of leadership in achieving organizational goals. Leaders provide a structured approach that can generate a plan of action that most effectively and efficiently meets organizational goals. An inclusive planning process also allows individuals to identify, contribute to, understand, and achieve well-defined objectives.
Slide 6
This slide highlights the impact of effective leadership on employee morale and motivation. To improve the organization, leaders encourage employees to contribute freely and openly, engage in constructive discussions on new ideas, and make use of their diverse experiences and perspective
Instructor’s Notes:
Leaders have an open and engaging relationship with people, demonstrating that the people are valued and are an integral part of the organization. This relationship also develops a closer alignment between individual and organizational objectives.
Slide 7
This slide discusses the connection between leadership and company culture. Leaders are aware of how the workplace culture evolves. Understanding the dynamic nature of the workplace helps them guide their team members through these changes.
Slide 8
This slide gives an overview of Theories of Leadership. Theories of leadership attempt to explain how and why individuals become leaders.
Slide 9
This slide talks about the importance of Theories of Leadership. Since effective leadership plays a crucial role in the success and expansion of a business or industrial organization, it is essential to refer to the theories of leadership to understand the characteristics or traits of an influential leader.
Slide 10
This slide lists types of leadership theories. These are: Transactional or management theory, theory of Contingencies, theory of transformation, theory of situations, behavioral theory, great man theory, trait theory, functional theory, and integrated psychological theory.
Slide 11
This slide discusses transactional theory of leadership. Transactional or managerial leadership emphasizes the value of hierarchy for enhancing organizational effectiveness. According to this theory, employees are rewarded for achieving their given objectives.
Slide 12
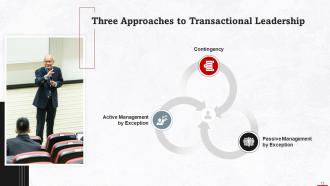
This slide highlights the three approaches to transactional leadership. These are; contingency, active management by exception, and passive management by exception.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Contingency: This theory of leadership employs reinforcement theory and extrinsic motivation based on a system of incentives, rewards, and punishment. Employees earn rewards and benefits if they achieve their goals
- Active Management by Exception: Transactional leaders automatically rely on active monitoring to foresee issues and act in response to problems
- Passive Management by Exception: Transactional leaders stay out of their team's way and intervene only when employee performance standards aren't being fulfilled
Slide 13
This slide points out the key characteristics of transactional leaders. Such leaders are often direct, practical, and less open to change. They aim to follow
Slide 14
This slide discusses SMART Goals that by transactional leaders use. A transactional leader seeks to have employees deliver specific results that are articulated and measurable and are often referred to as SMART Goals. These goals are: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Specific: Goals should be as specific as possible. The narrower and more precise a goal is, the clearer and more straight-forward the steps to achieving it will be
- Measurable: Measurable goals ensure that progress can be tracked
- Achievable: Achievable refers to ensuring the goal is realistic and achievable or maintained within the specified time frame
- Relevant: Relevant refers to ensuring the goal itself aligns with values and long-term goals and objectives
- Time-Bound: Being time-bound ensures that the goal is set with an appropriate time frame
Slide 15
This slide highlights the advantages of transactional leadership. It is efficient and can help achieve short-term goals fast. It delivers consistent results using established procedures and protocols across large and dispersed organizations.
Slide 16
This slide lists the disadvantages of transactional leadership. Instead of focusing on change, transactional leadership prioritizes maintaining the status quo, which may make the management and company inflexible.
Slide 17
This slide talks about the theory of contingencies in leadership. The Contingency Theory of Leadership believes there is no optimum way to structure an organization. Instead, the best leadership approach will depend on the situation.
Slide 18
This slide talks about the importance of the theory of contingencies. Approaching leadership with a contingent lens allows more individuals to explore it and better understand themselves. It also helps them in identifying the circumstances in which they may be effective leaders.
Slide 19
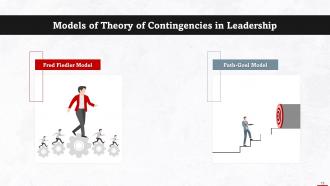
This slide lists important models of theory of contingencies. These are: Fred Fiedler and Path-Goal.
Slide 20
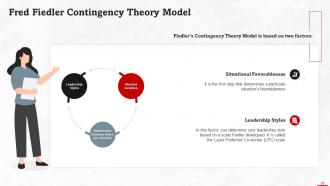
This slide gives information about Fred Fiedler’s model on contingency theory. Fiedler’s Contingency Theory Model is based on two factors: Leadership Styles and Situational Favourableness.
Slide 21
This slide discusses situational favourableness. It depends on three factors: Leader-Member Relations, Task Structure, and Leader’s Position Power.
Slide 22
This slide illustrates the Least Preferred Co Worker or LPC Scale. To understand your leadership style, you have to determine two things. The person who you’ve least enjoyed working with and then rating how you feel about this person for each factor and adding up the score.
Instructor’s Notes:
The model presents eight situations based on 3 factors. The idea is to understand which leaders do well under which scenarios. For instance, a relationship-oriented leader who has high position-power and good leader-member relations is less likely to perform well on a task that is highly structured, when compared with to a task-oriented leader.
Slide 23
This slide talks about Path-Goal model on contingency theory. According to the Path-Goal model, leaders are adaptable. Leaders can adapt their style to suit circumstances. The theory proposes two contingency variables: Environmental factors and employee traits.
Slide 24
This slide defines the four behaviors or styles of leadership that are a part of the Path-Goal Theory of Contingency. These are: Supportive Leadership, Participative Leadership, Directive Leadership, and Achievement Oriented Leadership.
Slide 25
This slide discusses the theory of transformation in leadership. According to this leadership theory, effective leaders motivate their teams to perform above and beyond their capabilities. Leaders create a vision for team members and encourage them to realize it.
Slide 26
This slide illustrates the model of transformational leadership. This includes: Inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, individualized consideration, and idealized influence.
Slide 27
This slide lists the key traits of a transformational leader. A transformational leader is inspirational & adaptable, encourages the development of employees, etc.
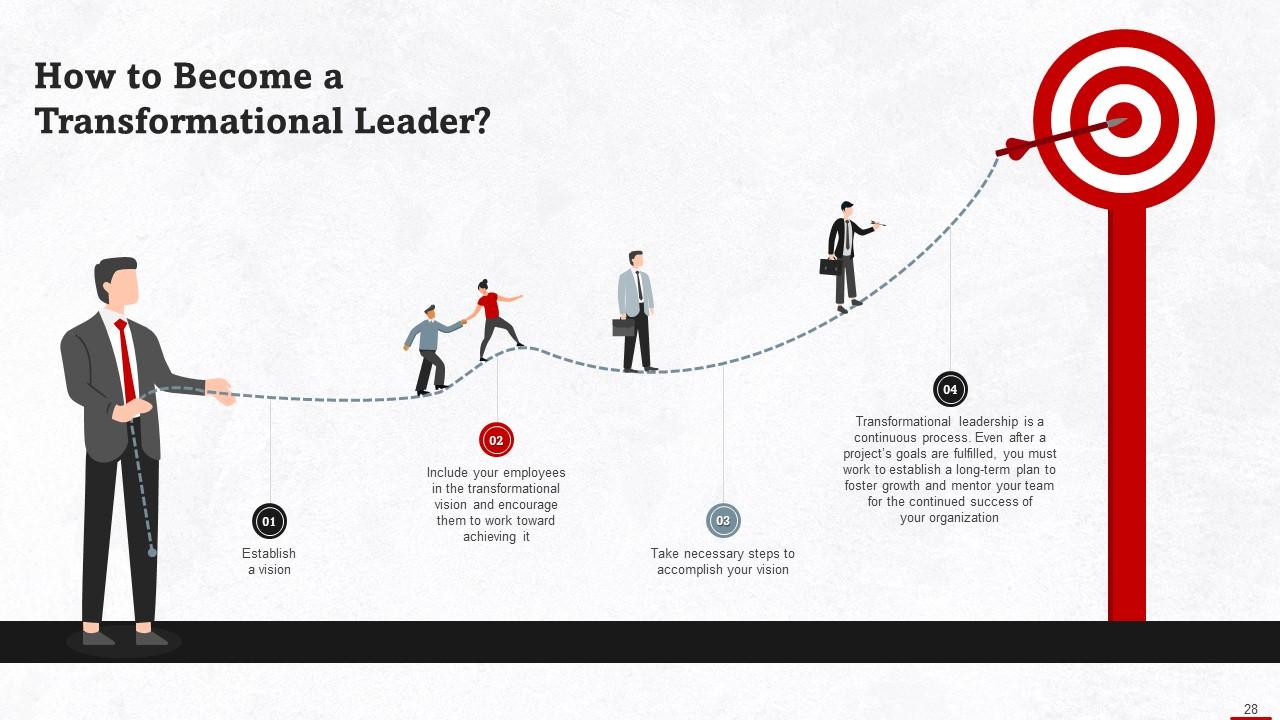
Slide 28
This slide discusses ways to become a transformational leader. Establish a vision, include your employees and encourage them to work toward achieving it.
Slide 29
This slide lists the advantages of transformational leadership. It considers the ethical concerns of any situation, which contributes to a more authentic and trustworthy work environment. Its major impact is a reduction in turnover rates.
Slide 30
This slide highlights the disadvantages of transformational leadership. Transformational leadership tends to focus on the needs of individuals over the needs of the whole team or the organization. This can result in negative outcomes.
Slide 31
This slide discusses the theory of situations in leadership. Like the contingency theory, this idea emphasizes the importance of context and maintains that a leader should adapt to the shifting context to achieve goals and make judgments.
Slide 32
This slide highlights the four leadership styles of situational theory. These are: telling, directing, or guiding; selling, coaching, or explaining; participating, collaborating, or facilitating; and delegating, empowering, or monitoring.
Slide 33
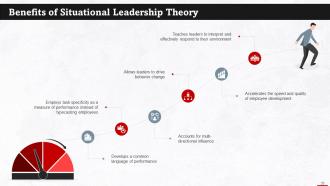
This slide lists the advantages of situational leadership. It allows leaders to drive behavior change, develops a common language of performance, accounts for multi-directional influence, etc.
Slide 34
This slide highlights the core competencies of situational leadership. As per the theory, these are: Analyzing an individual’s performance-readiness to complete a specific task, and adopting leader behavior based on the analysis, etc.
Slide 35
This slide gives an overview of the behavioral theory in leadership. The behavioral theory of leadership states that a person's leadership abilities are a product of their environment. It holds that leaders are not born but are formed and trained.
Slide 36
This slide lists types of leaders according to the behavioral theory. These are: People-oriented, participative, task-oriented, indifferent, status-quo, dictatorial, country club, sound, opportunistic, and paternalistic.
Slide 37
This slide gives information about People-Oriented Leadership theory. People-oriented leaders cultivate and exhibit behaviors that enable them to meet the needs of the people they interact with, including their clients, superiors, and employees
Instructor’s Notes:
People-Oriented Leaders regularly enhance their relations with their team members and motivate them to perform to the best of their abilities
Slide 38
This slide talks about Participative Leadership theory. Participative leaders ensure the active participation of all team members in decision-making. These leaders emphasize functional communication, collaboration, and feedback to enhance the workflow and productivity of their projects.
Slide 39
This slide gives information about Task-Oriented Leadership theory. Task-oriented leaders focus on setting goals and achieving organizational objectives, primarily focusing on task execution rather than people management.
Slide 40
This slide talks about Indifferent Leadership theory. Indifferent leaders monitor their team's performance from a distance and may not actively contribute to the organization's workflow
Slide 41
This slide gives information about Status-Quo Leadership theory. Status-quo leaders emphasize both increasing company productivity and employee satisfaction. Such leaders follow a balanced approach to execute tasks timely while providing support and constant encouragement to fellow team members.
Slide 42
This slide talks about Dictatorial Leadership theory. Dictatorial leaders generally focus on achieving results rather than the well-being of their team members. These leaders may also pressurize employees to perform well during challenging or demanding situations.
Slide 43
This slide gives information about Country Club Leadership theory. These leaders give high priority to their employees' overall happiness and satisfaction levels. These leaders believe that a team that is looked after and cared for often yields successful results.
Slide 44
This slide talks about Sound Leadership theory. These leaders give equal priority to boosting company productivity and employee morale, although it can be challenging to balance the two.
Instructor’s Notes:
Sound leaders find the inner motivation to derive satisfaction in supporting their team's progress.
Slide 45
This slide gives information about Opportunistic Leadership theory. These professionals operate with a mix of certain behaviors. These leaders can fit and adjust their leadership styles to meet the demands of the situation.
Slide 46
This slide talks about Paternalistic Leadership theory. Paternalistic leaders are goal-oriented, but flexible on how and at what pace these are achieved. These leaders often set ambitious goals and reward employees who accomplish these.
Slide 47
This slide lists the advantages of behavioral leadership. It encourages participative decision-making to ensure effective operations, emphasizes concern for team member and promotes collaboration, etc.
Slide 48
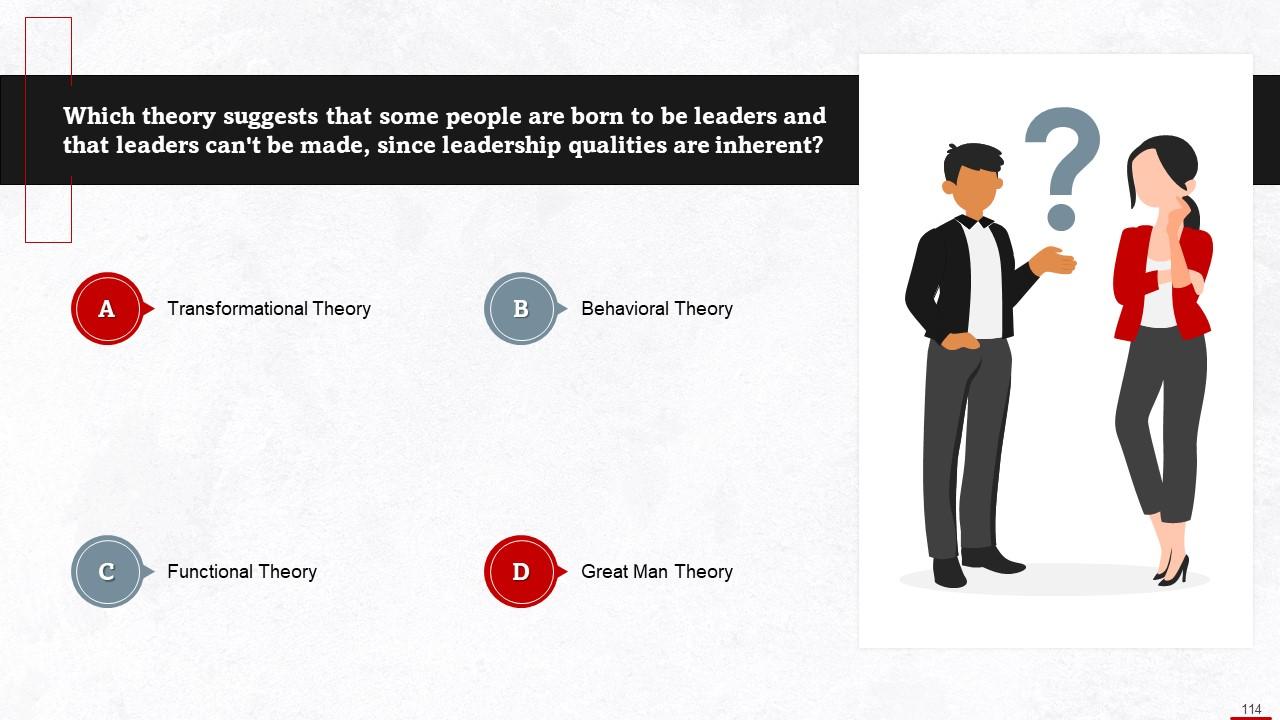
This slide gives an overview of the great man theory in leadership. As per the Great Man Theory of Leadership, some people are born to be leaders. It adds that great leaders can't be made, as leadership qualities are inherent.
Slide 49
This slide discusses the two assumptions of great man theory. This theory is based on two assumptions: Leaders are born with traits that prepare them to lead and individuals become great leaders when there’s a need. Great leaders tend to lead effectively when a critical situation arises.
Slide 50
This slide lists the characteristics that a leader displays as per The Great Man Theory. This theory suggests that a leader has certain inherent characteristics that help them lead effectively and efficiently. These are: Decisiveness, charisma, appeal, etc.
Slide 51
This slide highlights limitations of the great man theory. These are: There is no scientific research supporting it the theory removes the possibility and ambition of learning how to become an effective leader, etc.
Slide 52
This slide gives an overview of The Trait Theory of Leadership. It expands on the great man theory and suggests that effective leaders have specific personality traits and features of behavior.
Slide 53
This slide highlights the traits of a leader. These include: Achievement desire, honesty, integrity, leadership motivation, cognitive ability, self-confidence, business acumen, and emotional maturity.
Slide 54
This slide lists the advantages of the trait theory. It provides detailed knowledge and understanding of the leader element in the leadership process, it is a naturally pleasing theory, etc.
Slide 55
This slide highlights disadvantages of the trait theory. Some subjective judgment is inevitable in determining who is regarded as a 'good' or 'successful' leader, there is a disagreement over which traits are the most important for an effective leader, etc.
Slide 56
This slide gives an overview of the functional theory of leadership. The functional leadership model is dedicated to determining what actions and behaviors establish effective leadership and sharing that information with all stakeholders rather than empowering a single person to lead.
Slide 57
This slide lists the key components of functional theory. These are: Prioritized needs, goal-orientation, focused actions, flexibility, organizational skills, motivation, control, modeled behavior, and guided approach.
Slide 58
This slide discusses prioritized needs as a key component of the functional theory. The guiding principle of this theory is to ensure that the model meets the needs of the task, the group and each individual’s needs.
Slide 59
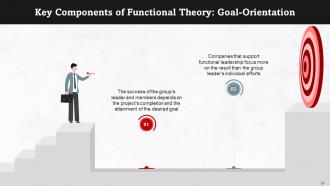
This slide talks about being goal-driven as a key component of the functional theory. The success of the group's leader and members depends on the project's completion and the attainment of the desired goal.
Slide 60
This slide discusses being action-focused as the key component of functional theory. According to the functional leadership model, everyone involved in the team is a leader. While there may be a single person in charge of organizing and maintaining the group, each team member has specific tasks and responsibilities that contribute to success.
Slide 61
This slide talks about flexibility as the key component of the functional theory. While a single manager or supervisor may have started the project or assignment, in most cases, their individual leadership swiftly dissipates into a collective of unified workers to best achieve the project's objectives.
Slide 62
This slide discusses organizational skills as the key component functional theory. Once all needs and tasks have been adequately determined, discussed, and assigned, the project becomes highly autonomous. Therefore, clear organization and structure are vital for success.
Slide 63
This slide talks about motivation as a key component of the functional theory. One of the primary responsibilities of a functional leader is to ensure that all team members are motivated and empowered to complete their assigned tasks.
Slide 64
This slide discusses control as a key component of functional theory. While determining needs at the start of the project, a functional leader should know exactly what resources and tools their team members require.
Slide 65
This slide talks about modeled behavior as a key component of the functional theory. Functional leaders should dedicate themselves to their assigned tasks, interact with team members positively and professionally and communicate clearly and transparently
Slide 66
This slide gives information about guided approach. While the team members essentially work autonomously, a leader must provide oversight and guidance to the team.
Slide 67
This slide lists advantages of the functional theory. Functional leadership helps in enhancing team cohesion, empowering individuals, developing skills, and redefining leadership.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Enhancing Team Cohesion: This theory strives to develop team cohesion through the establishment of team needs and assigning equivalent duties to team members
- Empowering Individuals: Functional leadership empowers each team member to work autonomously and develop their abilities
- Developing Skills: All team members have the opportunity to develop leadership skills, even if they're not the team's official leader
- Redefining Leadership: In most traditional leadership models, the designated supervisor maintains their leadership position exclusively. In the functional model, every team member can take on some leadership responsibility
Slide 68
This slide discusses how to follow the functional model effectively. The steps are as follows: Review the tasks, assign duties, identify needs, provide motivation, model behavior, check in regularly, and assess objectives.
Instructor’s Notes:
- Review the Task: Begin by reviewing the task, first as the leader and then with the group as a unit. Ensure that team members understand the goals and necessary actions to achieve those goals. Outline the general tasks the team will need to complete to meet the objective
- Assign Duties: Delegate individual tasks and duties to each team member. Answer any questions they might have about deadlines, task specifics, or the project in general. Ensure every member of the team is clear on what is expected of them
- Identify Needs: Establish the group's needs to meet the end goal, including the organization's overall needs, the team's general needs, and each individual's specific needs based on their assigned duties and tasks
- Provide Motivation: As the team begins working on their individual tasks, motivate them to keep productivity and morale high amongst the team
- Model Behavior: Even as a functional leader, you'll have your own tasks and responsibilities to maintain. Model the behavior and work ethic you wish to see from your employees by demonstrating appropriate focus, attention, and interaction
- Check in Regularly: Check in at regular intervals with your team to ensure they're on track to meet deadlines and have the required resources. Do your best to keep these interactions brief and allow the team members to work autonomously
- Assess Objectives: Once the project is complete, meet as a group to discuss and evaluate what went well and what else the team can do to improve workflow and general success
Slide 69
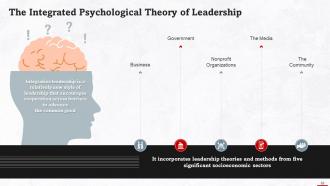
This slide gives an overview of the integrated psychological theory of leadership. Integrative leadership is a relatively new style of leadership that encourages cooperation across barriers to advance the common good. The James Scouller Model of Leadership explains this theory in detail.
Slide 70
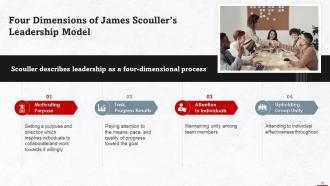
This slide highlights the four dimensions of James Scouller’s integrated psychological theory model. These are: Motivating purpose, task progress results, attention to individuals, and upholding group unity.
Slide 71
This slide gives information about the objectives of James Scouller’s Leadership model. These are: to help leaders understand their responsibilities, and develop their skills while being true to their character.
Slide 72
This slide illustrates James Scouller’s 3P model of leadership. The 3 Ps stand for public, private, and personal leadership. Scouller's idea suggests that for leaders to be effective in all four dimensions, they must work simultaneously on these three levels.
Slide 73
This slide gives an introduction to styles of leadership. A leadership style is a leader's approach to accomplishing their team's goal by motivating employees to work towards it and focusing on their well-being.
Slide 74
This slide lists key styles of leadership. These are authoritative, pace-setting, democratic, autocratic, affiliative, coaching, laissez-faire, servant, bureaucratic, and visionary leadership styles.
Slide 75
This slide gives an introduction to the authoritative style of leadership. Authoritative leadership is a management style in which the leader has complete control. An authoritative leader establishes goals, determines the processes, and supervises steps necessary to reach those goals even without active support from team members.
Slide 76
This slide gives an introduction to the pace-setting style of leadership. A pace-setting leader establishes ambitious standards and expects team members to meet those goals precisely as specified.
Instructor’s Notes:
Pace-setting leaders use the abilities of motivated and competent team members. Such leaders make meeting goals feel urgent and exciting
Slide 77
This slide gives information about the democratic style of leadership. A democratic leader considers their team's opinion and feedback while making decisions. This style is effective as it encourages everyone to participate in all processes and share views.
Slide 78
This slide gives information about the Autocratic style of leadership. Autocratic leadership is contrary to democratic leadership. In this, one leader or member of the company makes decisions on behalf of the organization.
Slide 79
This slide gives an introduction to the affiliative style of leadership. It is a practical strategy used to build relationships and harmonize a disjointed team in an organization
Slide 80
This slide gives information about the coaching style of leadership. A coaching leader emphasizes identifying and nurturing the individual strengths of each team member. They work to develop strategies that will enable teams to work together effectively and efficiently.
Slide 81
This slide gives an introduction to the Laissez Faire style of leadership. Laissez-faire means “let them do”. This leadership approach is the least intrusive and ensures that the decision-making authority lies with team members.
Slide 82
This slide gives information about the servant style of leadership. According to the ideology of servant leadership, one should engage with others to establish authority rather than power, whether they are subordinates or coworkers. This system represents a decentralized organizational structure.
Slide 83
This slide gives an introduction to the bureaucratic style of leadership. Bureaucratic leaders follow rules. Unlike autocratic leaders, they might listen and consider the input of their team members but might reject any input that doesn’t align with company policy or past practices.
Slide 84
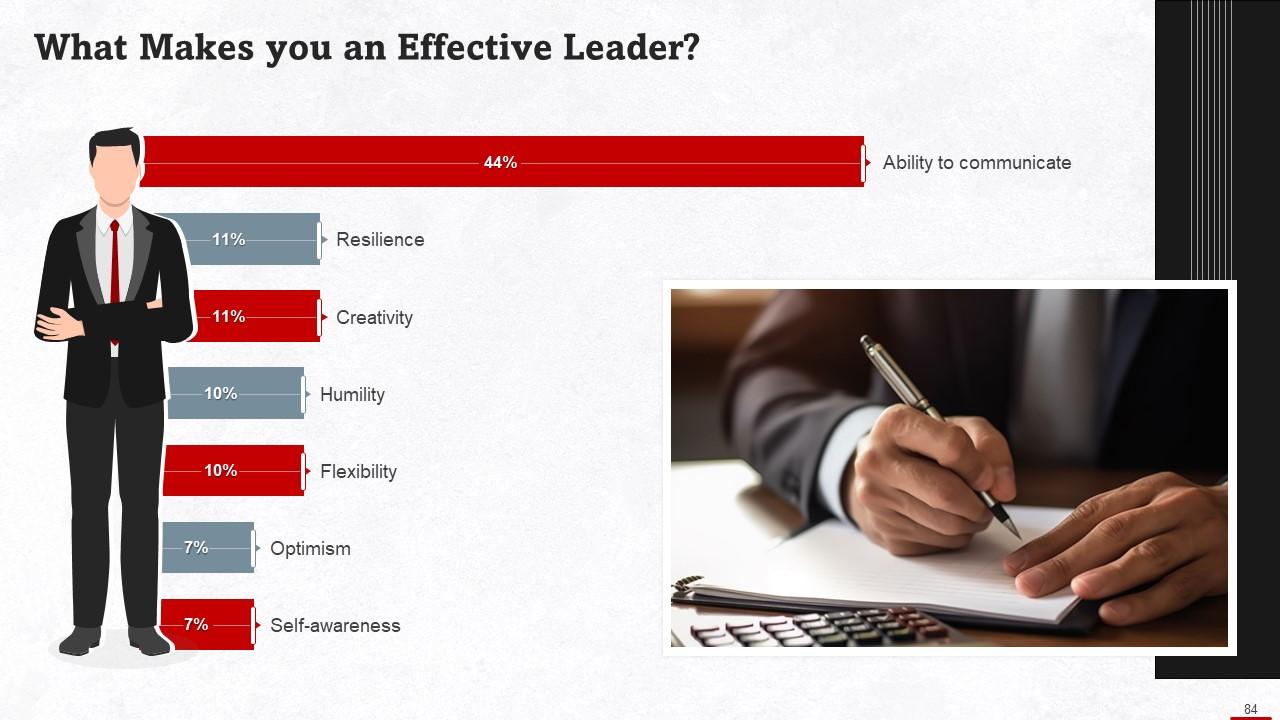
This slide depicts statistics related to the key traits of an effective leader. Good communication is considered the most important characteristic of an effective leader.
Slide 85
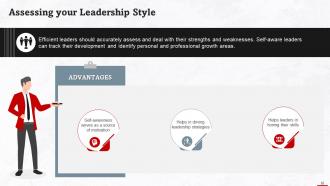
This slide gives information about assessing your leadership style by analyzing your strengths and weaknesses. Self-aware leaders can track their development and identify personal and professional growth areas. Self-awareness serves as a source of motivation, helps in driving leadership strategies, and assists leaders in honing their skills.
Instructor’s Notes:
Leaders who assess their leadership style can create a plan of action and identify the areas that need improvement. This helps them determine their potential growth prospects and succeed in professional endeavors.
Slide 86
This slide highlights two techniques to assess your leadership style. These are reflective journaling, and checklist & survey method.
Slide 87
This slide discusses reflective journaling as a technique to assess your leadership style. The first step of journaling is to identify and document the learning experiences at work, followed by reflecting on these experiences, and finally, drawing conclusions to determine areas of development.
Slide 88
This slide lists the advantages of the reflective journaling technique to assess your leadership style. It helps reflect on the obstacles leaders face, what the favorable factors were, and how things could have been handled to get the desired outcome.
Slide 89
This slide talks about the checklist and survey method to assess your leadership style. This method entails assessing your leadership style by surveying yourself using checklists.
Slide 90
This slide lists the advantages of checklist and survey method to assess your leadership style. This method helps in the identification, sorting, and recording of primary competencies required for handling specific jobs, provides valuable insight into how an individual has evolved as a leader, etc.
Slide 91 to 92
These slides present some important factors to determine your leadership style.
Slide 93
This slide highlights the dos and don’ts of leadership. Leaders should recognize their impact on others, encourage positive behavior and create a healthy work environment. Leaders should not place blame on others for undesired outcomes, try to please everyone, etc.
Slide 94
This slide depicts an activity on leadership that aims to teach the importance of teamwork, patience, and problem-solving skills. This challenge is also a meant to recognize the members who are able to take on leadership roles.
Slide 95
This slide illustrates a role-playing activity that teaches leaders how to address negative situations effectively. It also helps in developing strategic and critical thinking to solve problems.
Slide 96 to 102
These slides include a case study on business leadership and management.
Slide 103 to 107
These slides present a business leadership case study on a pharmaceutical company XYZ.
Slide 108
This slide summarizes the session with its listing of listing the key takeaways.
Art Of Leadership Training Ppt with all 125 slides:
Use our Art Of Leadership Training Ppt to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.
-
A beautiful, professional design paired with high-quality images and content that is sure to impress. It is a must-use PPT template in my opinion.
-
Love how there are no boring templates here! The design is fresh and creative, just the way I like it. Can't wait to edit and use them for my extended projects!